How much is health insurance? It’s a question that crosses many minds, and for good reason. The cost of healthcare is a significant factor in most people’s budgets, and understanding how health insurance premiums are calculated is essential to making informed decisions about coverage.
This guide delves into the intricate world of health insurance costs, exploring the factors that influence premiums, key components of insurance plans, and strategies to navigate and potentially lower your expenses. From deductibles and co-pays to age, location, and health status, we’ll uncover the elements that contribute to your overall health insurance costs.
Understanding Health Insurance Costs
Health insurance premiums, the monthly payments you make for coverage, can vary widely. Several factors determine how much you pay, and understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your health insurance.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
The cost of health insurance is influenced by a combination of factors, including:
- Age: Older individuals generally have higher premiums due to their increased likelihood of needing medical care.
- Location: Premiums can vary depending on the cost of living and healthcare providers in your geographic area.
- Tobacco Use: Smokers often pay higher premiums because smoking increases health risks.
- Plan Type: Different health insurance plans have varying levels of coverage and cost. For instance, plans with lower deductibles and copayments usually have higher premiums.
- Family Size: Premiums generally increase with the number of people covered under the plan.
- Employer Contributions: If your employer offers health insurance, they may contribute a portion of the premium, reducing your out-of-pocket costs.
- Health Status: While insurance companies cannot discriminate based on pre-existing conditions, individuals with higher healthcare needs may see higher premiums.
Types of Health Insurance Plans and Cost Variations
Health insurance plans are categorized into different types, each with unique coverage features and associated costs:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): HMOs typically have lower premiums but require you to use in-network providers. They often have lower out-of-pocket costs but may have limited choice in healthcare providers.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): PPOs offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, both in-network and out-of-network. They generally have higher premiums than HMOs but may have higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): EPOs are similar to HMOs, requiring you to use in-network providers. They often have lower premiums than PPOs but may have limited coverage for out-of-network services.
- Point of Service (POS): POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs, offering some flexibility in provider choice but with higher premiums than HMOs.
- High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): HDHPs have lower premiums but require you to pay a higher deductible before coverage kicks in. They are often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA), which allows you to save pre-tax dollars for healthcare expenses.
Average Health Insurance Costs in the United States
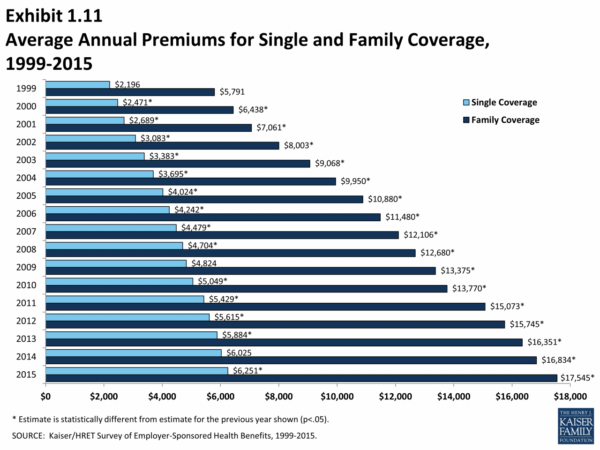
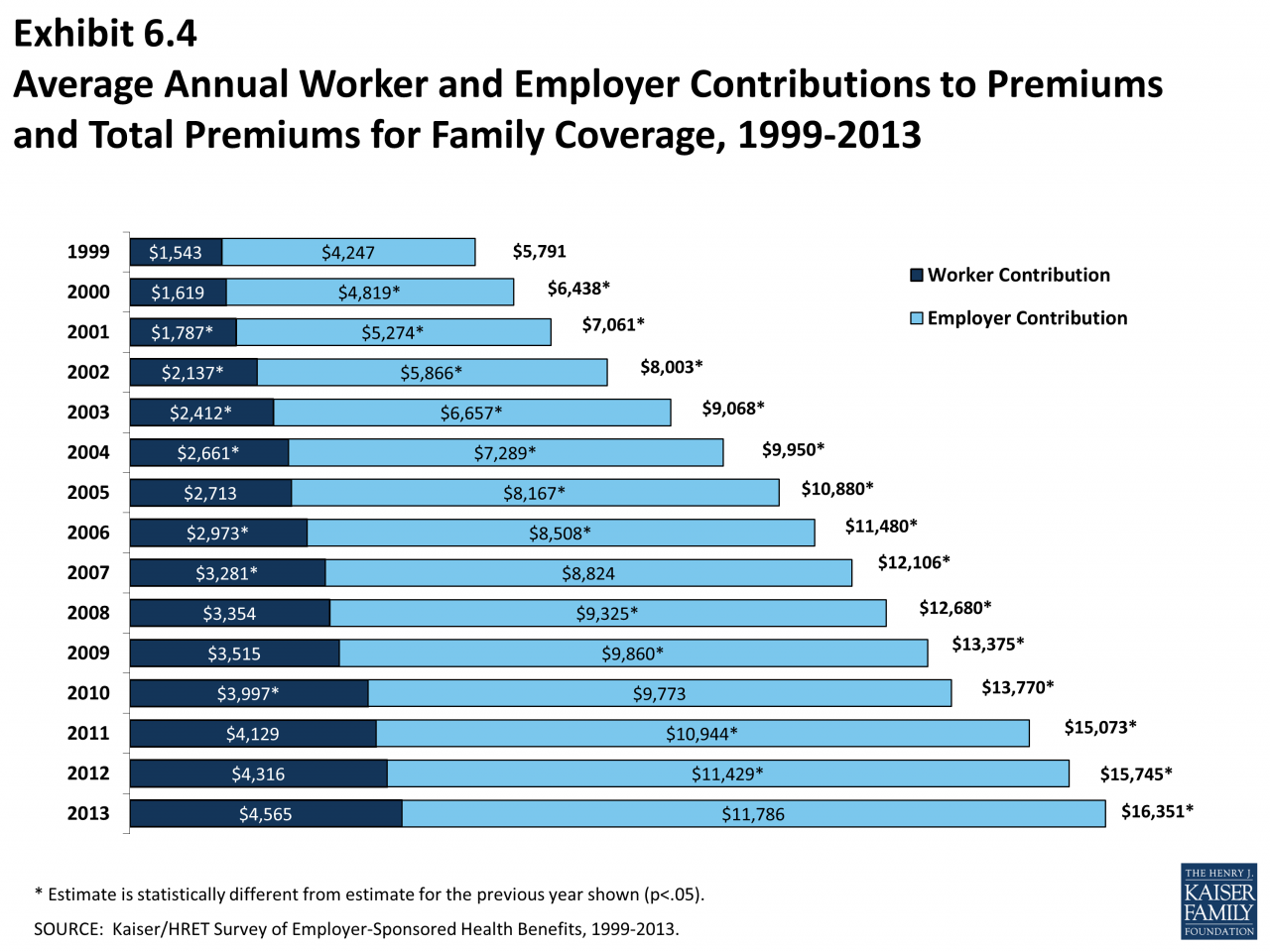
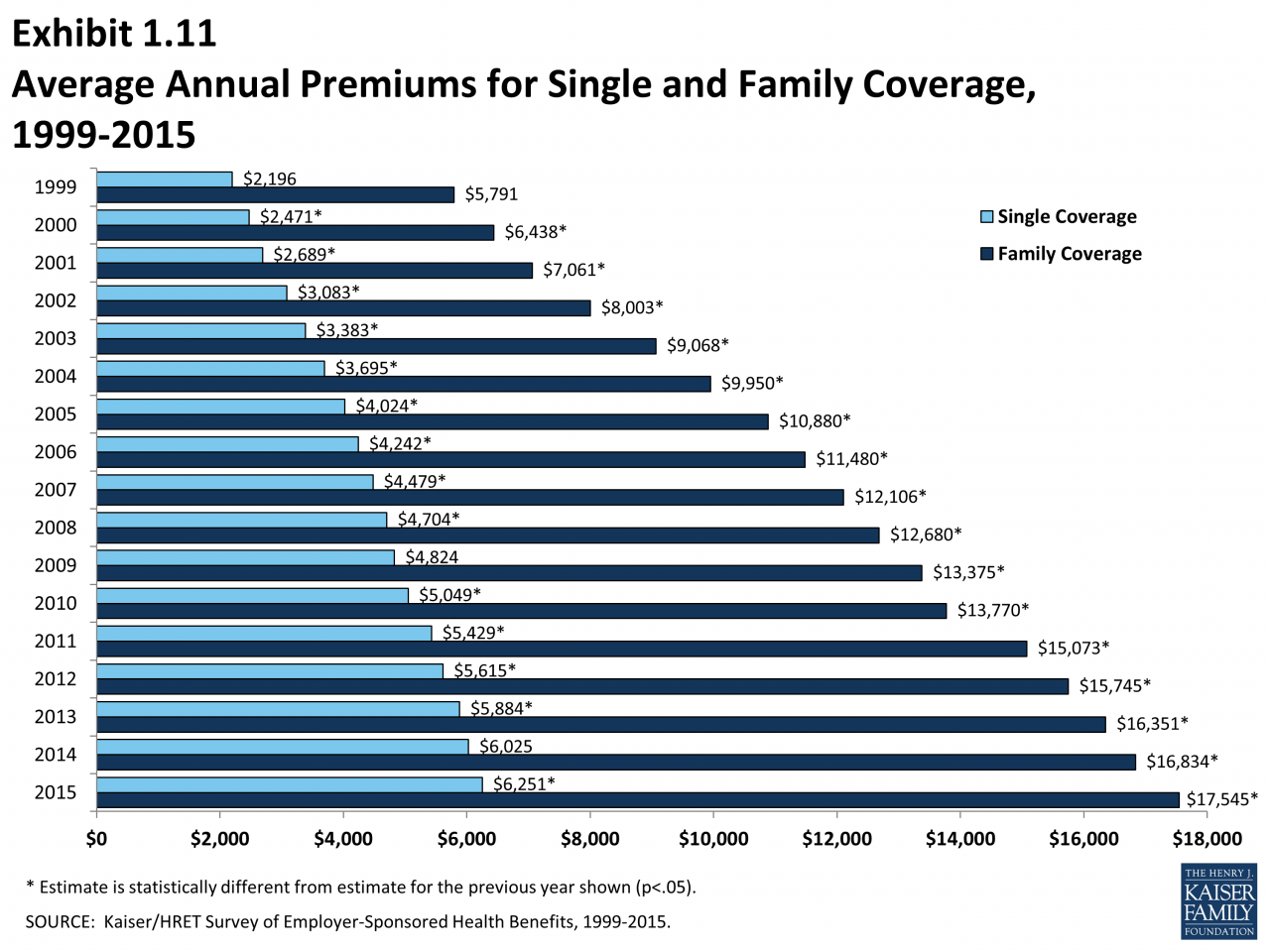
The average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance in the United States was $7,739 for individual coverage and $22,221 for family coverage in 2022, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation.
These costs can vary significantly based on factors such as age, location, plan type, and health status.
Key Components of Health Insurance Costs
Understanding the various components that make up your health insurance costs is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage. Here’s a breakdown of some key factors that influence your premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums.
Deductibles
Deductibles represent the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your health insurance plan starts covering your healthcare expenses. A higher deductible typically translates to lower monthly premiums, while a lower deductible means higher monthly premiums.
- For example, if you have a $1,000 deductible and incur $1,500 in medical expenses, you’ll pay the first $1,000 yourself, and your insurance will cover the remaining $500.
- Deductibles can be applied to various healthcare services, such as doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription drugs.
- Understanding your deductible helps you budget for potential healthcare expenses and anticipate your financial responsibility.
Co-pays and Coinsurance
Co-pays and coinsurance are fixed amounts or percentages you pay for specific healthcare services after meeting your deductible.
- Co-pays are fixed amounts paid for services like doctor visits, while coinsurance is a percentage of the cost you pay for services like hospital stays.
- For example, a co-pay for a doctor’s visit might be $25, while coinsurance for a hospital stay could be 20% of the total cost.
- These shared costs help manage healthcare expenses and encourage individuals to be more conscious of their healthcare utilization.
Out-of-Pocket Maximums
Out-of-pocket maximums are the maximum amount you’ll pay for covered healthcare expenses in a given year, including deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance.
This limit protects you from excessive financial burden, even if you experience significant healthcare costs.
- For instance, if your out-of-pocket maximum is $5,000, once you reach that amount, your health insurance will cover 100% of your remaining eligible healthcare expenses for the rest of the year.
- Out-of-pocket maximums provide financial protection and peace of mind, knowing that your out-of-pocket costs are capped.
Factors Affecting Individual Premiums: How Much Is Health Insurance

Your health insurance premium is the amount you pay monthly or annually for your coverage. Several factors can influence your individual premium, making it vary significantly from person to person. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your health insurance choices.
Age
Your age is a significant factor in determining your health insurance premium. Generally, younger individuals tend to have lower premiums than older individuals. This is because younger people are statistically less likely to require expensive medical care. As you age, the risk of developing health conditions increases, leading to higher premiums.
Location
Your location can also affect your health insurance premium. Premiums vary based on the cost of living and healthcare expenses in your geographic area. Areas with a higher cost of living and more expensive healthcare services typically have higher premiums.
Health Status
Your health status is another crucial factor influencing your premium. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions often face higher premiums. This is because insurance companies assess the risk of covering individuals with known health issues, which can lead to higher claims.
Family Size and Coverage
The number of people covered under your health insurance plan also affects your premium. Adding dependents, such as a spouse or children, will increase your premium. This is because you are covering more people under the same plan, which increases the potential for claims.
Employer Contributions and Subsidies
If you receive health insurance through your employer, your employer may contribute to your premium. The amount of your employer’s contribution can significantly impact your individual premium. Additionally, you may be eligible for government subsidies to help offset the cost of your health insurance, depending on your income and other factors.
Navigating Health Insurance Options
Choosing the right health insurance plan can feel overwhelming, given the wide range of options and varying costs. Understanding your needs and carefully comparing plans is crucial to finding the best fit for your situation.
Comparing Health Insurance Plans
A helpful approach to navigating health insurance options is to compare different plans based on their coverage and cost. This can be done by using a table that Artikels key features of various plans.
| Plan Type | Coverage | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) | Lower monthly premiums, higher deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs | Generally lower premiums, but higher costs for medical services until the deductible is met |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | More flexibility in choosing providers, but higher premiums than HMOs | Higher premiums than HMOs, but more flexibility in choosing providers |
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | Lower premiums, but limited network of providers | Lower premiums, but limited network of providers |
| Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) | Similar to HMOs, but with a slightly wider network | Similar to HMOs, but with a slightly wider network |
Researching and Selecting a Plan
A systematic approach can help individuals research and select the best health insurance plan for their needs. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Assess your health and medical needs. Consider your current health status, any pre-existing conditions, and anticipated healthcare needs in the coming year.
- Determine your budget. Estimate your monthly premium and out-of-pocket expenses based on your income and financial situation.
- Research available plans. Use online comparison tools, consult with a broker, or contact insurance providers directly to gather information on different plans.
- Compare plans based on coverage and cost. Pay attention to deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Consider the provider network. Ensure that your preferred doctors and hospitals are included in the plan’s network.
- Read the plan documents carefully. Understand the terms and conditions, including exclusions and limitations.
- Choose a plan that meets your needs and budget. Select the plan that offers the best value for your money and provides adequate coverage for your health needs.
Asking Questions to Insurance Providers
When comparing health insurance plans, it is essential to ask insurance providers specific questions to gain a comprehensive understanding of their offerings. Here is a checklist of questions:
- What is the monthly premium for the plan?
- What is the deductible for the plan?
- What are the copayments and coinsurance for different services?
- What is the out-of-pocket maximum for the plan?
- What is the provider network for the plan?
- Are there any pre-existing condition exclusions?
- What are the plan’s coverage limitations?
- What are the options for appealing a denied claim?
- Are there any other benefits included in the plan, such as prescription drug coverage or dental and vision care?
Cost-Saving Strategies for Health Insurance
Navigating the world of health insurance can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to managing costs. But with the right strategies, you can reduce your premiums and keep your healthcare expenses in check.
Understanding Cost-Saving Strategies
Reducing your health insurance premiums requires a multi-pronged approach. It involves making informed choices about your plan, actively managing your health, and taking advantage of available resources.
Choosing the Right Plan
- Compare Plans Carefully: Don’t just settle for the first plan you see. Shop around and compare plans from different insurers. Consider factors like coverage, deductibles, co-pays, and network size.
- Consider High-Deductible Plans with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): If you’re generally healthy and can afford a higher deductible, a high-deductible plan with an HSA can be a good option. HSAs allow you to save pre-tax dollars for healthcare expenses, which can reduce your overall costs.
- Explore Employer-Sponsored Plans: If you’re employed, check out the health insurance plans offered by your employer. These plans often offer competitive rates and valuable benefits.
- Enroll During Open Enrollment: Open enrollment periods are the time to switch plans or make changes to your existing coverage. Don’t miss this opportunity to review your options and find a plan that fits your needs and budget.
Managing Your Health
- Preventive Care: Regular checkups, screenings, and vaccinations can help prevent serious health issues, potentially saving you money in the long run. Most plans cover these services at no cost to you.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can lower your risk of developing chronic conditions, reducing your healthcare costs. This includes eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
- Medication Management: Ask your doctor about generic alternatives to brand-name medications. Generic drugs often cost significantly less and can be just as effective.
Utilizing Financial Tools
- Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs): FSAs allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars for eligible healthcare expenses, such as deductibles, co-pays, and prescription drugs. This can reduce your taxable income and save you money on healthcare costs.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): HSAs are similar to FSAs but offer more flexibility. They can be used for a wider range of healthcare expenses, including over-the-counter medications, and the funds roll over year to year. HSAs are best suited for high-deductible health plans.
Additional Strategies, How much is health insurance
- Negotiate Medical Bills: Don’t be afraid to negotiate medical bills. Hospitals and providers are often willing to work with patients to reduce their out-of-pocket expenses.
- Consider Telehealth: Telehealth services offer virtual consultations with doctors, which can be a more convenient and affordable option for certain medical needs.
Final Summary
Navigating the complexities of health insurance can be daunting, but understanding the factors that contribute to costs empowers you to make informed choices. By understanding your options, comparing plans, and exploring cost-saving strategies, you can find a health insurance plan that meets your needs and fits your budget. Remember, preventive care, healthy lifestyle choices, and utilizing flexible spending accounts (FSAs) and health savings accounts (HSAs) can all play a role in managing healthcare expenses.
Questions Often Asked
What are some common health insurance plans?
Common plans include HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations), PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations), and EPOs (Exclusive Provider Organizations), each with its own cost structure and network of providers.
How do I know if I need health insurance?
In most cases, it’s highly recommended to have health insurance to protect yourself financially from unexpected medical expenses. If you’re unsure, consult with a financial advisor or insurance broker.
What is the best way to compare health insurance plans?
Use online comparison tools, contact insurance providers directly, and consider factors like coverage, cost, and provider network when making your decision.