- Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
- Types of Health Insurance Plans
- Understanding Deductibles, Copayments, and Coinsurance
- Cost-Saving Strategies for Health Insurance
- The Role of Government Subsidies and Tax Credits
- Health Insurance Marketplace and Open Enrollment: How Much Does.health Insurance Cost
- Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
- Health Insurance for Specific Needs
- Outcome Summary
- General Inquiries
How much does.health insurance cost – How much does health insurance cost? It’s a question on many people’s minds, and the answer isn’t always simple. The price of health insurance is influenced by a variety of factors, including your age, location, health status, and the type of coverage you choose. Even your lifestyle choices and pre-existing conditions can impact your premiums. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about your health insurance.
This guide explores the various aspects of health insurance costs, breaking down the different types of plans, cost-sharing mechanisms, and strategies for saving money. We’ll also discuss the role of government subsidies, the health insurance marketplace, and employer-sponsored coverage. Whether you’re a young adult just starting out, a family with children, or a senior citizen, this information will empower you to make the best choices for your individual needs.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
The price you pay for health insurance, known as your premium, is influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your health insurance plan.
Age
Age is a significant factor in determining health insurance premiums. Generally, older individuals tend to have higher premiums than younger individuals. This is because older people are more likely to experience health issues that require medical attention, leading to higher healthcare costs.
Location
The cost of health insurance can vary depending on your location. This is primarily due to differences in the cost of healthcare services, such as doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription drugs. For example, living in a densely populated urban area with high healthcare demand may result in higher premiums compared to a rural area with lower healthcare utilization.
Health Status
Your health status plays a crucial role in determining your health insurance premiums. Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer, are often required to pay higher premiums. This is because they are more likely to need medical care, leading to higher healthcare costs.
Coverage Options
The type of coverage you choose can also significantly impact your health insurance premiums. Plans with higher coverage levels, such as comprehensive plans with extensive benefits, generally have higher premiums than plans with lower coverage levels, such as basic plans with limited benefits.
Lifestyle Choices
Your lifestyle choices can also influence your health insurance premiums. For example, individuals who engage in unhealthy habits such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption may be required to pay higher premiums. This is because these habits can increase the risk of developing health problems, leading to higher healthcare costs.
Pre-existing Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer, may be required to pay higher premiums. This is because they are more likely to need medical care, leading to higher healthcare costs. Health insurance companies consider the potential risk associated with pre-existing conditions when setting premiums.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Choosing the right health insurance plan is crucial for ensuring you have adequate coverage when you need it. The type of plan you choose will influence your out-of-pocket costs, the healthcare providers you can access, and the services covered.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
HMOs are known for their lower premiums, but they offer limited provider choices and require referrals for specialist care.
- Coverage: HMOs typically have a network of healthcare providers, and you must choose a primary care physician (PCP) within that network. You’ll need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist.
- Costs: HMOs usually have lower monthly premiums than other plans. They may have lower copayments and deductibles, but you’ll likely face higher out-of-pocket costs for care outside the network.
- Benefits: HMOs emphasize preventive care and often provide comprehensive coverage for routine checkups and screenings. They can be a good option for individuals who need regular access to healthcare services and are comfortable with a limited provider network.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to see specialists without a referral. However, they usually have higher premiums.
- Coverage: PPOs have a network of providers, but you have more flexibility to see out-of-network providers. While you’ll typically pay less for in-network care, you’ll have higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network services.
- Costs: PPOs usually have higher monthly premiums than HMOs. They may have higher copayments and deductibles, but you’ll likely have lower out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care compared to an HMO.
- Benefits: PPOs provide greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and offer coverage for both in-network and out-of-network care. They are a good option for individuals who value flexibility and may need to see specialists frequently.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
EPOs are a hybrid of HMOs and PPOs, offering lower premiums than PPOs but with fewer provider options than HMOs.
- Coverage: EPOs have a limited network of providers, similar to HMOs. You’ll need a referral from your PCP to see a specialist. Unlike HMOs, you may not be covered for out-of-network care.
- Costs: EPOs typically have lower monthly premiums than PPOs but higher premiums than HMOs. They may have lower copayments and deductibles than PPOs.
- Benefits: EPOs offer a balance between cost and flexibility. They can be a good option for individuals who want lower premiums than PPOs but are comfortable with a limited provider network.
Examples
- Scenario 1: A healthy young individual who rarely needs healthcare services and prefers lower premiums might opt for an HMO.
- Scenario 2: An individual with a chronic condition who requires regular specialist care and wants flexibility in choosing providers might choose a PPO.
- Scenario 3: A family with a limited budget but needing access to a specific specialist within a network might choose an EPO.
Understanding Deductibles, Copayments, and Coinsurance
Health insurance plans often involve cost-sharing mechanisms, which are designed to encourage responsible healthcare utilization and to spread the costs of healthcare across a larger pool of individuals. These cost-sharing mechanisms include deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
Deductibles
A deductible is a fixed amount you must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your health insurance plan starts paying. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, you would need to pay the first $1,000 of covered medical expenses yourself. Once you reach your deductible, your health insurance plan will start covering the remaining costs, typically according to your plan’s coinsurance percentage.
Copayments
Copayments are fixed amounts you pay for specific healthcare services, such as doctor’s visits, prescription drugs, or emergency room visits. These payments are usually made at the time of service. For instance, your copayment for a doctor’s visit might be $25, while your copayment for a prescription drug could be $10. Copayments are generally applied regardless of whether you have met your deductible.
Coinsurance
Coinsurance is a percentage of the covered healthcare costs that you are responsible for paying after you have met your deductible. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you would pay 20% of the covered costs after your deductible has been met, and your health insurance plan would pay the remaining 80%.
Cost-Sharing Scenarios
The following table illustrates how deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance work in practice for different healthcare services:
| Service | Deductible | Copayment | Coinsurance | Out-of-Pocket Cost | Total Cost |
|—|—|—|—|—|—|
| Doctor’s Visit | $1,000 | $25 | 20% | $25 | $100 |
| Prescription Drug | $1,000 | $10 | 20% | $10 | $50 |
| Hospital Stay | $1,000 | N/A | 20% | $1,000 + 20% of remaining cost | $5,000 |
Note: These are just examples, and the actual costs will vary depending on your specific health insurance plan.
It’s important to understand the different cost-sharing mechanisms in your health insurance plan so that you can make informed decisions about your healthcare.
Cost-Saving Strategies for Health Insurance

Navigating the complexities of health insurance can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to finding ways to lower your premiums. Thankfully, several strategies can help you reduce your out-of-pocket expenses and make your health insurance more affordable.
Strategies to Reduce Premiums
Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce your health insurance premiums:
- Shop around for plans: Comparing quotes from different insurance companies can help you find the most affordable plan that meets your needs. Online comparison tools and insurance brokers can simplify this process.
- Consider a higher deductible: Opting for a higher deductible can lower your monthly premiums, as you agree to pay more out-of-pocket for medical expenses before your insurance kicks in. This strategy is suitable for individuals who are generally healthy and less likely to require frequent medical care.
- Take advantage of discounts: Many insurance companies offer discounts for factors such as good health, non-smoking status, and participation in wellness programs. Ask your insurer about available discounts to see if you qualify.
- Enroll during open enrollment: Enrolling in a plan during the open enrollment period can provide you with more choices and potentially lower premiums compared to enrolling outside this period.
- Negotiate your rate: Contact your insurance company to inquire about potential rate adjustments or discounts. Be prepared to explain your situation and why you believe a lower rate is justified.
Preventive Care and Healthy Lifestyle
Investing in preventive care and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact your health insurance costs:
- Regular checkups and screenings: Early detection and prevention of health issues can help avoid costly treatments in the long run. Regular checkups, screenings, and vaccinations can significantly lower your healthcare expenses.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and abstaining from smoking can lower your risk of developing chronic diseases, which can lead to substantial medical costs.
Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) and Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
These accounts offer tax advantages and potential savings on healthcare expenses:
- Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs): FSAs allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for eligible medical expenses. This can reduce your taxable income and save you money on healthcare costs.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): HSAs are available to individuals enrolled in high-deductible health plans. They allow you to contribute pre-tax dollars to an account that can be used to pay for qualified medical expenses. The funds in an HSA roll over year to year, providing long-term savings potential.
The Role of Government Subsidies and Tax Credits
The cost of health insurance can be a significant financial burden for many individuals and families. To make health insurance more affordable, the government offers a variety of subsidies and tax credits to eligible individuals and families. These programs can help offset the cost of premiums, deductibles, and other out-of-pocket expenses.
Eligibility Criteria and Application Process
Eligibility for government subsidies and tax credits is determined based on factors such as income, family size, and age. To apply for these programs, individuals typically need to complete an application through the Health Insurance Marketplace, also known as Healthcare.gov. The application process involves providing information about income, household size, and other relevant details. Based on the information provided, the Marketplace determines eligibility and calculates the amount of subsidy or tax credit an individual is entitled to.
Types of Subsidies and Tax Credits
The government offers various subsidies and tax credits to help individuals and families afford health insurance. These programs are designed to make coverage more accessible and affordable for those who meet certain income requirements. Here’s a summary of the available programs:
| Program | Income Level | Family Size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premium Tax Credit | Below 400% of the federal poverty level | Varies | A tax credit that helps reduce the cost of monthly premiums. |
| Cost-Sharing Reductions | Below 250% of the federal poverty level | Varies | Lower out-of-pocket costs for deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. |
| Medicaid | Below 138% of the federal poverty level | Varies | A government-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. |
| Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) | Varies by state | Children under 19 | A program that provides health insurance coverage to children in families with modest incomes. |
Note: Eligibility criteria and specific program details may vary depending on the state and individual circumstances. It is essential to consult with the Health Insurance Marketplace or a qualified healthcare professional for accurate and up-to-date information.
Health Insurance Marketplace and Open Enrollment: How Much Does.health Insurance Cost
The Health Insurance Marketplace, also known as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplace, is a platform that helps individuals and families find and enroll in health insurance plans that meet their needs and budget. It provides a centralized location to compare plans from different insurance companies and access government subsidies that can lower the cost of coverage.
Open enrollment periods are specific times of year when you can sign up for or change your health insurance plan. Understanding these periods and their deadlines is crucial, as missing them can result in significant financial penalties or limited plan choices.
Open Enrollment Periods
Open enrollment periods are typically set by the federal government and vary depending on the state. During these periods, individuals can enroll in a health insurance plan through the Marketplace, regardless of whether they have experienced a qualifying life event.
- Annual Open Enrollment: This is the main enrollment period for most individuals. It typically runs from November 1st to January 15th, with coverage starting on January 1st of the following year.
- Special Enrollment Periods: These are limited opportunities to enroll in or change health insurance outside of the regular open enrollment period. They are available to individuals who experience certain life events, such as getting married, having a baby, or losing coverage through their employer.
Consequences of Missing Open Enrollment
Missing open enrollment can have several consequences:
- Penalty for not having health insurance: Individuals who do not have health insurance during the year are subject to a penalty. This penalty can be significant and is assessed when filing your taxes.
- Limited plan choices: If you miss open enrollment, you may have fewer plan options available to you. The Marketplace may only offer limited plans outside of the enrollment period, which might not meet your specific needs or budget.
- Higher premiums: You may face higher premiums if you enroll in a plan outside of open enrollment. Insurance companies often charge higher rates for those who enroll later in the year.
Navigating the Health Insurance Marketplace
The Health Insurance Marketplace can be a complex platform to navigate. Here are some tips and resources to help you find the right plan:
- Use the Marketplace website: The Marketplace website provides a user-friendly platform to compare plans, calculate costs, and enroll in coverage. You can access the website at [https://www.healthcare.gov/](https://www.healthcare.gov/).
- Contact a certified broker or agent: Certified brokers and agents can provide personalized assistance in navigating the Marketplace and selecting a plan that meets your specific needs.
- Understand your eligibility for subsidies: The Marketplace offers subsidies to individuals and families who meet certain income requirements. These subsidies can significantly reduce the cost of coverage.
- Compare plans carefully: Don’t just focus on the monthly premium. Compare the deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance for each plan.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Health Insurance Plan
Several factors are important to consider when selecting a health insurance plan:
- Your health needs: If you have pre-existing conditions, you’ll need to ensure the plan covers your specific needs.
- Your budget: Consider your monthly premium, deductible, copayments, and coinsurance.
- Your doctor network: Make sure the plan includes your preferred doctors and hospitals.
- Your coverage needs: Consider what services you need, such as prescription drugs, mental health care, and preventive services.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Employer-sponsored health insurance is a common way for individuals to obtain health coverage in the United States. This type of insurance is offered by employers as a benefit to their employees, typically as part of a comprehensive benefits package.
Employer-sponsored health insurance can be a valuable resource for employees, providing access to affordable and comprehensive coverage. However, it’s important to understand both the benefits and limitations of this type of insurance.
Benefits and Limitations of Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Employer-sponsored health insurance offers several advantages, including:
- Lower Premiums: Employers often contribute a significant portion of the premium costs, making the insurance more affordable for employees. This is especially beneficial for individuals who may not be able to afford coverage on their own.
- Group Rates: By pooling together employees, employers can negotiate lower group rates with insurance companies, resulting in lower premiums for everyone.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Employer-sponsored plans typically offer comprehensive coverage, including hospitalization, surgery, prescription drugs, and preventive care. This ensures employees have access to a wide range of healthcare services.
- Tax Advantages: Premiums paid by employers are often tax-deductible for the company, while premiums paid by employees are often tax-deductible for the individual. This can lead to significant savings on taxes.
However, there are also some limitations to consider:
- Limited Choice: Employees may have limited choices in terms of health insurance plans offered by their employer. This could mean they don’t have access to the plan that best suits their individual needs or preferences.
- Job Security: Access to employer-sponsored health insurance is often tied to employment. If an employee loses their job, they may lose their health insurance as well, leaving them without coverage until they find new employment.
- Potential for Higher Deductibles and Co-pays: Some employer-sponsored plans may have higher deductibles and co-pays than individual plans, which could lead to higher out-of-pocket costs for employees.
- Changes in Coverage: Employers may change their health insurance plans or benefits packages from year to year, which can lead to disruptions in coverage for employees.
Comparison of Costs and Coverage Options
The costs and coverage options offered by different employers can vary significantly. This is influenced by factors such as:
- Industry: Some industries, such as healthcare or education, tend to offer more generous health insurance benefits than others, such as retail or hospitality.
- Company Size: Larger companies may have more bargaining power with insurance companies and be able to negotiate lower premiums and better coverage options.
- Location: The cost of healthcare varies by location, so employers in areas with higher healthcare costs may offer more expensive plans.
- Plan Type: Employers may offer a range of health insurance plan types, such as HMOs, PPOs, and POS plans. Each plan type has its own costs and coverage options.
Impact of Employer Contributions on Employee Premiums, How much does.health insurance cost
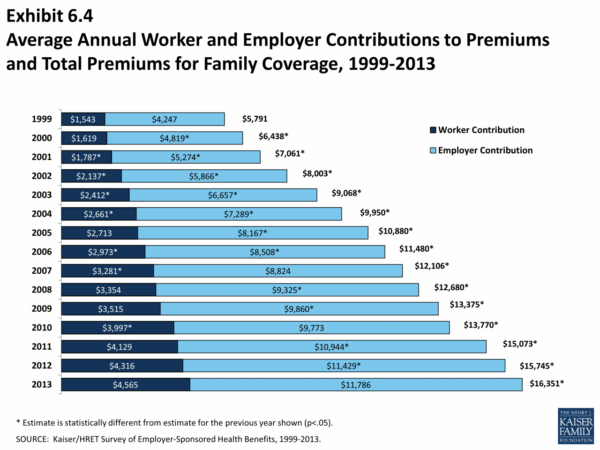
The amount that employers contribute towards employee premiums can significantly impact the cost of health insurance for employees.
Employers often contribute a certain percentage of the total premium cost, while employees pay the remaining portion. The employer’s contribution can vary widely depending on the company’s size, industry, and financial situation.
For example, an employer might contribute 75% of the premium cost, while the employee pays the remaining 25%. This would make the insurance more affordable for the employee, as they are only responsible for a smaller portion of the total cost.
Higher employer contributions can lead to lower employee premiums, making health insurance more affordable and accessible. Conversely, lower employer contributions can result in higher employee premiums, which could make coverage less affordable for some employees.
Health Insurance for Specific Needs
Health insurance needs vary depending on individual circumstances, such as age, health status, and family size. Certain groups, like seniors, students, and families, require specific considerations when choosing health insurance. Additionally, specialized plans address particular needs, such as dental or vision coverage.
Health Insurance for Seniors
Seniors have unique health insurance needs due to their increased susceptibility to health issues and the potential for higher healthcare costs. Medicare, a federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, provides essential coverage for seniors. However, Medicare does not cover all healthcare expenses, and seniors may need to supplement their coverage with a Medicare Advantage plan or a Medigap policy. Medicare Advantage plans offer additional benefits, while Medigap policies help cover out-of-pocket costs associated with original Medicare. Seniors should carefully consider their health status, budget, and coverage preferences when choosing a Medicare plan.
Health Insurance for Students
Students often face unique health insurance challenges, particularly those enrolled in colleges or universities outside their home state. Many colleges and universities offer student health insurance plans, but these plans may not be comprehensive enough to meet all needs. Students should evaluate their coverage options, considering factors like pre-existing conditions, coverage for mental health services, and access to healthcare providers. Students may also be eligible for coverage under their parents’ plans, depending on their age and state regulations.
Health Insurance for Families
Families require health insurance plans that cater to the diverse needs of their members, including children, adults, and potentially seniors. Family health insurance plans typically offer coverage for a range of services, including preventive care, hospitalization, and prescription drugs. Families should consider factors like coverage for dependents, family deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums when choosing a plan. Some plans offer discounts for multiple family members, while others may provide coverage for specific conditions or treatments relevant to children or seniors.
Specialized Health Insurance Plans
In addition to traditional health insurance plans, specialized plans cater to specific healthcare needs, such as dental or vision coverage. Dental insurance plans cover preventive care, such as cleanings and checkups, as well as restorative treatments, like fillings and crowns. Vision insurance plans provide coverage for eye exams, glasses, and contact lenses. Specialized plans can be purchased individually or through an employer. Individuals should evaluate their healthcare needs and budget to determine if a specialized plan is necessary.
Resources for Health Insurance Decisions
Several resources and organizations can assist individuals in making informed health insurance decisions. The Health Insurance Marketplace, also known as Healthcare.gov, provides a platform for comparing plans and enrolling in coverage. State-based health insurance marketplaces offer similar services within specific states. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) provides information and guidance on Medicare, Medicaid, and other health insurance programs. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) offers resources and tools for consumers to understand health insurance policies and regulations.
Outcome Summary
Navigating the world of health insurance can be complex, but with the right information, you can make informed decisions about your coverage. Remember, it’s essential to consider your individual needs, budget, and health status when selecting a plan. By understanding the factors that influence costs, exploring available options, and taking advantage of cost-saving strategies, you can find affordable and comprehensive health insurance that meets your needs. Whether you choose to purchase individual coverage through the marketplace, enroll in employer-sponsored insurance, or explore other options, having a clear understanding of the costs involved will help you make the best choices for your health and financial well-being.
General Inquiries
What are some common cost-saving strategies for health insurance?
There are several ways to potentially reduce your health insurance premiums, including choosing a higher deductible plan, participating in a health savings account (HSA), and making healthy lifestyle choices.
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO?
An HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) typically requires you to choose a primary care physician within the network and get referrals for specialists. PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations) offer more flexibility, allowing you to see providers outside the network, though it may cost more.
What is open enrollment for health insurance?
Open enrollment is a specific period during which you can sign up for or change your health insurance plan. Missing open enrollment could limit your options or result in paying a penalty.
How do I find out if I qualify for government subsidies for health insurance?
You can use the Health Insurance Marketplace website or contact a health insurance agent or broker to determine your eligibility for subsidies based on your income and family size.