Does Google Search violate antitrust law? This question has been a topic of intense debate for years, as Google’s dominance in the search engine market has raised concerns about potential anti-competitive practices. While Google argues that its services benefit consumers and drive innovation, critics point to its vast market share and alleged manipulation of search results to favor its own products. This complex issue involves intricate legal arguments, economic analysis, and the implications for consumer choice and the future of the internet.
The debate surrounding Google’s search practices revolves around the core principles of antitrust law, which aim to protect competition and prevent monopolies from stifling innovation. Antitrust laws are designed to ensure a level playing field for businesses and prevent consumers from being exploited by dominant companies. In the technology sector, these principles are particularly relevant, as companies like Google have rapidly gained significant market power.
Google’s Arguments in Defense: Does Google Search Violate Antitrust Law
Google argues that its dominance in search is a result of its commitment to providing users with the best possible search experience, driven by innovation and a constant pursuit of improvement. They emphasize that their search engine’s benefits to consumers outweigh any potential antitrust concerns.
Google’s Search Engine Benefits to Consumers
Google asserts that its search engine offers numerous benefits to consumers, including:
- Comprehensive and relevant results: Google’s search algorithms are designed to deliver the most relevant and comprehensive results, ensuring users find what they need quickly and efficiently.
- User-friendly interface: Google’s search interface is intuitive and easy to use, even for novice users. Its clean design and simple features make it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Constant innovation: Google continuously invests in research and development, constantly improving its search algorithms and introducing new features to enhance user experience. Examples include the introduction of voice search, image search, and personalized search results.
- Free access: Google’s search engine is free to use for all, providing equal access to information regardless of socioeconomic background.
Google’s Commitment to Innovation and Competition, Does google search violate antitrust law
Google highlights its commitment to innovation and competition, arguing that its dominance is a result of its constant efforts to improve its search engine and provide users with the best possible experience.
- Research and development: Google invests heavily in research and development, constantly seeking to improve its search algorithms and introduce new features. This commitment to innovation drives its competitive edge and ensures its continued relevance in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
- Open source contributions: Google actively contributes to open-source projects, fostering a collaborative environment and promoting innovation within the tech industry. This demonstrates its commitment to sharing knowledge and advancing the field of search technology.
- Partnerships and collaborations: Google collaborates with various organizations and businesses, including universities, research institutions, and other tech companies, to foster innovation and improve search capabilities. This collaborative approach ensures that Google remains at the forefront of technological advancements and provides users with the best possible search experience.
Google’s Efforts to Address Concerns Regarding Its Search Practices
Google acknowledges concerns regarding its search practices and has taken steps to address them. These include:
- Transparency initiatives: Google has implemented transparency initiatives, providing users with more information about how its search algorithms work and how results are ranked. This aims to build trust and demonstrate its commitment to fairness and transparency in search results.
- Policy changes: Google has made policy changes to address concerns regarding biased search results and the promotion of its own products and services. These changes aim to ensure that search results are unbiased and reflect the diversity of information available online.
- Engaging with regulators: Google actively engages with regulators and participates in discussions regarding antitrust concerns. This demonstrates its willingness to address concerns and work collaboratively to ensure a fair and competitive market.
Legal and Regulatory Landscape

Google’s dominance in search has attracted significant scrutiny from antitrust regulators and legal challenges. The company’s practices have been investigated and litigated extensively, with potential ramifications for both Google’s future and the broader technological landscape.
Ongoing Investigations and Lawsuits
Numerous investigations and lawsuits have been launched against Google, focusing on its search practices. These legal challenges examine various aspects of Google’s business, including its alleged preference for its own services, manipulation of search results, and anti-competitive practices.
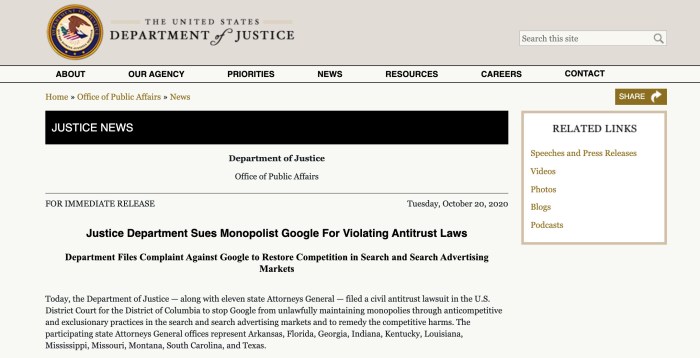
- United States Department of Justice (DOJ) Antitrust Lawsuit (2020): The DOJ filed a lawsuit against Google, alleging that the company monopolized the search and search advertising markets. The suit claimed that Google engaged in anti-competitive practices, such as favoring its own services in search results and entering into exclusive agreements with device manufacturers to pre-install Google Search.
- European Commission Antitrust Fines (2017, 2019): The European Commission imposed two significant fines on Google for violating antitrust laws. The first fine, in 2017, targeted Google’s shopping comparison service, accusing the company of favoring its own shopping results over those of competitors. The second fine, in 2019, focused on Google’s Android operating system, alleging that the company unfairly restricted mobile device manufacturers from using alternative search engines.
- State Attorneys General Antitrust Lawsuit (2020): A coalition of state attorneys general filed a lawsuit against Google, echoing the DOJ’s claims of monopolization and anti-competitive practices in the search and advertising markets. The suit alleged that Google engaged in practices that stifled competition and harmed consumers.
Potential Outcomes of Legal Challenges
The legal challenges against Google could have several potential outcomes, with significant implications for the company and the tech industry.
- Structural Remedies: Courts could order Google to divest certain assets or businesses, such as its search engine or advertising platforms. This would aim to break up Google’s dominance and create a more competitive market.
- Behavioral Remedies: Courts could impose restrictions on Google’s business practices, such as prohibiting it from favoring its own services in search results or engaging in exclusive agreements with device manufacturers. These remedies would seek to curb Google’s anti-competitive behavior without requiring structural changes.
- Financial Penalties: Google could face substantial fines if found guilty of violating antitrust laws. These penalties would aim to deter future violations and compensate for any harm caused to consumers and competitors.
Implications for Antitrust Law and Technology Regulation
The legal challenges against Google have broader implications for antitrust law and technology regulation. They raise important questions about the role of dominant tech companies in the digital economy and the effectiveness of existing antitrust laws in addressing their market power.
- Evolving Antitrust Framework: The cases against Google have prompted discussions about whether traditional antitrust principles are sufficient to address the unique challenges posed by digital markets. Some argue that new laws and regulations are needed to address the dominance of tech giants like Google.
- Impact on Innovation: There is debate about whether breaking up Google or imposing stricter regulations would stifle innovation. Some argue that competition is essential for innovation, while others claim that Google’s size and resources allow it to invest heavily in research and development.
- Consumer Welfare: The legal challenges against Google also raise questions about the impact of its practices on consumer welfare. While Google’s services are often free, some argue that its dominance limits consumer choice and restricts competition, potentially leading to higher prices or reduced quality in the long run.
Final Summary
The question of whether Google Search violates antitrust law is not easily answered. While Google’s dominance in the search engine market is undeniable, its impact on competition and consumer choice remains a subject of ongoing debate. The legal and regulatory landscape is evolving, and the outcome of ongoing investigations and lawsuits will have significant implications for the future of antitrust law and the technology industry. Ultimately, striking a balance between fostering innovation and protecting competition is a complex challenge that will require careful consideration and thoughtful solutions.
FAQ Summary
What are the potential consequences of violating antitrust laws?
Violating antitrust laws can result in significant penalties, including fines, injunctions, and even the breakup of companies. These consequences aim to deter anti-competitive behavior and restore fair competition in the market.
How does Google’s dominance impact competition in the search engine market?
Google’s dominance can limit competition by making it difficult for smaller search engines to gain a foothold in the market. This can lead to reduced innovation and fewer choices for consumers.
What are some examples of Google’s search algorithms favoring its own products?
Some critics allege that Google’s search algorithms prioritize its own products and services, such as Google Maps and Google Shopping, over those of competitors. This practice can give Google an unfair advantage in the market.
What are Google’s arguments in defense of its search practices?
Google argues that its search algorithms are designed to provide the most relevant and useful results to users. They also claim that their dominance is a result of providing superior products and services that meet consumer needs.
What is the broader impact of these antitrust cases on the future of technology regulation?
The outcomes of these cases could shape the future of technology regulation, potentially leading to stricter oversight of dominant tech companies and a greater emphasis on competition and consumer protection.