- Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
- Types of Health Insurance Plans
- Understanding Deductibles, Copayments, and Coinsurance
- Cost Estimation Tools and Resources
- Navigating the Health Insurance Marketplace
- Government Subsidies and Financial Assistance
- Cost Considerations for Specific Health Needs
- Strategies for Reducing Health Insurance Costs
- Conclusion: How Much Does Health Insurance Cost
- Q&A
How much does health insurance cost? It’s a question that weighs heavily on the minds of many, as healthcare expenses continue to rise. Understanding the factors that influence premiums, the different types of plans available, and the cost-sharing mechanisms involved is crucial for making informed decisions about your health coverage. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of health insurance costs, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the complex world of healthcare financing.
From the impact of age, location, and health status to the nuances of deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, we will delve into the intricacies of health insurance costs. We will also explore government subsidies, financial assistance programs, and strategies for reducing your expenses. By understanding these key aspects, you can empower yourself to find affordable and suitable health insurance that meets your individual needs.
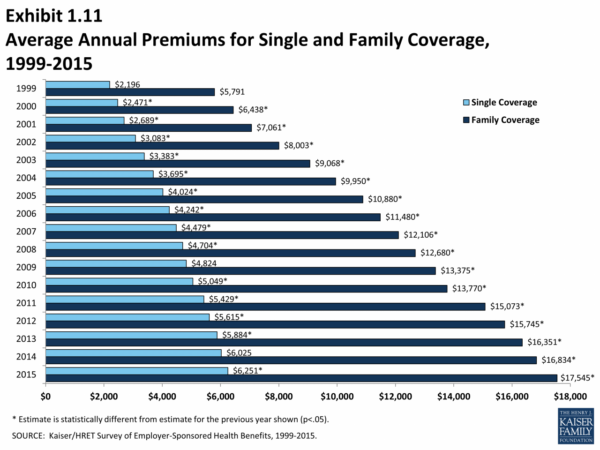
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs

Health insurance premiums are calculated based on a variety of factors, and understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your coverage. The price you pay for health insurance is determined by a complex set of factors, including your individual circumstances, the type of coverage you choose, and the market conditions.
Age
Age is one of the most significant factors that influences health insurance premiums. As you get older, you are more likely to require healthcare services, which increases the risk for insurers. Consequently, older individuals typically pay higher premiums compared to younger individuals.
Location
The cost of healthcare varies significantly across different geographic locations. Health insurance premiums reflect these regional differences. For example, premiums in urban areas with higher healthcare costs tend to be higher than premiums in rural areas.
Health Status
Your health status is a major factor in determining your health insurance premiums. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a history of chronic illnesses often face higher premiums due to the increased risk of healthcare utilization.
Coverage Options
The type of coverage you choose significantly impacts your premiums. Comprehensive plans that cover a wide range of services and benefits usually come with higher premiums compared to basic plans with limited coverage.
Lifestyle Choices
Your lifestyle choices can also affect your health insurance premiums. For instance, individuals who engage in unhealthy habits like smoking or excessive alcohol consumption may face higher premiums because of the increased risk of health problems.
Family Size
The size of your family can also influence your health insurance premiums. Larger families generally have higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of healthcare needs.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel overwhelming, especially with the various plan types available. Understanding the key differences between these plans is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your needs and budget.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
HMOs offer a more structured approach to healthcare. They typically have a lower monthly premium than other plans, but require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network. You’ll need a referral from your PCP to see specialists or receive other services.
Key Features of HMOs:
- Lower Premiums: HMOs generally have lower monthly premiums compared to PPOs and POS plans.
- Network Restrictions: You are limited to seeing doctors and specialists within the HMO’s network.
- Referral Requirement: You typically need a referral from your PCP to see specialists or receive other services.
- Preventive Care Coverage: HMOs often cover preventive care services like checkups and screenings without requiring a copay or deductible.
- Limited Out-of-Network Coverage: HMOs usually offer limited or no coverage for out-of-network services, except in emergency situations.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
PPOs offer greater flexibility compared to HMOs. They allow you to see doctors and specialists both in and out of their network, although costs may be higher for out-of-network care.
Key Features of PPOs:
- Higher Premiums: PPOs typically have higher monthly premiums than HMOs.
- Network Flexibility: You can see doctors and specialists both in and out of the PPO’s network, but you’ll pay more for out-of-network services.
- No Referral Requirement: You usually don’t need a referral from your PCP to see specialists.
- Higher Out-of-Network Coverage: PPOs generally offer more coverage for out-of-network services compared to HMOs.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
EPOs are similar to HMOs in that they require you to choose a PCP within the network and require referrals to see specialists. However, unlike HMOs, EPOs generally do not offer any coverage for out-of-network services, even in emergencies.
Key Features of EPOs:
- Lower Premiums: EPOs often have lower premiums compared to PPOs, but higher than HMOs.
- Network Restrictions: You are limited to seeing doctors and specialists within the EPO’s network.
- Referral Requirement: You typically need a referral from your PCP to see specialists.
- No Out-of-Network Coverage: EPOs generally do not offer any coverage for out-of-network services, even in emergencies.
Point-of-Service (POS), How much does health insurance cost
POS plans combine features of both HMOs and PPOs. They offer a network of doctors and specialists, but also allow you to see providers outside the network for a higher cost.
Key Features of POS Plans:
- Premiums: POS premiums fall between HMOs and PPOs.
- Network Flexibility: You can see doctors and specialists both in and out of the network, but you’ll pay more for out-of-network services.
- Referral Requirement: You may or may not need a referral from your PCP to see specialists, depending on the specific plan.
- Higher Out-of-Network Coverage: POS plans offer more coverage for out-of-network services than HMOs, but less than PPOs.
Comparing Health Insurance Plan Types
| Plan Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| HMO | Lower premiums, good preventive care coverage | Network restrictions, referral requirements, limited out-of-network coverage |
| PPO | Network flexibility, no referral requirement, higher out-of-network coverage | Higher premiums, higher costs for out-of-network services |
| EPO | Lower premiums, good preventive care coverage | Network restrictions, referral requirements, no out-of-network coverage |
| POS | Flexibility, some out-of-network coverage | Higher premiums, potential for higher out-of-pocket costs |
Understanding Deductibles, Copayments, and Coinsurance
Navigating the world of health insurance often involves encountering terms like deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. These cost-sharing mechanisms play a crucial role in determining your out-of-pocket expenses for healthcare services. Understanding how they work is essential for making informed decisions about your health insurance coverage.
Cost-Sharing Mechanisms
These cost-sharing mechanisms are designed to encourage individuals to be more mindful of their healthcare utilization while also sharing the financial burden of healthcare costs with insurance providers.
- Deductible: This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your health insurance plan starts covering your healthcare expenses. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, you would need to pay the first $1,000 of your healthcare costs before your insurance kicks in. Once you reach your deductible, your insurance will start covering a percentage of your remaining healthcare expenses.
- Copayment: This is a fixed amount you pay for specific healthcare services, such as doctor’s visits, prescriptions, or hospital stays. Copayments are typically a smaller amount compared to deductibles and are paid at the time of service. For example, you might have a $20 copayment for a doctor’s visit or a $10 copayment for a prescription.
- Coinsurance: This is a percentage of the cost of a healthcare service that you are responsible for paying after your deductible has been met. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you would pay 20% of the cost of a covered healthcare service after your deductible has been met. The remaining 80% would be covered by your insurance.
Real-World Examples
Let’s consider some real-world examples to illustrate how these cost-sharing mechanisms work:
- Deductible: Imagine you have a $1,000 deductible and you need to have a surgery that costs $5,000. You would be responsible for paying the first $1,000 out-of-pocket. Once you reach the $1,000 deductible, your insurance would start covering the remaining $4,000, based on your coinsurance percentage.
- Copayment: You go to the doctor for a routine checkup and your copayment is $20. You pay $20 at the time of the visit, and your insurance covers the remaining cost of the visit.
- Coinsurance: You need a new medication that costs $100. Your deductible has already been met, and your coinsurance is 20%. You would be responsible for paying 20% of the $100, which is $20. Your insurance would cover the remaining $80.
Typical Ranges
Here’s a table illustrating the typical ranges of deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance across different health insurance plans:
| Plan Type | Deductible Range | Copayment Range | Coinsurance Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) | $1,400 – $7,000+ | $10 – $50+ | 10% – 30%+ |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | $500 – $3,000+ | $15 – $40+ | 10% – 30%+ |
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | $0 – $500+ | $10 – $30+ | 10% – 30%+ |
Cost Estimation Tools and Resources
Navigating the complex world of health insurance can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding costs. Fortunately, various online tools and resources are available to help individuals estimate their potential health insurance expenses. These tools provide a valuable starting point for comparison and planning, offering personalized estimates based on specific factors.
Online Health Insurance Cost Estimators
These tools typically require basic information about the user, such as age, location, desired coverage level, and family size. They utilize this data to generate a personalized estimate of monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs. Some popular online health insurance cost estimators include:
- Healthcare.gov: This government-run website offers a comprehensive tool for exploring health insurance options and estimating costs based on individual circumstances. Users can input their ZIP code, age, income, and other relevant details to receive personalized plan estimates.
- eHealth: This private marketplace provides a user-friendly platform for comparing health insurance plans from various providers. The website’s cost estimation tool allows users to input their location, age, and desired coverage level to receive tailored estimates.
- HealthPocket: This website offers a unique approach to health insurance cost estimation by focusing on individual health needs and coverage preferences. Users can customize their search based on factors like pre-existing conditions, desired benefits, and preferred provider networks.
Limitations of Cost Estimation Tools
While these tools provide valuable insights into potential health insurance costs, it’s crucial to understand their limitations. Cost estimations are not always accurate and may not reflect all individual circumstances.
- Limited Data: Cost estimation tools often rely on limited data and may not account for all individual factors that can influence premiums, such as specific health conditions or lifestyle choices. This can lead to inaccurate estimates.
- Dynamic Market: The health insurance market is constantly evolving, with premiums and coverage options changing frequently. Cost estimations may become outdated quickly, especially in regions with high competition or regulatory changes.
- Individual Circumstances: Cost estimations may not account for individual circumstances that can impact premiums, such as specific health conditions, employment status, or family size. This can lead to inaccurate estimations for individuals with unique needs.
Utilizing Cost Estimation Tools Effectively
Despite their limitations, cost estimation tools can be valuable resources for navigating the health insurance market. To maximize their usefulness, consider the following:
- Multiple Tools: Use multiple cost estimation tools to compare estimates and identify potential discrepancies. This can help ensure that you are receiving a comprehensive understanding of potential costs.
- Detailed Information: Provide as much detailed information as possible to the cost estimation tools, including specific health conditions, coverage preferences, and family size. This can lead to more accurate estimates.
- Contact Insurers: Once you have a general understanding of potential costs from cost estimation tools, contact individual insurance providers directly to discuss specific plans and obtain personalized quotes.
Navigating the Health Insurance Marketplace
The health insurance marketplace, also known as the Health Insurance Exchange, provides a platform for individuals and families to shop for and enroll in health insurance plans that meet their needs and budget. Understanding the process of navigating this marketplace is crucial to finding the right coverage and maximizing your savings.
Enrollment Periods and Eligibility Requirements
The health insurance marketplace operates on specific enrollment periods, during which you can apply for or change your coverage. The primary enrollment period typically runs from November 1st to January 15th each year, with coverage starting on January 1st of the following year. However, there are also special enrollment periods available for specific life events, such as getting married, having a baby, or losing other health insurance coverage.
Eligibility for marketplace plans is based on factors such as income, household size, and citizenship status. The marketplace offers financial assistance in the form of tax credits to help eligible individuals and families afford coverage. To determine your eligibility and the amount of financial assistance you may qualify for, you can use the marketplace’s online tools or contact a certified application counselor.
Comparing Plans and Selecting Coverage
The health insurance marketplace offers a wide range of plans from different insurance companies, allowing you to compare options and choose the one that best suits your needs and budget. You can use the marketplace’s website or mobile app to filter plans based on factors such as:
- Monthly premium: This is the amount you pay each month for your health insurance coverage.
- Deductible: This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket for medical expenses before your insurance coverage kicks in.
- Co-payments: These are fixed amounts you pay for specific services, such as doctor visits or prescriptions.
- Coinsurance: This is a percentage of medical expenses you pay after your deductible has been met.
- Network: This refers to the doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers covered by your insurance plan.
When comparing plans, it’s important to consider your healthcare needs and usage patterns. For example, if you have a chronic condition, you might prioritize plans with lower co-payments for specific services related to your condition. Similarly, if you rarely use healthcare services, a plan with a higher deductible and lower monthly premium might be more cost-effective.
Tips for Maximizing Savings and Finding Affordable Options
Finding affordable health insurance can be challenging, but there are several strategies you can employ to maximize your savings:
- Shop around and compare plans: Don’t settle for the first plan you see. Take the time to explore different options and compare their costs and benefits.
- Consider a plan with a higher deductible: Plans with higher deductibles generally have lower monthly premiums. If you rarely use healthcare services, this could be a cost-effective option.
- Explore financial assistance options: The marketplace offers tax credits to help eligible individuals and families afford coverage. Be sure to check your eligibility and apply for any available assistance.
- Consider preventive care: Preventive care services, such as annual checkups and vaccinations, are often covered at no cost. Taking advantage of these services can help you stay healthy and avoid expensive medical treatments in the future.
- Use generic medications when possible: Generic medications are often significantly cheaper than brand-name medications, while providing the same therapeutic benefits.
- Ask for price estimates before receiving medical care: Before scheduling a procedure or test, inquire about the estimated cost to avoid unexpected bills.
Government Subsidies and Financial Assistance
The cost of health insurance can be a significant financial burden for many individuals and families. Fortunately, the government offers a variety of subsidies and financial assistance programs to help make health insurance more affordable. These programs can significantly reduce the cost of premiums, deductibles, and other out-of-pocket expenses.
These programs are designed to make health insurance accessible to individuals and families who may otherwise struggle to afford it. Eligibility for these programs is based on factors such as income, family size, and age.
Eligibility Criteria and Application Process
To qualify for government subsidies and financial assistance, individuals must meet certain eligibility criteria. These criteria typically include:
- Income: Individuals must have an income that falls below a certain threshold. The specific income limits vary depending on the program and the individual’s family size.
- Age: Some programs have age restrictions, such as being under 65 years old or being a senior citizen.
- Citizenship or residency: Most programs require individuals to be U.S. citizens or legal residents.
- Other factors: Other factors, such as disability status or enrollment in certain government programs, may also affect eligibility.
The application process for government subsidies and financial assistance varies depending on the specific program. However, most programs require individuals to provide information about their income, family size, and other relevant details. Individuals can typically apply for these programs online, by phone, or through a healthcare provider.
Examples of Financial Assistance Programs
Here are some examples of government programs that provide financial assistance for health insurance:
- The Affordable Care Act (ACA) Premium Tax Credits: This program provides subsidies to help individuals and families afford health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace. The amount of the tax credit is based on income and family size. For example, a family of four with an income of $50,000 per year may receive a tax credit of $5,000 per year to help offset the cost of their health insurance premiums.
- Medicaid: This program provides health insurance coverage to low-income individuals and families. Medicaid eligibility varies by state, but it typically covers individuals with incomes below a certain threshold. In some states, Medicaid covers individuals with higher incomes, such as pregnant women or children. For example, a single individual with an income of $15,000 per year may qualify for Medicaid.
- The Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP): This program provides health insurance coverage to children in families with incomes above the Medicaid eligibility level but who still cannot afford private health insurance. CHIP eligibility varies by state, but it typically covers children with incomes up to twice the federal poverty level. For example, a family of four with an income of $40,000 per year may qualify for CHIP.
Cost Considerations for Specific Health Needs
Understanding how health insurance plans cover specific health needs is crucial for making informed decisions. Factors like chronic illnesses or pregnancy can significantly impact your healthcare costs. It’s essential to evaluate your specific health requirements when choosing a plan.
Chronic Illnesses
Chronic illnesses often require ongoing medical care, medications, and specialized treatments, which can lead to substantial healthcare expenses. Health insurance plans offer varying levels of coverage for chronic conditions.
- Some plans may have higher premiums but offer comprehensive coverage, including prescription drugs, therapies, and doctor visits.
- Other plans may have lower premiums but have higher deductibles or copayments, leading to higher out-of-pocket costs for individuals with chronic illnesses.
It’s essential to compare plans and understand their coverage for specific chronic conditions.
Consider factors like the plan’s formulary (list of covered drugs), provider network, and limitations on services like physical therapy or home health.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy and childbirth are significant events that require comprehensive healthcare coverage.
- Prenatal care, labor and delivery, and postpartum care are essential services covered by most health insurance plans.
- However, coverage can vary significantly, impacting out-of-pocket costs.
- Some plans may have limited coverage for certain pregnancy-related services, such as genetic testing or breastfeeding support.
- Others may have higher deductibles or copayments for pregnancy-related care.
It’s crucial to choose a plan that offers comprehensive coverage for pregnancy and childbirth, including prenatal and postpartum care.
Strategies for Reducing Health Insurance Costs
Lowering your health insurance premiums and out-of-pocket expenses can significantly impact your budget. Fortunately, several strategies can help you reduce these costs without compromising your health coverage.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle can significantly impact your health insurance costs. When you prioritize your well-being, you reduce your risk of developing chronic conditions, which often lead to higher medical expenses. By incorporating healthy habits into your daily routine, you can potentially lower your premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Participating in Wellness Programs
Many health insurance providers offer wellness programs that incentivize healthy behaviors and provide resources to support your well-being. These programs can include discounts on gym memberships, rewards for completing health screenings, and access to online health resources. Participating in these programs can lead to lower premiums and contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
Exploring Alternative Healthcare Options
Alternative healthcare options can provide cost-effective solutions for certain health needs. Consider exploring options such as:
- Telemedicine: Telemedicine allows you to consult with healthcare professionals remotely through video conferencing or phone calls. This can be a convenient and cost-effective alternative for non-emergency medical consultations.
- Retail Clinics: Retail clinics located in drugstores or other convenient locations offer basic healthcare services at lower costs than traditional doctor’s offices. They can handle common ailments like flu, ear infections, and skin rashes.
- Urgent Care Centers: Urgent care centers provide immediate medical attention for non-life-threatening conditions at lower costs than emergency rooms. They can handle minor injuries, illnesses, and other urgent medical needs.
Negotiating Your Premium
You can often negotiate your health insurance premiums by:
- Comparing Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers and compare plans based on your needs and budget. This allows you to find the most competitive rates.
- Exploring Group Plans: If you’re eligible for a group health insurance plan through your employer or an organization, you may be able to access lower premiums and more comprehensive coverage.
- Considering Higher Deductibles: A higher deductible typically translates to lower premiums. However, be sure to consider your financial capacity to cover a higher deductible if you need medical care.
Making Informed Healthcare Choices
By making informed healthcare choices, you can control your out-of-pocket expenses.
- Generic Medications: Generic medications are typically much cheaper than brand-name drugs but offer the same effectiveness. Consult your doctor to see if a generic alternative is available for your prescribed medication.
- Preventive Care: Regularly scheduling preventive screenings and check-ups can help detect health issues early, potentially reducing the need for more expensive treatments later.
- Understanding Your Coverage: Thoroughly review your health insurance policy to understand your coverage limits, deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. This knowledge allows you to make informed decisions about healthcare services and avoid unexpected costs.
Seeking Financial Assistance
If you’re struggling to afford your health insurance premiums or out-of-pocket expenses, explore financial assistance options.
- Government Subsidies: The Affordable Care Act (ACA) offers subsidies to individuals and families who meet certain income requirements. These subsidies can help lower your monthly premiums and make health insurance more affordable.
- State and Local Programs: Many states and local governments offer programs that provide financial assistance for healthcare costs, including prescription drug coverage and mental health services.
- Charity Organizations: Some non-profit organizations provide financial assistance for medical expenses to individuals facing financial hardship.
Conclusion: How Much Does Health Insurance Cost
Navigating the world of health insurance can be overwhelming, but armed with the right information, you can make informed decisions that ensure your financial well-being and access to quality healthcare. By understanding the factors that influence costs, exploring the various plan options, and leveraging available resources, you can find a health insurance plan that provides adequate coverage without breaking the bank. Remember, your health is your most valuable asset, and investing in appropriate insurance is a wise step towards securing your future.
Q&A
What are the most common reasons for health insurance premiums to increase?
Premiums can increase due to factors like rising healthcare costs, changes in the risk pool (e.g., more people enrolling with pre-existing conditions), and adjustments to government regulations.
Can I switch health insurance plans during the year?
Generally, you can only switch health insurance plans during the annual open enrollment period, unless you experience a qualifying life event, such as losing your job or getting married.
What are some strategies for reducing out-of-pocket expenses?
Consider options like choosing a plan with a lower deductible, participating in wellness programs, and exploring preventive care options to minimize out-of-pocket costs.
How often should I review my health insurance needs?
It’s advisable to review your health insurance needs annually, especially if your health status changes, your family size grows, or your income fluctuates.