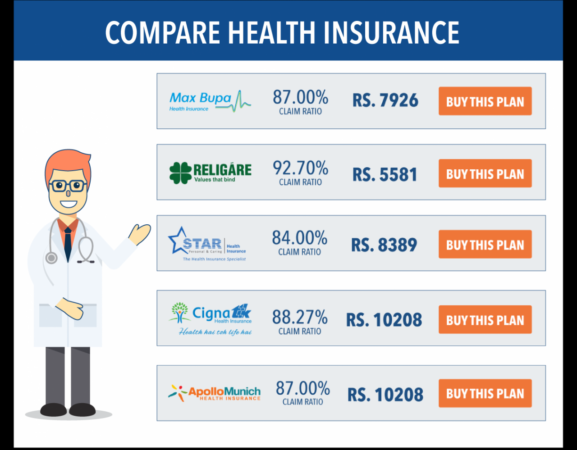
Competition in the Australian private health insurance market 2016 was a dynamic landscape shaped by factors like market size, insurer strategies, and consumer preferences. The market was characterized by a handful of dominant players vying for market share, each employing unique pricing models, product offerings, and distribution channels. The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) played a crucial role in regulating the market, ensuring fairness and transparency.
Consumer choices were driven by a complex interplay of factors, including price, coverage benefits, and brand reputation. Technological advancements and digital marketing strategies also influenced the market, creating new opportunities for insurers to reach and engage with potential customers. This period saw the rise of online platforms and mobile applications, transforming how consumers accessed and compared health insurance options.
Market Overview in 2016
The Australian private health insurance market in 2016 was a significant sector, playing a crucial role in providing healthcare access to a substantial portion of the population. This market was characterized by its competitive landscape, with several major players vying for market share.
Market Size and Structure
The Australian private health insurance market in 2016 was a sizable sector, with a significant number of individuals and families relying on private health insurance for their healthcare needs. The market was structured around a few major players, each with a considerable market share. These insurers offered a range of products and services, catering to diverse needs and budgets.
Market Share of Major Insurers
The market share held by major insurers in 2016 reflected the competitive landscape.
- Medibank Private, the largest private health insurer in Australia, held a significant market share, demonstrating its strong position in the market.
- Bupa, another major player, also commanded a substantial market share, indicating its extensive reach and customer base.
- NIB, a prominent player in the private health insurance market, held a considerable market share, reflecting its competitive offerings and strong brand presence.
Growth Trends and Key Drivers
The Australian private health insurance market in 2016 was characterized by growth, driven by several key factors.
- An aging population contributed to increased demand for private health insurance, as older individuals often require more healthcare services.
- Rising healthcare costs, coupled with the increasing complexity of medical treatments, led many individuals to seek private health insurance for financial protection.
- Government policies, such as the Medicare levy surcharge, encouraged individuals to consider private health insurance as a way to avoid financial penalties.
Competitive Landscape: Competition In The Australian Private Health Insurance Market 2016

The Australian private health insurance market in 2016 was characterized by a high level of competition among a diverse range of players. This competition manifested in various aspects, including product offerings, pricing strategies, and distribution channels.
Key Players
The Australian private health insurance market in 2016 was dominated by a handful of major players, including:
- Medibank Private
- Bupa
- NIB
- HCF
- Australian Unity
These insurers held significant market share and competed fiercely for customers.
Product Offerings
The major insurers offered a wide range of health insurance products, catering to different needs and budgets. These products included:
- Hospital cover: This type of cover provides financial assistance for hospital stays, surgeries, and other medical procedures.
- Extras cover: This type of cover provides financial assistance for a range of medical expenses, including dental, optical, physiotherapy, and ambulance services.
- Combined hospital and extras cover: This type of cover combines the benefits of both hospital and extras cover, providing comprehensive health insurance protection.
Insurers differentiated their products by offering various levels of cover, from basic to comprehensive, and by including different benefits and exclusions.
Pricing Strategies
Insurers employed a variety of pricing strategies to attract customers. These strategies included:
- Bundled pricing: Insurers offered discounted premiums for customers who purchased multiple products, such as hospital and extras cover.
- Age-based pricing: Insurers charged higher premiums to older customers, reflecting their higher risk of requiring medical care.
- Health-based pricing: Insurers charged higher premiums to customers with pre-existing medical conditions, reflecting their higher risk of claiming benefits.
Insurers also used promotional offers, such as discounts for new customers or for customers who referred friends and family.
Distribution Channels
Insurers used a variety of distribution channels to reach their target market. These channels included:
- Direct sales: Insurers employed sales representatives to sell their products directly to customers.
- Broker networks: Insurers partnered with insurance brokers who provided advice and sold their products to customers.
- Online platforms: Insurers offered online quotes and applications, allowing customers to purchase their products online.
Insurers also used a variety of marketing channels to promote their products, including television advertising, online advertising, and social media marketing.
Competitive Advantages and Disadvantages
Each key player in the Australian private health insurance market had its own unique competitive advantages and disadvantages.
Medibank Private
Medibank Private, the largest private health insurer in Australia, had a strong brand reputation and a wide distribution network. The company also offered a comprehensive range of products and services, including health insurance, health and wellness programs, and health management services. However, Medibank Private’s size and market dominance also made it a target for regulatory scrutiny.
Bupa
Bupa was a global health and care provider with a strong international presence. The company offered a wide range of products and services, including health insurance, aged care, and medical centers. Bupa’s international reach gave it access to a broader pool of resources and expertise. However, Bupa’s focus on global expansion meant that it may not have been as focused on the Australian market as some of its competitors.
NIB
NIB was a smaller insurer that focused on providing value for money. The company offered a range of products and services, including health insurance, dental insurance, and travel insurance. NIB’s focus on affordability made it attractive to budget-conscious customers. However, NIB’s smaller size meant that it may not have had the same resources or brand recognition as some of its larger competitors.
HCF
HCF was a not-for-profit insurer that focused on providing affordable health insurance to its members. The company offered a range of products and services, including health insurance, health and wellness programs, and health management services. HCF’s not-for-profit status meant that it was not driven by profit maximization, allowing it to focus on providing value to its members. However, HCF’s not-for-profit status also meant that it may not have had the same resources or marketing budget as some of its for-profit competitors.
Australian Unity
Australian Unity was a mutual insurer that offered a range of products and services, including health insurance, superannuation, and financial advice. The company had a strong focus on customer service and community engagement. Australian Unity’s mutual structure meant that it was owned by its members, giving them a say in how the company was run. However, Australian Unity’s smaller size meant that it may not have had the same resources or brand recognition as some of its larger competitors.
Regulatory Environment
The Australian private health insurance market is subject to a robust regulatory framework designed to ensure fair competition, protect consumers, and promote market stability. The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) plays a pivotal role in overseeing this sector.
APRA’s Role in Regulating the Private Health Insurance Market
APRA’s primary responsibility is to ensure the financial soundness and prudential management of private health insurers. This involves setting and enforcing prudential standards, monitoring insurers’ financial performance, and intervening when necessary to protect policyholders’ interests.
- Prudential Standards: APRA sets prudential standards that insurers must adhere to, covering areas such as capital adequacy, risk management, and governance. These standards aim to ensure that insurers have sufficient financial resources to meet their obligations to policyholders.
- Financial Monitoring: APRA closely monitors the financial performance of private health insurers, analyzing their solvency, liquidity, and profitability. This helps identify potential risks and early warning signs of financial distress.
- Intervention and Supervision: APRA has the power to intervene in the affairs of insurers that fail to meet prudential standards or pose a risk to policyholders. This may involve requiring insurers to take corrective action, imposing penalties, or even placing them under administration.
Impact of Key Regulations and Legislation
The regulatory environment significantly influences the competitive landscape in the private health insurance market. Key regulations and legislation include:
- Private Health Insurance Act 1973 (PHIA): This Act provides the overarching framework for the regulation of private health insurance in Australia. It establishes the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) as the primary regulator, sets out the licensing requirements for insurers, and defines the scope of coverage and benefits.
- Private Health Insurance (Prudential Supervision) Act 1998: This Act provides APRA with the power to set and enforce prudential standards for private health insurers, ensuring their financial stability and the protection of policyholders’ interests.
- Private Health Insurance (Administration) Act 1988: This Act establishes the Private Health Insurance Administration Council (PHIAC), which administers the private health insurance system and provides information and support to consumers.
- Private Health Insurance Amendment (Lifetime Health Cover) Act 2008: This Act introduced the Lifetime Health Cover (LHC) loading, which applies to individuals who delay taking out private health insurance. The LHC loading increases with age, encouraging individuals to take out insurance earlier in life.
Challenges and Opportunities Presented by the Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment presents both challenges and opportunities for private health insurers.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to complex regulations can be costly for insurers, particularly smaller players. The need to comply with prudential standards, reporting requirements, and consumer protection regulations can strain their resources.
- Innovation and Competition: While regulations aim to protect consumers and ensure market stability, they can sometimes stifle innovation and competition. For example, strict product approval processes can hinder the development of new and innovative health insurance products.
- Consumer Awareness and Engagement: The regulatory environment can impact consumer awareness and engagement with private health insurance. Complex regulations and product information can make it difficult for consumers to understand their options and make informed choices.
- Opportunities for Differentiation: Despite the challenges, the regulatory environment also presents opportunities for insurers to differentiate themselves. By demonstrating strong compliance, offering innovative products, and providing excellent customer service, insurers can build trust and attract customers.
Consumer Behavior
In 2016, the Australian private health insurance market was characterized by a diverse range of consumer preferences and behaviors. Understanding these factors is crucial for insurers to develop effective strategies to attract and retain customers.
Factors Influencing Consumer Choices
Consumers’ decisions regarding private health insurance are driven by a complex interplay of factors, including personal circumstances, financial considerations, and perceptions of value.
- Age and Health Status: Younger individuals with limited health concerns may be less likely to prioritize private health insurance, while older individuals with pre-existing conditions or a higher risk of hospitalization are more likely to seek coverage.
- Income and Financial Situation: Private health insurance premiums can be a significant financial burden, particularly for low-income earners. Consumers often weigh the cost of premiums against the potential benefits of coverage.
- Family Structure: Individuals with families, particularly those with children, are more likely to consider private health insurance to cover potential healthcare costs.
- Lifestyle and Health Awareness: Consumers who engage in risky behaviors or have specific health concerns, such as those with a family history of certain diseases, may be more likely to seek private health insurance.
The Role of Price, Benefits, and Brand Reputation
Price, benefits, and brand reputation are key factors influencing consumer decision-making in the private health insurance market.
- Price: Consumers are highly sensitive to price, particularly in a competitive market. Insurers often offer various premium tiers and discounts to attract price-conscious customers.
- Benefits: The level and scope of coverage offered by different insurance plans play a crucial role in consumer choices. Consumers prioritize benefits that align with their individual needs and health risks.
- Brand Reputation: Consumers tend to favor insurers with a strong reputation for reliability, customer service, and claims processing. Brand loyalty can be a significant factor in influencing purchasing decisions.
Emerging Trends in Consumer Preferences and Expectations
Consumer preferences and expectations in the private health insurance market are constantly evolving.
- Value for Money: Consumers increasingly demand value for money, seeking plans that offer comprehensive coverage at competitive prices.
- Transparency and Clarity: Consumers expect clear and transparent information about policy terms, benefits, and exclusions.
- Digital Convenience: Consumers are increasingly comfortable with online platforms for managing their health insurance policies, including claims submission and communication with insurers.
- Personalized Solutions: Consumers are seeking personalized solutions tailored to their individual needs and health risks. This includes customized plans, wellness programs, and health management tools.
Market Trends and Innovations
The Australian private health insurance market in 2016 witnessed a surge in technological advancements and innovative approaches, transforming the way insurers interacted with consumers and delivered services. These developments significantly impacted the competitive landscape, influencing consumer behavior and driving industry evolution.
Impact of Technological Advancements
The increasing adoption of digital technologies significantly influenced the private health insurance market in 2016.
- Online platforms and mobile applications became more prevalent, offering consumers convenient access to information, policy comparisons, and online quote requests. This enabled insurers to reach a wider audience and enhance customer engagement.
- Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) played a crucial role in improving risk assessment, pricing strategies, and fraud detection. Insurers leveraged these technologies to optimize their operations and enhance customer experiences.
- Telemedicine and remote healthcare services gained traction, offering patients access to medical consultations and diagnoses without physically visiting a doctor. This trend reduced healthcare costs and improved access to services for individuals in remote areas.
Emerging Trends in Product Innovation and Service Delivery
Insurers actively responded to evolving consumer needs and preferences by introducing innovative products and services.
- Personalized health insurance plans tailored to individual needs and risk profiles became increasingly popular. This allowed insurers to offer more competitive and relevant coverage options.
- Value-added services such as health and wellness programs, fitness trackers, and preventative health screenings were integrated into insurance plans. This approach aimed to promote healthy lifestyles and reduce healthcare costs in the long run.
- Bundled insurance packages combining health insurance with other services, such as travel insurance or life insurance, gained traction. This strategy offered consumers convenience and potential cost savings.
Role of Digital Marketing and Online Platforms, Competition in the australian private health insurance market 2016
Digital marketing and online platforms played a pivotal role in shaping the competitive landscape of the Australian private health insurance market in 2016.
- Search engine optimization () and pay-per-click (PPC) advertising allowed insurers to reach a targeted audience and enhance brand visibility online.
- Social media marketing enabled insurers to engage with consumers, build brand loyalty, and promote their products and services.
- Online comparison websites provided consumers with a platform to compare insurance policies from different providers, fostering price transparency and competition.
Last Word

The Australian private health insurance market in 2016 was a dynamic and evolving landscape, driven by a combination of regulatory oversight, competitive pressures, and consumer behavior. Key players in the market constantly adapted their strategies to meet the changing needs and expectations of customers. Technological advancements and the rise of digital platforms played a significant role in shaping the competitive landscape, offering new avenues for insurers to reach and engage with potential customers. This period witnessed a shift towards greater transparency and accountability, as regulators and consumers demanded more value and innovation from the industry.
User Queries
What were the major players in the Australian private health insurance market in 2016?
Some of the major players in the market included Medibank Private, Bupa, nib, HBF, and Australian Unity.
How did technological advancements impact the market in 2016?
Technological advancements led to the development of online platforms and mobile applications, allowing consumers to compare plans and purchase policies online. This increased transparency and convenience for consumers.
What were some of the key regulations affecting the private health insurance market in 2016?
Key regulations included the Private Health Insurance Act 1973 and the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) guidelines. These regulations aimed to ensure fairness, transparency, and financial stability within the industry.
What were some of the emerging trends in consumer preferences for health insurance in 2016?
Consumers increasingly valued transparency, value for money, and personalized services. There was a growing demand for digital tools and online platforms to manage their health insurance policies.