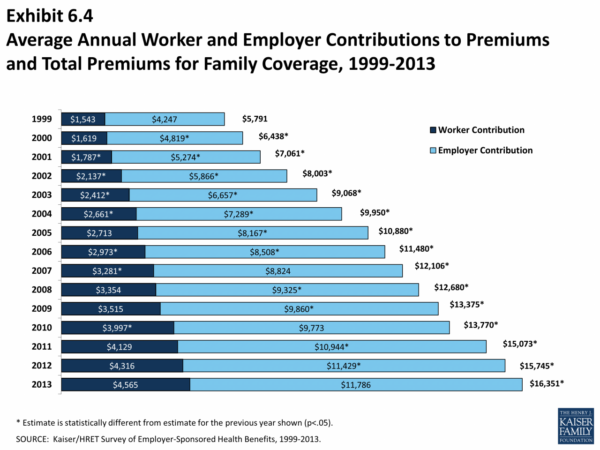
How much does it cost to get health insurance? It’s a question many people ask, and the answer can vary greatly depending on a variety of factors. From your age and location to the type of coverage you need, the cost of health insurance can be influenced by a complex web of considerations. This guide explores the key factors that determine your health insurance premiums, providing insights into the different types of plans available and strategies to save money.
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel overwhelming, but understanding the basics can empower you to make informed decisions. This guide will break down the key elements of health insurance, including plan types, coverage options, and cost-saving strategies. Whether you’re looking for individual or group coverage, or exploring government-sponsored programs, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to find the right plan for your needs and budget.
Government-Sponsored Health Insurance Programs

Government-sponsored health insurance programs play a crucial role in providing healthcare coverage to millions of Americans, particularly those who may not be able to afford private insurance. These programs are designed to ensure access to essential healthcare services, promoting better health outcomes and reducing the financial burden associated with medical expenses.
Medicare and Medicaid
Medicare and Medicaid are two prominent government-sponsored health insurance programs in the United States. They offer coverage to distinct populations based on specific eligibility criteria.
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with certain disabilities. It provides coverage for a range of healthcare services, including hospitalization, doctor’s visits, and prescription drugs.
Medicaid, on the other hand, is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to low-income individuals and families, as well as people with disabilities. Medicaid eligibility is determined by state-specific income and asset guidelines.
Eligibility Requirements
To be eligible for Medicare, individuals must meet certain age or disability requirements.
- Individuals aged 65 or older are automatically eligible for Medicare, regardless of income or health status.
- Individuals under 65 with certain disabilities, such as end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), may also qualify for Medicare.
For Medicaid eligibility, individuals must meet specific income and asset thresholds.
- Income limits vary by state and household size, but generally, individuals must earn below a certain income level to qualify for Medicaid.
- Medicaid also considers asset levels, such as savings and home equity, when determining eligibility.
Benefits of Medicare and Medicaid
Medicare and Medicaid provide a range of benefits, including:
- Hospitalization: Both programs cover inpatient hospital stays, including surgery, intensive care, and other medical procedures.
- Doctor’s Visits: Medicare and Medicaid cover routine checkups, specialist appointments, and other outpatient services.
- Prescription Drugs: Medicare Part D and Medicaid offer prescription drug coverage, although the specific drugs covered and the cost-sharing requirements may vary.
- Preventive Care: Both programs emphasize preventive services, such as screenings for cancer, diabetes, and other health conditions.
Impact on Healthcare Access and Affordability
Medicare and Medicaid have significantly impacted healthcare access and affordability in the United States.
- Increased Access to Healthcare: These programs have expanded access to healthcare for millions of Americans, particularly those who might otherwise struggle to afford it.
- Reduced Financial Burden: By covering a significant portion of healthcare costs, Medicare and Medicaid have reduced the financial burden associated with medical expenses for many individuals and families.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Access to healthcare through these programs has been linked to improved health outcomes, including lower rates of preventable hospitalizations and mortality.
Cost-Saving Strategies for Health Insurance: How Much Does It Cost To Get Health Insurance
Finding affordable health insurance can be challenging, but there are several strategies you can implement to reduce your costs. Understanding your options and making informed decisions can lead to significant savings.
Comparing Quotes from Different Insurance Providers
It’s crucial to compare quotes from multiple insurance providers to find the best coverage at the most competitive price. Online comparison tools can help you quickly gather quotes from various insurers, allowing you to compare plans side-by-side and identify the most suitable option.
Choosing a High-Deductible Plan, How much does it cost to get health insurance
High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) typically have lower monthly premiums than traditional plans. However, they require you to pay a higher deductible before your insurance coverage kicks in. This can be a cost-effective option if you are generally healthy and anticipate low healthcare expenses.
Participating in Wellness Programs
Many insurance providers offer wellness programs that encourage healthy habits and provide incentives for participation. These programs can include discounts on premiums, rewards for completing health screenings, and access to fitness resources. By engaging in these programs, you can potentially lower your healthcare costs and improve your overall health.
Understanding Health Insurance Terms
Navigating the world of health insurance can be confusing, especially with all the unfamiliar terms and concepts. To make things clearer, let’s delve into some essential health insurance terms that will help you understand your coverage and costs.
Common Health Insurance Terms
Understanding common health insurance terms is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage. Let’s break down some of the key terms:
- Deductible: This is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services before your insurance starts covering costs. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, you’ll need to pay the first $1,000 in medical expenses yourself before your insurance kicks in.
- Co-pay: This is a fixed amount you pay for specific healthcare services, like doctor’s visits or prescriptions, after you’ve met your deductible. For example, you might have a $20 co-pay for a doctor’s visit.
- Coinsurance: This is a percentage of the cost of healthcare services you pay after meeting your deductible. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you’ll pay 20% of the cost of a hospital stay, while your insurance covers the remaining 80%.
- Out-of-pocket maximum: This is the maximum amount you’ll have to pay for healthcare expenses in a year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance will cover 100% of your remaining healthcare costs.
Cost-Sharing Components of a Health Insurance Plan
Here’s a table that visually represents the different cost-sharing components of a health insurance plan:
| Cost-Sharing Component | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Deductible | Amount you pay before insurance starts covering costs. | $1,000 |
| Co-pay | Fixed amount you pay for specific services. | $20 for a doctor’s visit |
| Coinsurance | Percentage of the cost you pay after meeting the deductible. | 20% of the cost of a hospital stay |
| Out-of-pocket maximum | Maximum amount you pay in a year. | $6,000 |
Final Review
Understanding the cost of health insurance is essential for making informed decisions about your healthcare. By considering the factors that influence premiums, exploring different plan types, and implementing cost-saving strategies, you can find a plan that provides the coverage you need at a price you can afford. Remember to shop around, compare quotes, and utilize available resources to make the best choice for your individual circumstances.
FAQ Guide
How do I know if I qualify for government-sponsored health insurance programs?
Eligibility requirements for programs like Medicare and Medicaid vary based on factors such as age, income, and disability status. You can find detailed information and eligibility criteria on the official websites of these programs.
What is the difference between a deductible and a co-pay?
A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your health insurance coverage kicks in. A co-pay is a fixed amount you pay for a specific service, like a doctor’s visit or prescription.
Are there any tax benefits associated with health insurance premiums?
Yes, in many cases, health insurance premiums are tax-deductible. The specific tax benefits may vary depending on your individual circumstances and the type of plan you have. Consult with a tax professional for personalized advice.