Can you reimburse employees for health insurance? This question arises frequently as employers seek innovative ways to offer benefits and attract talent. Reimbursement programs offer a flexible alternative to traditional employer-sponsored health insurance plans, allowing employees to customize their coverage and potentially save money. However, understanding the legal complexities, tax implications, and practical considerations is crucial for both employers and employees.
This article delves into the nuances of employee health insurance reimbursement programs, exploring the legal framework, employer and employee perspectives, different program structures, and practical considerations. We’ll also compare reimbursement programs with traditional health insurance plans and highlight alternative benefits employers might offer.
Legal Considerations
Reimbursing employees for health insurance premiums can be a valuable benefit, but it’s crucial to understand the legal and tax implications. This section will Artikel the relevant federal and state laws, potential tax consequences for both employers and employees, and provide examples of key legislation and regulations.
Federal Laws and Regulations, Can you reimburse employees for health insurance
Federal laws and regulations play a significant role in determining the legality of employer-sponsored health insurance reimbursement programs. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- The Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA): ERISA governs employee benefit plans, including health insurance. It sets standards for plan administration, funding, and disclosure. Employers offering health insurance reimbursement programs must comply with ERISA’s provisions, ensuring the plan is properly documented, administered, and communicated to employees.
- The Internal Revenue Code (IRC): The IRC governs the tax treatment of employee benefits, including health insurance. It Artikels specific rules for employer-sponsored health insurance plans, including eligibility requirements, premium contributions, and tax deductibility.
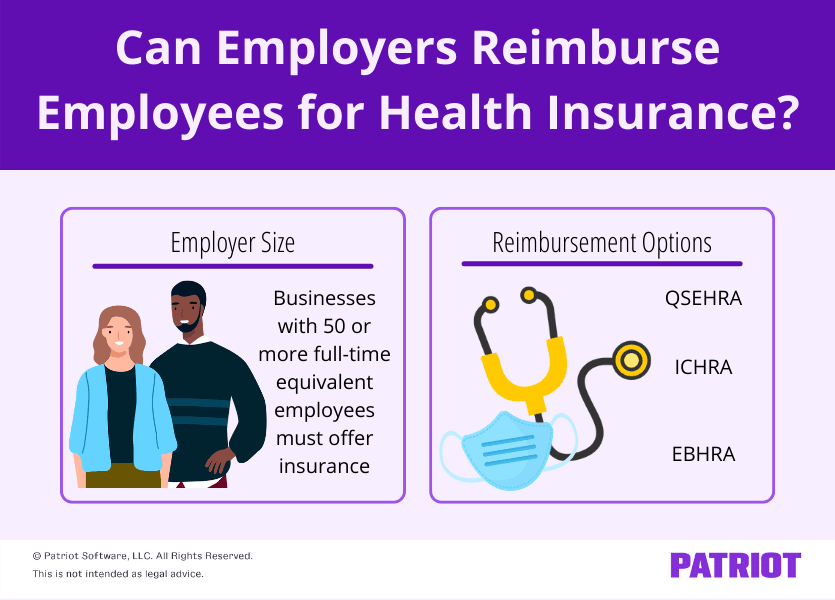
- The Affordable Care Act (ACA): The ACA introduced several provisions impacting health insurance, including the requirement for employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees to offer health insurance or face penalties. While the ACA doesn’t explicitly address health insurance reimbursement programs, it’s crucial to consider its implications when designing such programs.
State Laws and Regulations
In addition to federal laws, state laws and regulations can also impact the legality of health insurance reimbursement programs. Many states have their own laws governing health insurance, employee benefits, and taxation. For example, some states may have specific requirements for employer-sponsored health insurance plans, including minimum coverage levels or benefit mandates.
- State Insurance Laws: Each state has its own insurance laws that regulate the sale and administration of health insurance plans. These laws may impose specific requirements on employer-sponsored health insurance plans, including coverage mandates, premium limits, and enrollment procedures.
- State Tax Laws: State tax laws can also impact the tax treatment of health insurance reimbursement programs. Some states may offer tax deductions or credits for employer contributions to health insurance, while others may impose taxes on employee reimbursements.
Tax Implications
The tax treatment of health insurance reimbursement programs can vary depending on the specific plan design and the applicable federal and state laws.
- Employer Tax Implications: Employers offering health insurance reimbursement programs may be able to deduct their contributions as a business expense. However, the deductibility of these contributions can be subject to specific rules and limitations under the IRC.
- Employee Tax Implications: Employees receiving health insurance reimbursements may be required to include the reimbursements as taxable income. However, there are exceptions to this rule, such as when the reimbursements are used to cover qualified medical expenses.
Examples of Relevant Legislation and Regulations
- ERISA Section 401: This section of ERISA Artikels the requirements for establishing and administering employee benefit plans, including health insurance plans.
- IRC Section 105: This section of the IRC addresses the tax treatment of employer-provided health insurance benefits.
- ACA Section 1501: This section of the ACA imposes the employer shared responsibility payment for employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees who do not offer health insurance coverage.
Employer Perspectives

From an employer’s standpoint, reimbursing employees for their health insurance premiums can be a strategic move that benefits both the company and its workforce. This approach offers a flexible alternative to traditional employer-sponsored health plans, allowing employees to choose the coverage that best suits their individual needs.
Benefits for Employers
Reimbursing employees for health insurance premiums presents several advantages for employers:
- Cost Savings: Employers can potentially save money by offering reimbursement instead of traditional health insurance plans. This is because reimbursement plans typically involve lower administrative costs and allow employers to avoid the risk associated with fluctuating healthcare costs.
- Increased Employee Satisfaction: By providing reimbursement, employers empower employees to select health insurance plans that best align with their personal needs and preferences. This flexibility can lead to higher employee satisfaction and a sense of control over their healthcare choices.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: Offering reimbursement can be a valuable perk for employers seeking to attract and retain top talent. In a competitive job market, this benefit can differentiate a company and make it more appealing to potential employees.
- Simplified Administration: Compared to managing traditional health insurance plans, reimbursement programs are often simpler to administer. Employers can streamline the process by setting clear reimbursement guidelines and using automated systems for tracking and payment.
Drawbacks for Employers
While reimbursement offers several advantages, employers should also consider the potential drawbacks:
- Potential for Abuse: Employers need to establish clear guidelines and monitoring systems to prevent employees from abusing the reimbursement program. This could involve setting limits on the amount of reimbursement or requiring employees to provide proof of coverage.
- Complexity of Administration: Although reimbursement plans are generally simpler to administer than traditional plans, they still require careful planning and implementation. Employers need to ensure that the program is properly designed and communicated to employees.
- Employee Education: Employers must provide employees with clear information about the reimbursement program and guide them through the process of choosing and enrolling in health insurance plans. This includes explaining the program’s rules, eligibility criteria, and reimbursement procedures.
- Compliance with Regulations: Employers need to comply with all applicable federal and state laws regarding health insurance and reimbursement programs. This involves understanding the rules related to tax deductions, eligibility, and reporting requirements.
Cost and Benefits Comparison
The following table compares the costs and benefits of offering health insurance versus reimbursement:
| Feature | Health Insurance | Reimbursement |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher administrative costs, potential for higher premiums due to fluctuating healthcare costs | Lower administrative costs, potentially lower overall costs due to employee choice |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, employees typically have limited plan choices | High flexibility, employees can choose plans that best suit their individual needs |
| Employee Satisfaction | May vary depending on plan options and employee needs | Generally higher satisfaction due to employee choice and control |
| Attracting and Retaining Talent | Can be a competitive advantage | Can be a strong draw for talent seeking flexibility and control over healthcare |
| Administrative Complexity | More complex administration, requires managing plan options, enrollment, and claims | Simpler administration, requires setting reimbursement guidelines and tracking payments |
Closing Notes

Ultimately, deciding whether to offer health insurance reimbursement depends on a variety of factors, including the employer’s budget, employee demographics, and regulatory environment. By carefully considering the legal landscape, potential benefits and drawbacks, and alternative options, employers can make informed decisions about the best approach to employee health benefits.
General Inquiries: Can You Reimburse Employees For Health Insurance
What are the tax implications of health insurance reimbursement programs?
The tax implications can vary depending on the structure of the reimbursement program. Employers may be able to deduct the reimbursement payments as a business expense, while employees may be required to pay taxes on the reimbursement amount as income.
Can employees deduct health insurance premiums on their taxes?
In some cases, employees may be able to deduct health insurance premiums on their taxes, but this depends on their individual circumstances and eligibility for specific deductions.
Are there any specific regulations regarding reimbursement programs for self-employed individuals?
Yes, self-employed individuals may have different rules and regulations regarding health insurance reimbursement compared to employees of a company.
How do I find out if health insurance reimbursement is legal in my state?
You can consult with a legal professional or review your state’s labor laws and regulations for specific information on health insurance reimbursement programs.
