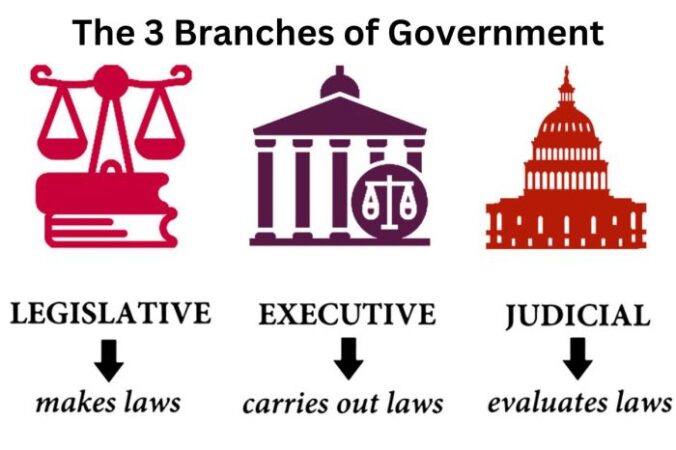
What branch of our government makes the laws sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The legislative branch, also known as Congress, is the heart of American lawmaking. It’s where ideas are debated, compromises are forged, and the laws that shape our nation are crafted.
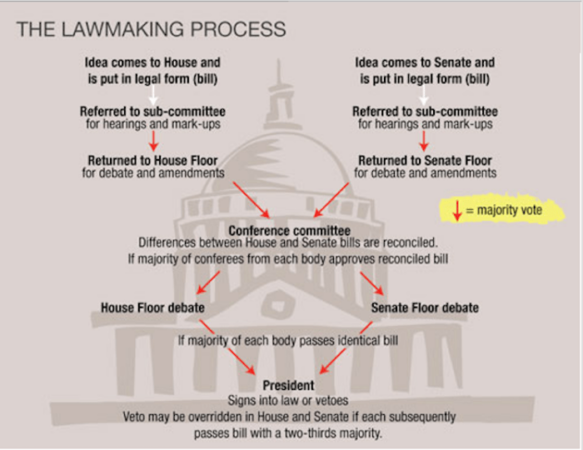
Comprised of the Senate and the House of Representatives, Congress has the power to introduce, debate, and pass bills that become the laws of the land. The process is complex, involving committees, subcommittees, and ultimately, a vote by both chambers. The President then has the power to sign the bill into law or veto it, which Congress can override with a two-thirds majority vote in both chambers.
Types of Laws Made by Congress

Congress, the legislative branch of the U.S. government, holds the power to create laws that govern the nation. These laws, also known as statutes, are a vital component of the American legal system, shaping the rights and responsibilities of citizens and institutions alike.
Types of Legislation
Congress can pass different types of legislation to address a wide range of issues. These include:
- Statutes: The most common type of law, statutes are formal written laws enacted by Congress. They cover a wide range of subjects, from criminal justice to environmental protection to economic policy. Examples include the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which prohibited discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin, and the Clean Air Act of 1970, which established national air quality standards and regulations.
- Resolutions: Resolutions are expressions of opinion or intent by Congress. They are not legally binding like statutes, but they can serve as a powerful statement of Congressional intent. There are two types of resolutions:
- Joint Resolutions: These require approval by both the House of Representatives and the Senate and are signed by the President. They are used to propose constitutional amendments, declare war, or create temporary commissions.
- Simple Resolutions: These are adopted by only one chamber of Congress and are used to express the chamber’s opinion on a particular issue. They are not submitted to the President for signature.
- Amendments: Amendments are changes to the U.S. Constitution. They are the most fundamental type of law, as they can alter the very structure of the government. To be ratified, an amendment must be approved by a two-thirds vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate and then ratified by three-fourths of the states.
Landmark Legislation, What branch of our government makes the laws
Congress has passed numerous landmark laws that have significantly shaped American society. Some notable examples include:
- The Social Security Act of 1935: This act established a system of old-age, survivors, and disability insurance, providing financial security for millions of Americans.
- The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938: This law established a national minimum wage, overtime pay, and restrictions on child labor.
- The Civil Rights Act of 1964: This landmark legislation outlawed discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin in public accommodations, employment, and education.
- The Voting Rights Act of 1965: This act outlawed discriminatory voting practices, such as literacy tests and poll taxes, that had been used to prevent African Americans from voting.
- The Clean Air Act of 1970: This law established national air quality standards and regulations to protect public health and the environment.
Public Laws vs. Private Laws
- Public Laws: These are laws that apply to the general public. They are published in the United States Statutes at Large.
- Private Laws: These are laws that apply to specific individuals, organizations, or situations. They are usually enacted to grant relief from a specific hardship or to authorize a particular action. They are not published in the United States Statutes at Large.
Types of Laws Passed by Congress
| Type of Law | Purpose | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Statutes | To establish rules and regulations that govern the nation. | Broad, affecting the general public. |
| Resolutions | To express the opinion or intent of Congress on a particular issue. | Limited, affecting only the chamber of Congress that adopts it. |
| Amendments | To change the U.S. Constitution. | Fundamental, affecting the entire structure of the government. |
Overriding a Presidential Veto
If the President vetoes a bill passed by Congress, Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate. This process demonstrates the system of checks and balances in the U.S. government, where each branch has the power to limit the actions of the others.
The Importance of the Legislative Branch
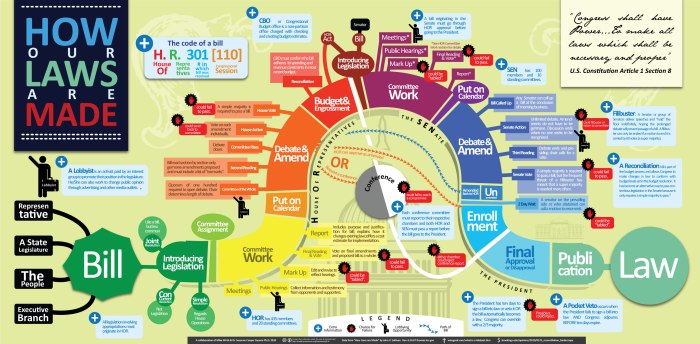
The legislative branch of the United States government, comprised of the Congress, plays a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s laws and policies. Its significance extends beyond simply enacting legislation; it serves as a cornerstone of the American system of checks and balances, ensuring that no single branch of government becomes too powerful.
The Legislative Branch and Checks and Balances
The principle of checks and balances, enshrined in the Constitution, ensures that no single branch of government can dominate the others. The legislative branch acts as a crucial check on the executive branch by approving or rejecting the President’s proposals and by controlling the federal budget. Congress also has the power to impeach and remove the President, Vice President, and other federal officials.
Representing the Interests of the People
Congress is designed to represent the diverse interests of the American people. The House of Representatives, with its members elected from specific districts, is intended to reflect the views of local communities. The Senate, with its two senators per state, ensures that the interests of smaller states are not overlooked. This system of representation allows for a wide range of viewpoints to be considered in the legislative process.
Public Input and Debate
The legislative process is characterized by extensive public input and debate. Before a bill becomes law, it undergoes numerous hearings and amendments, allowing citizens, interest groups, and experts to express their views. This open and transparent process helps to ensure that legislation reflects the will of the people and addresses the most pressing issues facing the nation.
Addressing Major Challenges
Throughout history, the legislative branch has played a critical role in addressing major challenges facing the nation. For instance, Congress passed landmark legislation during the Civil War, including the Emancipation Proclamation, which freed enslaved people in Confederate states. In the 20th century, Congress enacted the Social Security Act, establishing a system of retirement benefits for American workers. More recently, Congress has addressed issues such as climate change, healthcare reform, and economic recovery.
Key Responsibilities of the Legislative Branch
The following table Artikels the key responsibilities of the legislative branch and their impact on American society:
| Responsibility | Impact on American Society |
|—|—|
| Enacting Laws | Shapes the legal framework governing all aspects of American life, from individual rights to economic regulations. |
| Approving the Federal Budget | Determines how taxpayer dollars are allocated to various government programs and agencies. |
| Overseeing the Executive Branch | Holds the executive branch accountable for its actions through hearings, investigations, and confirmation processes. |
| Declaring War | Determines whether the United States will engage in military conflict. |
| Amending the Constitution | Has the power to propose amendments to the Constitution, reflecting the evolving values and needs of the nation. |
Conclusive Thoughts: What Branch Of Our Government Makes The Laws
The legislative branch plays a crucial role in ensuring checks and balances within the government, representing the interests of the people, and fostering public debate on important issues. It’s a dynamic system where the voices of the people are heard, and the laws that govern our lives are shaped. By understanding how Congress functions, we can better engage in the democratic process and ensure our voices are heard in the halls of power.
FAQ Corner
What are the key powers granted to Congress by the US Constitution related to lawmaking?
The US Constitution grants Congress the power to declare war, raise and support armies, regulate commerce, coin money, establish post offices, and much more. These powers are Artikeld in Article I of the Constitution.
How does Congress represent the interests of the people?
Congress is made up of elected representatives from each state, ensuring that the diverse voices of the American people are heard in the lawmaking process.
What are some examples of landmark legislation passed by Congress?
Examples include the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Clean Air Act, and the Affordable Care Act. These laws have had a profound impact on American society, addressing issues like civil rights, environmental protection, and healthcare.
What are the different types of laws Congress can make?
Congress can make statutes, resolutions, and amendments. Statutes are the most common type of law, while resolutions are used for expressing opinions or directing actions. Amendments change the US Constitution.