What is federal law? This fundamental question delves into the very foundation of a nation’s legal system, exploring the rules and regulations that govern our daily lives. Federal law, a powerful force shaping our society, encompasses a vast array of topics, from environmental protection to consumer rights, influencing everything from the products we buy to the air we breathe.
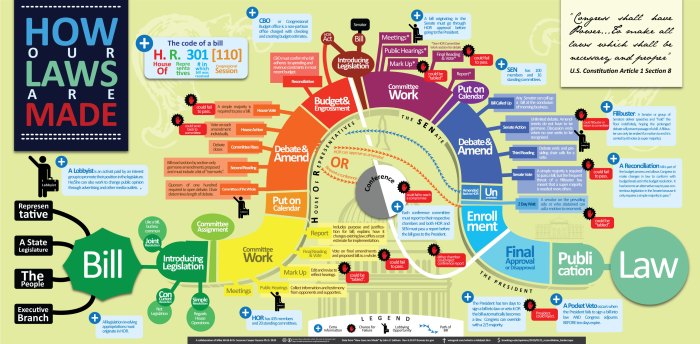
The concept of federal law extends beyond simple rules; it involves a complex interplay of institutions, processes, and principles. The Constitution, the bedrock of American law, establishes the framework for federal lawmaking, granting Congress the power to create statutes. These statutes, in turn, are interpreted and applied by the judiciary, ensuring that federal law remains relevant and adaptable to evolving societal needs.
Definition of Federal Law
Federal law is a fundamental component of a nation’s legal system, encompassing the rules and regulations created and enforced by the federal government. It establishes the framework for governing the country, protecting individual rights, and ensuring the smooth functioning of society.
Sources of Federal Law, What is federal law
Federal law originates from various sources, each with its own distinct authority and role in shaping the legal landscape.
- The Constitution: As the supreme law of the land, the Constitution Artikels the fundamental principles and powers of the federal government, defining its relationship with the states and citizens. It serves as the foundation for all other federal laws, ensuring their consistency with its provisions.
- Statutes: Passed by Congress and signed into law by the President, statutes are written laws that address specific issues or areas of concern. They can range from broad legislation covering national security to more specific regulations governing consumer protection or environmental protection.
- Regulations: Issued by federal agencies, regulations are detailed rules and procedures that implement and enforce the provisions of statutes. They provide guidance and clarity on how laws should be applied in practice, ensuring consistent interpretation and application across different situations.
- Judicial Decisions: Through the process of judicial review, courts interpret and apply federal laws to specific cases. Their decisions, known as precedents, set binding legal principles that guide future interpretations of the law.
Examples of Federal Laws
Federal laws touch upon various aspects of daily life, impacting individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.
- Tax Laws: The Internal Revenue Code, a complex set of statutes and regulations, governs the collection of taxes from individuals and businesses. These laws dictate how income is taxed, deductions are claimed, and tax liabilities are calculated.
- Environmental Regulations: The Clean Air Act, the Clean Water Act, and other environmental laws aim to protect natural resources and public health. They set standards for air and water quality, regulate the disposal of hazardous waste, and promote sustainable practices.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Laws like the Fair Credit Reporting Act and the Truth in Lending Act safeguard consumers from unfair or deceptive practices. They regulate credit reporting, lending practices, and other financial transactions, promoting transparency and accountability.
Types of Federal Laws

Federal laws in the United States are categorized based on their subject matter, reflecting the diverse range of issues addressed by the government. Understanding these categories helps in comprehending the scope and impact of federal legislation.
Categorization of Federal Laws by Subject Matter
Federal laws can be broadly classified into four main categories: criminal law, civil law, administrative law, and constitutional law. Each category encompasses a distinct set of rules and regulations governing specific aspects of society.
Criminal Law
Criminal law defines offenses against the state or society as a whole, outlining penalties for those who violate these laws. It aims to deter crime, protect public safety, and punish offenders.
- Examples:
- The Federal Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act (RICO) targets organized crime activities like racketeering, money laundering, and extortion.
- The Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1988 addresses drug-related offenses, including trafficking, possession, and manufacturing.
- The Patriot Act expands the government’s surveillance powers to combat terrorism, encompassing activities like wiretapping and data collection.
Civil Law
Civil law governs disputes between individuals, organizations, or the government, addressing issues related to property, contracts, torts (civil wrongs), and family matters. It aims to provide remedies for harm or wrongdoing, often involving financial compensation.
- Examples:
- The Fair Housing Act of 1968 prohibits discrimination in housing based on race, religion, national origin, sex, or familial status.
- The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) guarantees equal opportunities for individuals with disabilities in employment, public accommodations, transportation, and communication.
- The Clean Air Act regulates air pollution, setting standards for emissions from vehicles and industrial facilities.
Administrative Law
Administrative law governs the operations of government agencies and their interactions with the public. It establishes rules and procedures for agencies to follow in implementing and enforcing federal laws.
- Examples:
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the safety and efficacy of food, drugs, and medical devices.
- The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets standards for environmental protection and enforces regulations related to air, water, and land pollution.
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) promotes consumer protection and prevents unfair business practices.
Constitutional Law
Constitutional law interprets and applies the provisions of the U.S. Constitution, defining the fundamental rights and powers of the government and its citizens. It establishes the framework for all other federal laws.
- Examples:
- The First Amendment guarantees freedom of speech, religion, the press, assembly, and the right to petition the government.
- The Fourth Amendment protects individuals from unreasonable searches and seizures.
- The Fourteenth Amendment guarantees equal protection under the law and due process of law.
Substantive Law vs. Procedural Law
Federal law can be further categorized into substantive law and procedural law. Substantive law defines rights and obligations, while procedural law Artikels the process for enforcing those rights and obligations.
- Substantive law specifies the content of legal rules, defining the rights and obligations of individuals and organizations. For example, the Fair Labor Standards Act establishes minimum wage and overtime pay requirements for employees.
- Procedural law Artikels the steps and procedures for enforcing substantive laws. For instance, the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure govern the process for filing lawsuits, conducting discovery, and presenting evidence in federal courts.
The Future of Federal Law: What Is Federal Law

Federal law is a dynamic and evolving field, constantly adapting to the changing needs of society. The future of federal law will be shaped by a number of emerging trends, including the increasing use of technology, the growing influence of international law, and the need to address global challenges such as climate change.
Emerging Trends in Federal Lawmaking
The use of technology is transforming the way federal law is made, enforced, and interpreted. For example, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used in legal research, contract analysis, and even judicial decision-making. The increasing use of AI in legal processes raises a number of important questions about the role of human judgment, the potential for bias in AI systems, and the need for transparency and accountability in the use of AI in law.
The increasing influence of international law is another important trend shaping the future of federal law. Globalization and interconnectedness have led to a growing number of international agreements and treaties that affect domestic law. For example, the Paris Agreement on climate change has led to a number of domestic laws and regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
These trends are likely to continue in the future, leading to further changes in the way federal law is made, enforced, and interpreted.
Challenges and Opportunities Facing Federal Law in the Future
Federal law faces a number of challenges and opportunities in the future. One of the biggest challenges is climate change. Climate change is a global problem that requires a coordinated response from all levels of government, including the federal level. Federal law will need to play a key role in developing and implementing policies to mitigate climate change and adapt to its effects.
Technological advancements present both challenges and opportunities for federal law. For example, the development of autonomous vehicles raises questions about liability and safety. Federal law will need to adapt to these new technologies and ensure that they are used safely and responsibly.
The increasing interconnectedness of the world presents both challenges and opportunities for federal law. For example, the rise of cybercrime and terrorism requires a coordinated response from different countries. Federal law will need to work with other countries to address these challenges and ensure the security of its citizens.
Key Features of Federal Law in Different Countries
| Country | Key Features of Federal Law |
|—|—|
| United States | – A system of checks and balances between the federal government and the states.
– A strong emphasis on individual rights and liberties.
– A common law system based on precedent.
| Canada | – A federal system with a strong central government.
– A system of parliamentary democracy.
– A mixed legal system that combines elements of common law and civil law.
| Australia | – A federal system with a strong central government.
– A system of parliamentary democracy.
– A common law system based on precedent.
| Germany | – A federal system with a strong central government.
– A system of parliamentary democracy.
– A civil law system based on codified laws.
| France | – A unitary state with a strong central government.
– A system of semi-presidential democracy.
– A civil law system based on codified laws.
| Japan | – A unitary state with a strong central government.
– A system of parliamentary democracy.
– A civil law system based on codified laws.
| China | – A unitary state with a strong central government.
– A system of communist rule.
– A civil law system based on codified laws.
| India | – A federal system with a strong central government.
– A system of parliamentary democracy.
– A mixed legal system that combines elements of common law and civil law.
End of Discussion

Understanding federal law is crucial for every citizen, as it directly impacts our rights, responsibilities, and interactions with the government. Whether navigating the complexities of tax regulations or seeking protection under consumer protection laws, a grasp of federal law empowers us to navigate the legal landscape with confidence. As we move forward, the ever-changing world demands a dynamic and responsive federal legal system, one that adapts to technological advancements, environmental challenges, and the evolving needs of a globalized society.
FAQ Explained
What are some examples of federal laws that affect businesses?
Federal laws impacting businesses include anti-trust regulations, labor laws, environmental protection laws, and tax laws. These laws govern business practices, ensuring fair competition, worker safety, environmental sustainability, and responsible tax compliance.
How do federal laws differ from state laws?
Federal laws apply nationwide, while state laws are specific to each state. In some cases, federal law preempts state law, meaning that federal law takes precedence. For example, federal environmental regulations often preempt state environmental regulations.
How does the judiciary interpret and apply federal law?
The judiciary interprets and applies federal law through a process of judicial review. Courts analyze the language of the law, consider legislative intent, and rely on precedents established by previous court decisions. This process ensures consistency and fairness in the application of federal law.