Community based rehabilitation in Australia-in home services insurance takes center stage, providing a vital lifeline for individuals with disabilities seeking support within the familiar comfort of their own homes. This approach, rooted in the principles of empowerment and inclusion, empowers individuals to regain their independence and actively participate in their communities.
Australia’s commitment to community-based rehabilitation is reflected in the comprehensive range of in-home services available, delivered through a network of dedicated professionals, government agencies, and non-profit organizations. These services encompass a wide spectrum of needs, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and psychosocial support. Crucially, these services are often funded through a combination of government programs like the National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS), Medicare, and private health insurance, ensuring access for individuals with diverse financial backgrounds. This intricate tapestry of services and funding mechanisms underscores Australia’s dedication to providing equitable access to community-based rehabilitation, empowering individuals to live fulfilling lives.
Introduction to Community Based Rehabilitation in Australia
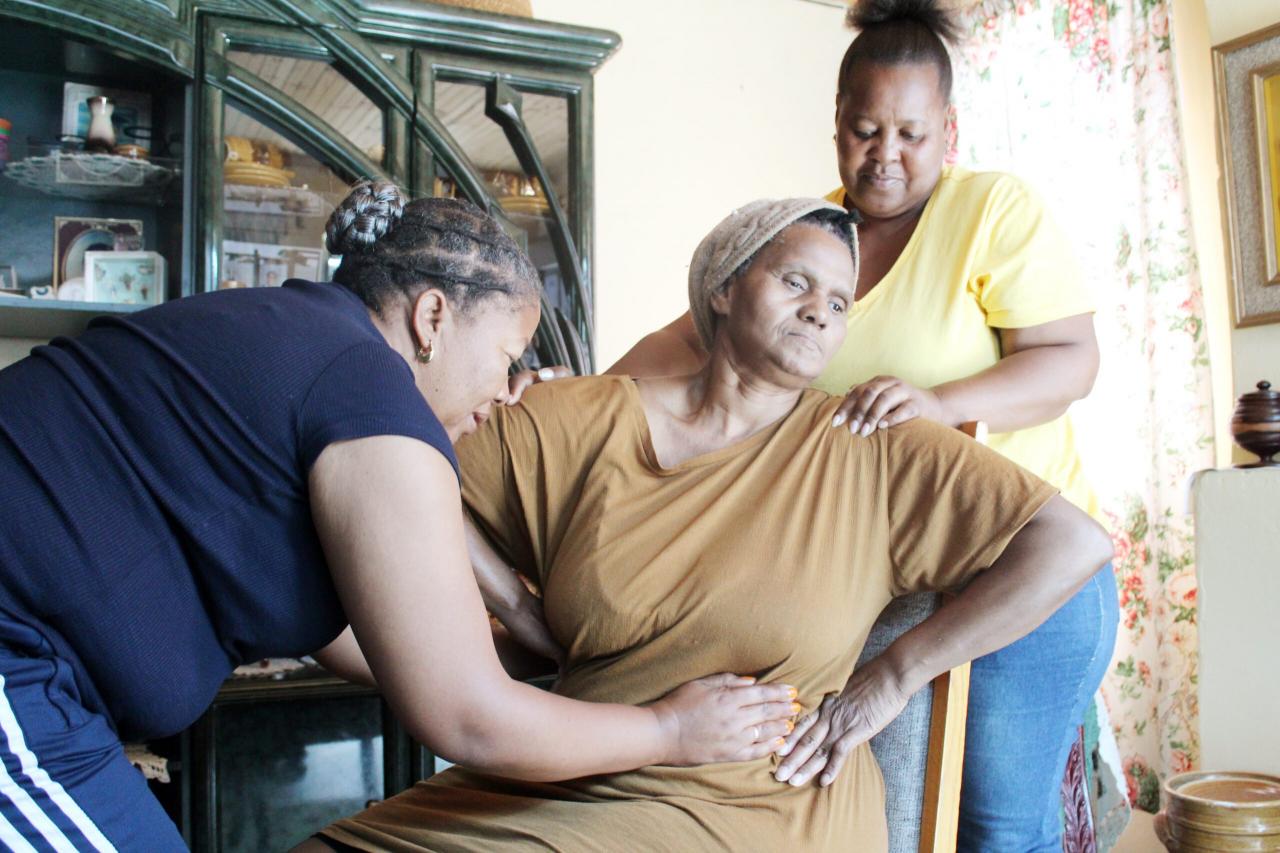
Community-based rehabilitation (CBR) is a holistic approach to rehabilitation that empowers individuals with disabilities to live fulfilling lives within their communities. This approach emphasizes the importance of community participation, accessibility, and the inclusion of people with disabilities in all aspects of society. In Australia, CBR plays a crucial role in providing accessible and equitable rehabilitation services, promoting independence, and fostering social inclusion for individuals with disabilities.
CBR in Australia is founded on the principles of empowerment, participation, and social inclusion. This approach acknowledges the unique needs and aspirations of individuals with disabilities and emphasizes their active participation in shaping their own rehabilitation journey.
Historical Development of CBR in Australia, Community based rehabilitation in australia-in home services insurance
The concept of CBR in Australia has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Early rehabilitation services were often institution-based, focusing on medical interventions and limited community engagement. However, the disability rights movement and a growing awareness of the importance of social inclusion led to a shift towards community-based models.
The 1990s saw the emergence of numerous CBR programs across Australia, driven by government policies and community initiatives. These programs aimed to provide comprehensive support services, including:
- Assistive technology and equipment
- Skills training and employment opportunities
- Social and recreational activities
- Advocacy and support services
The Australian government’s National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS), launched in 2013, has further strengthened the role of CBR in Australia. The NDIS provides funding for a wide range of supports, including CBR services, enabling individuals with disabilities to access tailored services that meet their individual needs and aspirations.
Examples of CBR Programs and Initiatives in Australia
Australia is home to a diverse range of CBR programs and initiatives, operating at both national and local levels. These programs cater to various disability groups and offer specialized services tailored to their specific needs.
- The National Disability Services (NDS): A leading provider of disability support services, NDS offers a range of CBR programs, including assistive technology, employment support, and community engagement initiatives.
- The Australian Network on Disability (AND): AND promotes the inclusion of people with disabilities in the workplace. They offer a range of CBR programs, including skills training, job placement, and workplace adjustments.
- The Australian Spinal Injuries Association (ASIA): ASIA provides support services for people with spinal cord injuries. Their CBR programs include home modifications, assistive technology, and peer support.
- Local community organizations: Numerous local community organizations across Australia provide CBR services tailored to their specific communities. These organizations often work closely with individuals with disabilities, their families, and local stakeholders to ensure that services meet their needs.
In-Home Services and Insurance Coverage
In-home services are a cornerstone of Community Based Rehabilitation (CBR) in Australia, offering individuals with disabilities the support they need to live fulfilling lives within their own homes. These services provide a range of assistance tailored to individual needs, promoting independence and community participation.
Types of In-Home Services
In-home services under CBR encompass a wide array of support, including:
- Personal care: Assistance with daily living activities such as bathing, dressing, and toileting.
- Domestic support: Help with household tasks like cleaning, laundry, and meal preparation.
- Therapy and rehabilitation: Physiotherapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and other therapies to improve physical and cognitive function.
- Social support: Companionship, social outings, and assistance with accessing community resources.
- Assistive technology: Provision and training on assistive devices to enhance independence and mobility.
- Home modifications: Adaptations to the home to improve accessibility and safety.
Insurance Coverage for CBR Services
Several insurance schemes in Australia cover CBR services, providing financial assistance to individuals with disabilities and their families.
National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS)
The NDIS is a significant government-funded scheme providing individualized support packages to Australians with disability. It offers funding for a wide range of CBR services, including in-home support, therapy, and assistive technology.
Eligibility Criteria for NDIS
To be eligible for NDIS, individuals must meet specific criteria, including:
- Permanent impairment or disability: The disability must be significant and ongoing, affecting daily life.
- Age: Individuals of all ages can be eligible for NDIS support.
- Residency: Individuals must reside in Australia.
- Functional impact: The disability must have a substantial impact on daily life activities.
Medicare
Medicare, Australia’s universal healthcare scheme, covers some essential healthcare services for individuals with disabilities, including:
- GP consultations: General practitioners can provide primary care and referrals for specialized services.
- Allied health services: Medicare covers limited sessions for certain allied health professionals, such as physiotherapists and occupational therapists.
- Hospitalization: Medicare covers hospital stays for medical treatment and rehabilitation.
Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance can provide additional coverage for CBR services beyond what Medicare offers, including:
- Allied health services: Private health insurance often covers a wider range of allied health services and more sessions than Medicare.
- Hospital care: Private health insurance can provide access to private hospitals and faster access to specialized treatments.
- Assistive technology: Some private health insurance policies may cover the cost of assistive devices.
Comparison of Insurance Coverage
| Scheme | Coverage | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| NDIS | Comprehensive support packages for a wide range of CBR services, including in-home support, therapy, and assistive technology. | Permanent impairment or disability, age, residency, and functional impact. |
| Medicare | Limited coverage for essential healthcare services, including GP consultations, some allied health services, and hospitalization. | Australian residency and citizenship. |
| Private Health Insurance | Additional coverage for allied health services, hospital care, and assistive technology. | Varies depending on the policy and insurer. |
Key Players and Stakeholders
Community-based rehabilitation (CBR) in Australia is a collaborative effort involving various stakeholders, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the delivery of effective services. Understanding the roles and responsibilities of these key players is essential to appreciate the complexity and interconnectedness of the CBR system.
Government Agencies
Government agencies play a significant role in shaping the policy framework, funding, and regulation of CBR services in Australia. They are responsible for establishing standards, providing financial support, and overseeing the quality of care delivered.
- Department of Health: This agency is responsible for developing national health policies and funding programs that support CBR services. It also provides guidance and resources to healthcare providers and stakeholders involved in CBR.
- National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS): The NDIS is a government-funded scheme that provides support and funding for people with disability. It plays a crucial role in enabling access to CBR services by providing funding for individualised support plans and ensuring that people with disability have a choice in their service providers.
- State and Territory Governments: State and territory governments are responsible for implementing CBR programs and services within their respective jurisdictions. They work closely with local communities and service providers to ensure that CBR services are accessible and responsive to local needs.
Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations play a vital role in providing a wide range of CBR services, often focusing on specific needs or populations. They are often driven by a commitment to social justice and community development, and their services are typically tailored to meet the unique needs of individuals and communities.
- Disability Support Organizations: These organizations provide a range of services to people with disability, including CBR services, assistive technology, and advocacy support. They often work closely with families and communities to ensure that individuals with disability are fully integrated into society.
- Community Health Centres: Community health centres provide a range of primary healthcare services, including CBR programs, to people in their local communities. They are often located in disadvantaged areas and provide culturally sensitive and accessible services.
- Mental Health Organizations: These organizations provide support and services to people with mental health conditions, including CBR programs that focus on recovery and community reintegration.
Private Providers
Private providers play an increasingly important role in delivering CBR services in Australia. They offer a variety of services, ranging from individual support to specialized therapies, and often work in partnership with government agencies and non-profit organizations.
- Home Care Agencies: These agencies provide a range of in-home support services, including personal care, domestic assistance, and support for daily living activities. They often work with people with disability and older adults to enable them to live independently in their own homes.
- Therapy Providers: Private therapy providers offer a range of specialized therapies, such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. They play a crucial role in helping individuals with disability to achieve their rehabilitation goals and improve their quality of life.
- Assistive Technology Providers: These providers offer a range of assistive technologies, such as mobility aids, communication devices, and computer software, to help people with disability participate in daily life and achieve their goals.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Effective CBR delivery relies heavily on collaboration and partnerships between various stakeholders. These partnerships are essential for ensuring that services are coordinated, integrated, and responsive to the needs of individuals and communities.
- Interagency Collaboration: Government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private providers work together to share information, coordinate services, and develop joint initiatives. This collaboration ensures that individuals with disability receive a holistic and integrated approach to their care.
- Community Engagement: CBR programs are most effective when they are developed and delivered in partnership with local communities. This involves working with community members, families, and support networks to understand their needs and preferences, and to ensure that services are culturally appropriate and responsive.
- Research and Innovation: Collaboration between researchers, practitioners, and policy makers is essential for advancing knowledge and developing innovative approaches to CBR. This collaboration helps to ensure that CBR services are evidence-based and responsive to emerging needs and challenges.
Benefits and Challenges of CBR
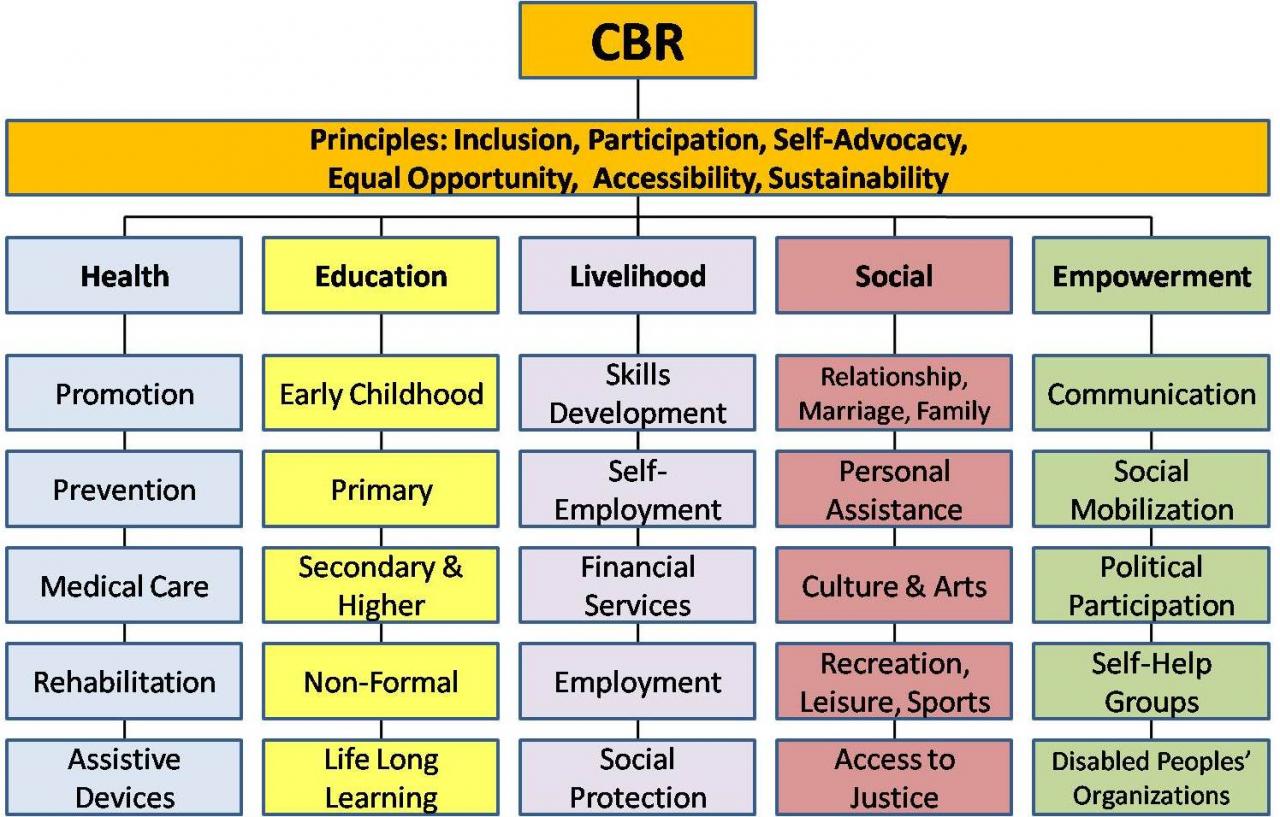
Community-based rehabilitation (CBR) in Australia offers a multifaceted approach to supporting individuals with disabilities, fostering their inclusion and enhancing their quality of life. CBR programs are designed to empower individuals to live fulfilling lives within their communities, promoting independence and reducing reliance on institutional care.
Benefits of CBR
CBR programs in Australia bring significant benefits to individuals with disabilities, their families, and the wider community. These benefits include:
- Increased Independence and Empowerment: CBR programs focus on developing individual skills and abilities, fostering independence and self-reliance. By providing access to training, assistive technology, and support services, individuals with disabilities are empowered to participate actively in their communities and make choices about their lives.
- Improved Quality of Life: CBR programs promote social inclusion and participation, enhancing the quality of life for individuals with disabilities. By connecting them with peers, community resources, and support networks, these programs foster a sense of belonging and reduce social isolation.
- Reduced Dependence on Institutional Care: CBR programs aim to keep individuals with disabilities living in their communities, reducing the need for institutional care. This approach is more cost-effective and promotes a person-centered approach to care, ensuring that individuals receive the support they need in familiar and comfortable environments.
- Strengthened Family Support: CBR programs provide families with education, training, and support, empowering them to effectively care for their loved ones with disabilities. This shared responsibility helps reduce the burden on families and creates a more inclusive and supportive environment.
- Community Development: CBR programs contribute to the development of inclusive and accessible communities for all. By promoting awareness and understanding of disability issues, these programs create a more welcoming and supportive environment for individuals with disabilities and their families.
Challenges of CBR
While CBR programs offer numerous benefits, they also face several challenges in Australia, including:
- Funding Constraints: CBR programs often face funding constraints, limiting their capacity to provide comprehensive and sustainable services. This can lead to waiting lists, limited access to services, and a shortage of resources for individuals with disabilities.
- Workforce Shortages: There is a shortage of skilled and qualified professionals in the disability sector, particularly in rural and remote areas. This can lead to a lack of trained staff to deliver CBR programs effectively, impacting the quality and availability of services.
- Access to Services: Individuals with disabilities, particularly those living in rural and remote areas, may face barriers to accessing CBR services. This can be due to geographical isolation, limited transportation options, or a lack of awareness about available programs.
- Coordination and Collaboration: Effective CBR programs require strong coordination and collaboration between various stakeholders, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, and community groups. This can be challenging due to different organizational structures, funding models, and priorities.
- Attitudes and Stigma: Despite progress in promoting inclusion, some attitudes and stigma towards disability still exist in the community. This can create barriers for individuals with disabilities, hindering their participation in society and limiting their access to opportunities.
Potential Solutions and Strategies
Addressing the challenges faced by CBR programs requires a multifaceted approach involving government, community organizations, and individuals with disabilities. Some potential solutions and strategies include:
- Increased Funding and Resources: Investing in CBR programs through increased funding and resources is crucial to ensure the sustainability and effectiveness of these services. This includes providing adequate funding for staff training, program development, and the provision of assistive technology.
- Workforce Development: Addressing the workforce shortage requires investing in workforce development initiatives, including training programs, scholarships, and incentives to attract and retain skilled professionals in the disability sector.
- Improved Access to Services: Expanding access to CBR services requires addressing barriers to participation, such as transportation difficulties, limited awareness, and cultural sensitivity. This can be achieved through partnerships with community organizations, transportation services, and cultural awareness training.
- Enhanced Coordination and Collaboration: Fostering collaboration between stakeholders, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, and community groups, is essential for the effective delivery of CBR programs. This can be facilitated through joint planning, shared funding models, and data sharing initiatives.
- Promoting Inclusion and Awareness: Addressing attitudes and stigma towards disability requires promoting inclusion and awareness through public education campaigns, community events, and media representation. This can help create a more welcoming and supportive environment for individuals with disabilities.
Future Directions and Trends
Community-based rehabilitation (CBR) in Australia is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting demographics, and evolving healthcare needs. This dynamic landscape presents exciting opportunities to enhance CBR services and improve outcomes for individuals with disabilities.
Integration of Technology and Telehealth
The integration of technology into CBR is revolutionizing service delivery and accessibility. Telehealth platforms, for instance, enable remote consultations, reducing geographical barriers and providing greater flexibility for individuals.
- Virtual reality (VR) is emerging as a powerful tool for rehabilitation, offering immersive experiences for individuals to practice skills and overcome physical limitations. VR applications can be used for physiotherapy exercises, occupational therapy tasks, and even social skills training.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is also playing a growing role in CBR, with AI-powered assistive devices and applications aiding individuals with daily tasks and improving their independence. For example, AI-powered voice assistants can provide personalized support, reminders, and access to information, enhancing the quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
- Wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, can monitor individuals’ physical activity levels, sleep patterns, and vital signs, providing valuable data for personalized rehabilitation plans and early intervention.
Impact of Policy Changes and Funding Reforms
Policy changes and funding reforms have a significant impact on the availability and accessibility of CBR services.
- The National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) has significantly increased funding for disability support services, including CBR, leading to greater access for individuals with disabilities. However, ongoing challenges remain regarding the allocation of funds and ensuring equitable access across different regions and demographics.
- Policy changes focusing on promoting community inclusion and supporting individuals to live independently will likely lead to a greater emphasis on CBR services. This shift could involve increasing funding for home-based support services, community participation programs, and accessible housing options.
Key Areas for Future Research and Development
Continued research and development are crucial to optimize CBR services and address emerging challenges.
- Developing evidence-based interventions tailored to the unique needs of individuals with disabilities, including those with complex or emerging conditions.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of technology-enabled CBR services, including telehealth, VR, and AI applications, to ensure they are meeting the needs of individuals and achieving desired outcomes.
- Exploring the impact of social determinants of health on access to and outcomes of CBR services. This includes factors such as socioeconomic status, geographical location, cultural background, and gender.
- Developing innovative models of CBR service delivery that are responsive to the changing needs of individuals with disabilities, including models that incorporate technology, promote community inclusion, and address social determinants of health.
Wrap-Up: Community Based Rehabilitation In Australia-in Home Services Insurance

In conclusion, community based rehabilitation in Australia-in home services insurance stands as a testament to the nation’s commitment to supporting individuals with disabilities in their pursuit of independence and well-being. Through a multifaceted approach that blends professional expertise, government support, and community engagement, this system provides individuals with the tools and resources they need to navigate their unique challenges and thrive in their chosen environments. As technology continues to evolve and societal perspectives shift, the future of community-based rehabilitation in Australia promises even greater inclusivity and opportunities for individuals with disabilities to live fulfilling lives.
FAQ Compilation
What are the eligibility criteria for accessing in-home services under the NDIS?
Eligibility for NDIS support is based on a person’s disability and their functional capacity. To be eligible, individuals must have a permanent impairment that affects their daily life and requires ongoing support. The NDIS assesses individual needs and determines the level of support required.
What are the common types of in-home services offered under community-based rehabilitation in Australia?
Common in-home services include:
- Personal care assistance
- Domestic support
- Therapy services (physical, occupational, speech)
- Assistive technology support
- Social and community participation support
- Mental health support
How can I find a community-based rehabilitation provider in my area?
You can find community-based rehabilitation providers in your area through the NDIS website, state government disability services websites, or by contacting your local community health center or disability support organization.
