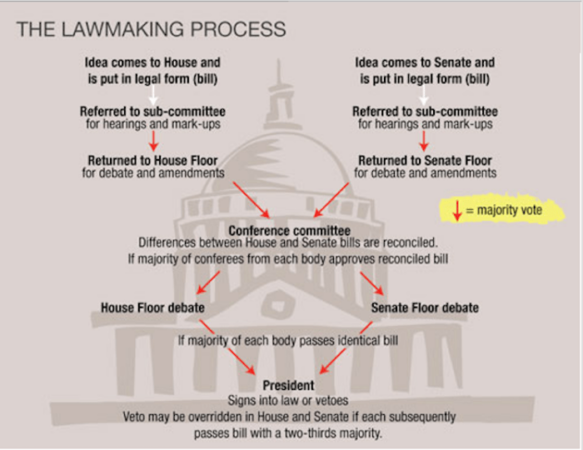
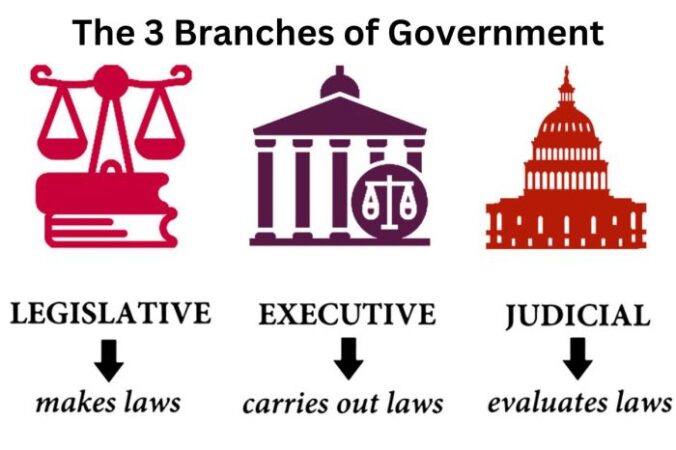
Who makes laws in usa – Who makes laws in the USA? This question delves into the heart of American democracy, where the power to create and enforce laws is shared among different branches of government. Understanding how laws are made is essential for any citizen, as it sheds light on the complex interplay between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. This exploration will delve into the intricate process of lawmaking, examining the roles and responsibilities of each branch, and highlighting the vital role of citizen participation.
The United States Constitution serves as the bedrock of the American legal system, establishing a framework for the separation of powers. This division ensures no single entity holds absolute authority, fostering a system of checks and balances that safeguards individual rights and liberties.
The Amendment Process

The U.S. Constitution is a living document that has been amended twenty-seven times since its ratification in 1788. The amendment process ensures that the Constitution can adapt to changing societal values and address emerging challenges. It is a complex process that requires a high level of consensus and reflects the principles of federalism and popular sovereignty.
The Amendment Process
The process of amending the Constitution is Artikeld in Article V of the Constitution. It involves two distinct stages: proposal and ratification.
Proposal
- An amendment can be proposed by a two-thirds vote of both houses of Congress.
- Alternatively, an amendment can be proposed by a national convention called by Congress at the request of two-thirds of the states.
Ratification
- Once an amendment has been proposed, it must be ratified by three-fourths of the states.
- States can ratify amendments through their state legislatures or through state conventions.
- The Constitution does not specify a time limit for ratification, but amendments generally are ratified within a few years.
Historical Significance of Major Constitutional Amendments
The amendment process has played a pivotal role in shaping the legal and political landscape of the United States. Here are some notable examples:
The Bill of Rights (Amendments 1-10)
- These amendments, ratified in 1791, protect fundamental individual rights, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the press, as well as the right to bear arms, protection from unreasonable searches and seizures, and the right to due process of law.
- The Bill of Rights was a response to concerns about the potential for government overreach and the need to safeguard individual liberties.
The Abolition of Slavery (Amendment 13)
- Ratified in 1865, this amendment abolished slavery and involuntary servitude in the United States.
- It was a landmark achievement in the struggle for equality and human rights, marking a fundamental shift in American society.
Voting Rights (Amendments 15, 19, 24, 26)
- These amendments expanded voting rights to African Americans (15th Amendment), women (19th Amendment), and individuals regardless of race (24th Amendment), and lowered the voting age to 18 (26th Amendment).
- They reflect the ongoing efforts to ensure equal political participation and expand the franchise to previously disenfranchised groups.
Amendments and the Lawmaking Process
Constitutional amendments have significantly influenced the lawmaking process in the United States. For example:
The 16th Amendment (1913)
- This amendment authorized Congress to levy an income tax.
- It has profoundly impacted the federal government’s revenue stream and its ability to fund social programs and infrastructure projects.
The 17th Amendment (1913)
- This amendment provided for the direct election of senators by the people.
- It shifted power away from state legislatures and increased the influence of popular opinion in the Senate.
The 22nd Amendment (1951)
- This amendment limited the number of terms a president can serve to two.
- It was enacted in response to President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s four terms in office and aimed to prevent the concentration of power in the executive branch.
Citizen Participation in Lawmaking

In a democratic society, citizens play a vital role in shaping the laws that govern them. While elected officials are responsible for creating and passing legislation, the public’s voice is crucial in influencing the lawmaking process. Citizens can engage in various ways to advocate for or against specific legislation, ensuring their interests are represented and considered.
Forms of Citizen Participation, Who makes laws in usa
Citizen participation in lawmaking takes various forms, each contributing to a more inclusive and responsive legislative process.
- Lobbying: This involves individuals or groups directly contacting lawmakers to express their views on a particular issue and advocate for specific legislation. Lobbyists can provide information, research, and arguments to influence lawmakers’ decisions. Examples include environmental groups lobbying for stricter pollution regulations or business organizations advocating for tax breaks.
- Voting: The most fundamental form of citizen participation, voting allows individuals to choose representatives who will make decisions on their behalf. By casting their ballots, citizens express their preferences for specific policies and priorities. This participation is essential for ensuring the government is accountable to the people.
- Protesting: Public demonstrations, marches, and rallies are powerful ways for citizens to express their concerns and demands regarding specific legislation. These protests can raise awareness about important issues, mobilize public opinion, and pressure lawmakers to take action.
- Contacting Elected Officials: Citizens can directly communicate with their representatives through letters, emails, phone calls, or attending town hall meetings. This allows them to express their opinions, ask questions, and hold officials accountable for their actions.
Importance of Civic Engagement
Civic engagement is paramount in a democratic society. It fosters a sense of shared responsibility and empowers citizens to actively participate in shaping their future.
Active citizen participation ensures that the lawmaking process reflects the diverse needs and concerns of the population, leading to more equitable and representative laws.
Summary
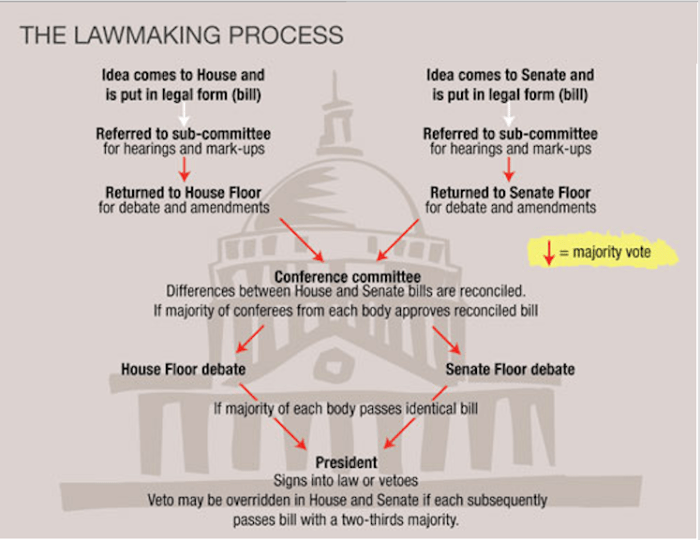
In conclusion, the process of lawmaking in the USA is a dynamic and intricate system that involves various branches of government and the active participation of citizens. From the introduction of bills in Congress to the Supreme Court’s interpretation of laws, each step plays a crucial role in shaping the legal landscape of the nation. Understanding this process is vital for informed civic engagement, allowing individuals to contribute to the ongoing dialogue and influence the direction of the law.
FAQ Summary: Who Makes Laws In Usa
What is the difference between a bill and a law?
A bill is a proposed law that has been introduced in Congress but has not yet been passed. A law is a bill that has been passed by both the House of Representatives and the Senate and has been signed into law by the President.
How can citizens get involved in the lawmaking process?
Citizens can participate in the lawmaking process through various means, including contacting their elected officials, attending town hall meetings, lobbying, voting, and participating in protests.
What is the role of the President in the lawmaking process?
The President has the power to sign bills into law, veto bills, and issue executive orders. The President can also propose legislation to Congress.
What is the role of the Supreme Court in the lawmaking process?
The Supreme Court has the power to interpret laws and determine whether they are constitutional. The Court’s decisions can shape or overturn existing laws.