- Understanding Life Insurance Policy Sales in Australia
- Methods for Selling Life Insurance Policies in Australia
- Factors Influencing the Value of a Life Insurance Policy
- Tax Implications of Selling a Life Insurance Policy
- Risks and Considerations
- Alternative Options to Selling a Life Insurance Policy
- Closing Notes: Can I Sell My Life Insurance Policy In Australia
- General Inquiries
Can I sell my life insurance policy in Australia? It’s a question many Australians ponder, especially when facing financial hardship or needing immediate access to funds. While it might seem unusual to sell something meant to protect your loved ones, the Australian market offers options for those seeking to cash in on their life insurance policies.
Understanding the legal framework, different policy types, and available methods for selling your policy are crucial steps in making an informed decision. This guide explores the intricacies of life insurance policy sales in Australia, offering insights into the process, factors influencing value, potential tax implications, and alternative options.
Understanding Life Insurance Policy Sales in Australia
Selling a life insurance policy in Australia is a complex process with legal implications. This guide aims to provide insights into the different types of policies, the legal framework surrounding them, and the common reasons why individuals choose to sell their policies.
Types of Life Insurance Policies in Australia
Australia offers a variety of life insurance policies, each tailored to specific needs and financial situations. Understanding the different types is crucial when considering selling a policy.
- Term Life Insurance: This policy provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10 to 30 years. It is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance, making it suitable for individuals seeking temporary coverage, such as during a mortgage term or while raising young children.
- Permanent Life Insurance: This type of policy offers lifelong coverage, providing a death benefit regardless of when the insured passes away. It often includes a savings component, allowing policyholders to build cash value over time. Permanent life insurance is typically more expensive than term life insurance due to its lifelong coverage and savings features.
- Whole Life Insurance: A type of permanent life insurance that provides a guaranteed death benefit and cash value growth at a fixed interest rate. This option offers stability and predictability but may not offer the same potential for growth as other permanent life insurance policies.
- Universal Life Insurance: This flexible permanent life insurance policy allows policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefit based on their changing needs. It offers greater control over policy features but can be more complex to understand and manage.
- Indexed Universal Life Insurance: This type of universal life insurance links the cash value growth to the performance of a specific market index, offering the potential for higher returns. However, it also carries the risk of potential losses if the index performs poorly.
Legal Framework Governing Life Insurance Policy Sales in Australia
The Australian life insurance industry is regulated by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA), which sets standards for financial institutions and insurance companies. APRA’s role includes ensuring the solvency of insurers and protecting policyholders’ interests.
- The Life Insurance Act 1995: This Act establishes the legal framework for life insurance in Australia, outlining the requirements for insurers and the rights of policyholders. It also regulates the sale of life insurance policies and ensures transparency in pricing and product information.
- The Corporations Act 2001: This Act governs the conduct of financial institutions, including insurance companies. It sets standards for financial reporting, corporate governance, and consumer protection.
- The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC): ASIC plays a vital role in regulating the financial services industry, including life insurance. It enforces consumer protection laws, investigates misconduct, and provides guidance to consumers.
Reasons for Selling Life Insurance Policies
Individuals may choose to sell their life insurance policies for various reasons.
- Financial Need: A sudden financial need, such as medical expenses or unexpected debt, may prompt individuals to sell their policy for immediate cash. This option provides a lump sum payment but comes with the loss of future coverage.
- Change in Circumstances: Changes in life, such as retirement, divorce, or the death of a spouse, may lead individuals to reassess their need for life insurance. If the policy is no longer relevant to their current circumstances, selling it may be a logical choice.
- Policy No Longer Suitable: As an individual’s financial situation and needs evolve, the initial life insurance policy may no longer be suitable. This could be due to changes in income, health status, or family structure. Selling the policy and purchasing a new one that better aligns with current circumstances can be a more efficient approach.
Methods for Selling Life Insurance Policies in Australia
In Australia, you can sell your life insurance policy in two main ways: through a life settlement company or directly to an individual or entity. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages, which are important to consider before making a decision.
Selling Through a Life Settlement Company
Life settlement companies specialize in purchasing life insurance policies from policyholders who no longer need them. This is a viable option for policyholders who want to access the cash value of their policy quickly and easily.
- Process: When you sell your policy to a life settlement company, you receive a lump sum payment in exchange for transferring ownership of the policy to the company. The company then becomes the beneficiary of the policy and pays the premiums until the insured person passes away. The amount you receive will depend on various factors, including your age, health, the policy’s death benefit, and the remaining premium payments.
- Advantages:
- Quick access to cash: Selling your policy to a life settlement company provides a fast and convenient way to access the cash value of your policy. You receive a lump sum payment immediately, which you can use for various purposes, such as paying off debts, funding retirement, or covering medical expenses.
- No need to continue paying premiums: Once you sell your policy, you are no longer responsible for paying the premiums. This can be a significant advantage if you are facing financial difficulties or simply want to be relieved of the financial burden of maintaining the policy.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower payout than death benefit: You will typically receive less than the full death benefit of the policy when you sell it to a life settlement company. The company needs to make a profit, so they will offer a discounted price for the policy.
- Complex process: Selling a life insurance policy through a life settlement company can be a complex process, involving legal and financial considerations. It is essential to work with a reputable and experienced company to ensure a smooth and fair transaction.
Selling Directly to an Individual or Entity
You can also sell your life insurance policy directly to an individual or entity, such as a family member, friend, or business associate. This option allows you to potentially receive a higher payout than you would from a life settlement company, but it also involves a greater degree of risk.
- Process: When selling directly, you will need to find a buyer who is willing to pay a fair price for your policy. You can advertise your policy online, through personal networks, or through a broker. The buyer will typically need to undergo a financial assessment to ensure they can afford the premiums and the eventual death benefit. Once the sale is finalized, you will receive a lump sum payment and the buyer becomes the new policyholder.
- Advantages:
- Potential for higher payout: You can potentially receive a higher payout when selling directly to an individual or entity, as there are no intermediary fees involved. This is particularly true if the buyer has a personal or financial interest in your life insurance policy.
- More control over the process: You have more control over the process when selling directly, as you can choose the buyer and negotiate the terms of the sale. This allows you to ensure that the transaction is fair and meets your needs.
- Disadvantages:
- Difficulty finding a buyer: It can be challenging to find a buyer who is willing to purchase your life insurance policy. You may need to advertise your policy widely and be prepared to negotiate with multiple potential buyers.
- Higher risk: Selling directly involves a greater degree of risk, as there is no guarantee that the buyer will be able to pay the premiums or that they will not default on the policy. This can leave you financially vulnerable if the buyer fails to meet their obligations.
Factors Influencing the Value of a Life Insurance Policy
The value of a life insurance policy for sale is influenced by various factors, including the policy’s characteristics, the insured’s circumstances, and market conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for both sellers and potential buyers to determine a fair price.
Factors Affecting the Value of a Life Insurance Policy
The following table summarizes the key factors that influence the value of a life insurance policy:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age of the Insured | The age of the insured at the time of sale. | Younger insureds generally have higher policy values as they have a longer life expectancy, leading to a higher potential payout. |
| Health of the Insured | The health status of the insured, including any pre-existing conditions or health risks. | Insureds with good health generally have higher policy values as they are considered less risky by insurers. |
| Policy Type | The type of life insurance policy, such as term life, whole life, or universal life. | Different policy types have varying cash values and death benefits, impacting their resale value. For example, whole life policies typically have higher cash values compared to term life policies. |
| Policy Term | The duration of the policy coverage, which can be for a fixed term or for life. | Policies with longer terms generally have higher values, as they provide coverage for a longer period. |
| Death Benefit | The amount of money paid to the beneficiary upon the insured’s death. | Policies with higher death benefits typically have higher values, as they provide greater financial protection. |
| Premium Payments | The amount of money paid by the insured for the policy coverage. | Policies with lower premiums generally have higher values, as they represent a lower cost for the buyer. |
| Cash Value | The accumulated value of the policy, which can be withdrawn or borrowed against. | Policies with higher cash values typically have higher resale values, as they provide additional financial benefits. |
| Market Conditions | The overall economic and financial market conditions, including interest rates and inflation. | Market conditions can influence the demand for life insurance policies, impacting their resale value. |
Tax Implications of Selling a Life Insurance Policy
Selling a life insurance policy in Australia can have tax implications, depending on the type of policy and the circumstances of the sale. It’s essential to understand these implications before making a decision.
Capital Gains Tax
When you sell a life insurance policy, any profit you make is considered a capital gain, subject to capital gains tax. Capital gains tax is levied on the difference between the sale price and your cost base. The cost base is the amount you paid for the policy, including any premiums and other expenses.
- For policies purchased after September 20, 1985, the capital gains tax rate is 50% of your marginal tax rate.
- For policies purchased before September 20, 1985, the capital gains tax rate is 33.33% of your marginal tax rate.
For example, if you sell a policy for $100,000 and your cost base is $50,000, your capital gain is $50,000. If your marginal tax rate is 32%, your capital gains tax liability would be $8,000 (50% of 32% of $50,000).
Tax Deductible Expenses
You can deduct certain expenses related to selling your life insurance policy, such as:
- Advertising and marketing costs
- Legal and accounting fees
- Travel expenses
These deductions can help reduce your overall tax liability.
Tax-Free Life Insurance Proceeds
It’s important to note that the proceeds from a life insurance policy are generally tax-free if paid out on the death of the insured person. This means that the beneficiary of the policy does not have to pay any tax on the money received.
Tax Implications of Policy Surrender
Surrendering a life insurance policy can also have tax implications. If you surrender your policy for a cash value, this is considered a capital gain, and you will be subject to capital gains tax. However, you may be able to deduct any premiums you paid for the policy.
Tax Advice, Can i sell my life insurance policy in australia
It’s always best to seek professional tax advice before selling a life insurance policy. A qualified tax advisor can help you understand the specific tax implications of your situation and ensure that you comply with all relevant tax laws and regulations.
Risks and Considerations

Selling a life insurance policy can be a complex financial decision, and it’s essential to weigh the potential risks and benefits carefully. While it might seem like a quick way to access cash, there are several factors to consider that could impact your financial well-being.
Potential Risks of Selling a Life Insurance Policy
- Loss of Coverage: Selling your life insurance policy means you’ll lose the death benefit that your beneficiaries would receive if you passed away. This could leave your loved ones financially vulnerable, especially if they rely on the policy for financial security.
- Lower Than Expected Proceeds: The actual amount you receive from selling your policy might be significantly less than the policy’s face value. This is because life insurance policy sales are often based on the policy’s cash surrender value, which can be considerably lower than the death benefit.
- Tax Implications: Depending on the type of policy and the circumstances of the sale, you might have to pay taxes on the proceeds. This could significantly reduce the amount of money you actually receive.
- Impact on Future Premiums: If you choose to buy a new life insurance policy after selling your existing one, the premiums might be higher due to your age and health status. This could make it difficult to afford the coverage you need.
Mitigation Strategies
- Seek Professional Financial Advice: Consulting with a qualified financial advisor can help you understand the potential risks and benefits of selling your life insurance policy. They can assess your individual circumstances, including your financial goals, risk tolerance, and dependents, to provide personalized advice.
- Explore Alternatives: Before making a decision, consider alternative ways to access cash, such as taking out a loan against your policy or withdrawing from a savings account. These options might offer more favorable terms than selling your policy.
- Negotiate with the Buyer: If you decide to sell your policy, try to negotiate a higher price with the buyer. You can leverage your policy’s features, such as the death benefit and the amount of time you’ve been paying premiums, to get a better deal.
- Understand the Terms of the Sale: Carefully review the terms and conditions of the sale, including the fees, the time frame for the transaction, and any potential penalties. This will help you make an informed decision.
Alternative Options to Selling a Life Insurance Policy
Selling your life insurance policy might not always be the most suitable option. Exploring alternative ways to access the cash value of your policy can offer advantages, depending on your circumstances.
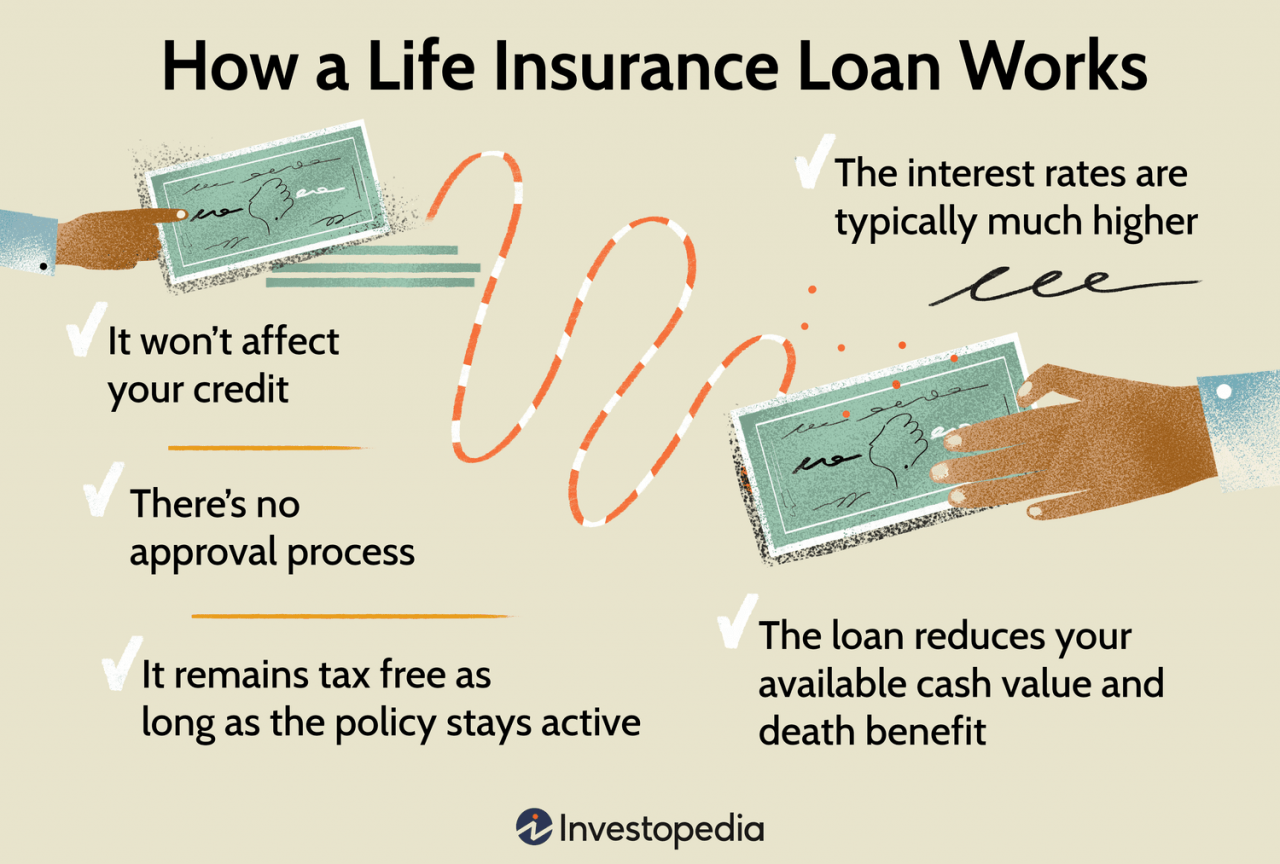
Policy Loans
Policy loans allow you to borrow against the cash value of your life insurance policy. You can access funds without surrendering the policy, providing flexibility and preserving your coverage.
Benefits of Policy Loans
- Preserves Coverage: Policy loans don’t terminate your life insurance coverage, unlike surrendering the policy.
- Tax-Deferred Interest: Interest accrued on policy loans is typically tax-deferred, meaning you won’t be taxed until you withdraw the funds or surrender the policy.
- Flexibility: You can borrow against the cash value as needed, offering financial flexibility.
Drawbacks of Policy Loans
- Interest Charges: Policy loans typically come with interest charges, which can accumulate over time if not repaid promptly.
- Impact on Death Benefit: Outstanding loan amounts, including interest, are deducted from the death benefit payable to your beneficiaries.
- Loan Limits: The amount you can borrow is typically limited to the policy’s cash value.
Surrendering a Life Insurance Policy
Surrendering a life insurance policy means terminating the policy and receiving the cash value. This option might be suitable if you no longer require life insurance coverage or need immediate access to funds.
Consequences of Surrendering a Life Insurance Policy
- Loss of Coverage: Surrendering your policy eliminates your life insurance coverage, leaving your beneficiaries without financial protection in the event of your death.
- Tax Implications: Depending on the policy type and your situation, surrendering a policy may result in taxable income.
- Potential Penalties: Some policies may have surrender penalties, reducing the cash value received.
Alternative Strategies for Accessing Cash Value
- Partial Withdrawals: Some policies allow you to withdraw a portion of the cash value without surrendering the policy. This can provide access to funds while maintaining coverage.
- Policy Dividends: Certain life insurance policies pay dividends to policyholders, which can be withdrawn or accumulated to increase the cash value.
- Policy Exchange: Consider exchanging your existing policy for a different type, such as a variable life insurance policy, that offers more flexibility in accessing the cash value.
Closing Notes: Can I Sell My Life Insurance Policy In Australia

Selling a life insurance policy in Australia can be a complex process, involving various factors and considerations. It’s essential to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and seek professional financial advice before making any decisions. By understanding the different methods, tax implications, and alternative options available, you can make a well-informed choice that aligns with your financial goals and circumstances.
General Inquiries
What are the common reasons for selling a life insurance policy in Australia?
Individuals often sell their life insurance policies due to financial hardship, unexpected medical expenses, or to access funds for investment purposes.
Is it always advisable to sell a life insurance policy?
Selling a life insurance policy should be carefully considered. It’s crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and ensure that it aligns with your overall financial goals and circumstances.
How can I find a reputable life settlement company in Australia?
Research and compare different life settlement companies. Look for companies with a proven track record, positive client testimonials, and transparent practices.





