Imagine a world where every electrical appliance, from your smartphone to a high-speed train, could seamlessly connect and function anywhere on the planet. This is the promise of international electricity standards, a complex and vital system that underpins the global flow of energy.
These standards, established by organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ensure that electrical devices and infrastructure operate safely and efficiently across borders. From the humble light bulb to sophisticated power grids, international electricity standards play a crucial role in shaping a connected and technologically advanced world.
Introduction to International Electricity Standards
In a world increasingly interconnected by technology and trade, the importance of international electricity standards cannot be overstated. These standards ensure compatibility, safety, and efficiency in the global electrical infrastructure, facilitating the seamless flow of electricity across borders and fostering international collaboration in the field.
International electricity standards have evolved over time, driven by the need to harmonize practices and ensure interoperability of electrical equipment. The development of these standards has been a collaborative effort involving various organizations, each playing a crucial role in shaping the global electrical landscape.
Key Organizations Involved in International Electricity Standards
The establishment and maintenance of international electricity standards are overseen by a network of organizations, each with its own area of expertise and influence. These organizations work together to develop and promote standards that meet the needs of a globalized world.
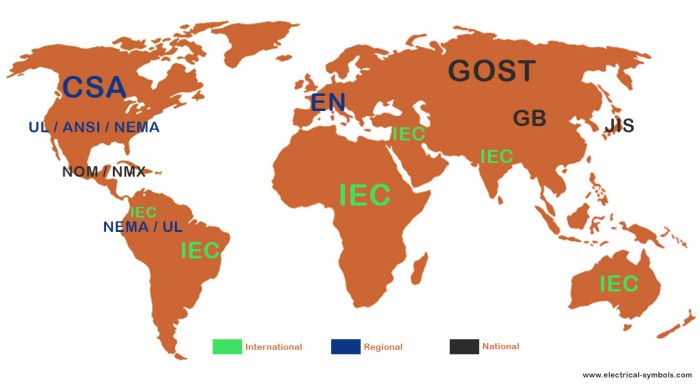
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): The IEC is the world’s leading organization for standardization in the field of electrotechnology. It develops and publishes international standards for electrical equipment, systems, and processes, covering a wide range of applications, from power generation and transmission to consumer electronics. The IEC’s standards are widely adopted globally, ensuring compatibility and safety in the electrical industry.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO): While the ISO focuses on a broader range of standards, it plays a significant role in setting standards related to electricity, particularly in areas such as quality management systems, environmental management, and safety. ISO standards are recognized globally, providing a framework for organizations to operate in a consistent and reliable manner.
- International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM): The BIPM is responsible for maintaining the International System of Units (SI), which forms the basis for international measurement standards. This includes electrical units like the volt, ampere, and ohm, ensuring consistency in measurements across the globe.
Major International Electricity Standards
International electricity standards play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and interoperability of electrical systems worldwide. They provide a common framework for design, testing, and certification of electrical equipment and installations, fostering global trade and promoting technological advancements.
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
The IEC is a global organization that develops and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic, and related technologies. It is the world’s leading organization for standardization in the field of electrical and electronic engineering.
- The IEC develops standards covering a wide range of electrical applications, including power generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization.
- IEC standards are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, and regulatory bodies to ensure that electrical products meet safety, performance, and compatibility requirements.
- IEC standards are widely adopted globally, and their adherence is often mandatory in many countries.
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
The IEEE is a professional organization for electrical and electronic engineers, known for its technical publications and standards development.
- IEEE standards cover a wide range of areas, including power systems, telecommunications, computing, and consumer electronics.
- IEEE standards are often developed in collaboration with other organizations, such as the IEC, to ensure compatibility and interoperability.
- IEEE standards are widely used in the United States and other countries, and they are often referenced in national and regional regulations.
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
ANSI is a private, non-profit organization that coordinates the development of voluntary consensus standards in the United States.
- ANSI does not develop standards itself but accredits organizations to develop and maintain standards.
- ANSI standards are widely adopted in the United States and are often referenced in national and regional regulations.
- ANSI standards are often based on international standards, such as those developed by the IEC and IEEE.
Comparison of International Electricity Standards
| Standard | Technical Specifications | Testing Procedures | Certification Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEC | Comprehensive and detailed specifications covering a wide range of electrical applications. | Rigorous testing procedures to ensure compliance with safety, performance, and compatibility requirements. | Mandatory certification in many countries, often through accredited testing laboratories. |
| IEEE | Focus on specific areas of electrical engineering, such as power systems, telecommunications, and computing. | Testing procedures are often developed in collaboration with other organizations, such as the IEC. | Certification is often voluntary but may be required by certain regulatory bodies. |
| ANSI | Standards are often based on international standards, such as those developed by the IEC and IEEE. | Testing procedures are typically aligned with those of the IEC and IEEE. | Certification is often voluntary but may be required by certain regulatory bodies. |
Scope and Application of International Electricity Standards
International electricity standards are applied across various aspects of the electrical industry, including:
- Power generation: Standards define safety and performance requirements for generators, turbines, and other power generation equipment.
- Power transmission: Standards specify the design and operation of transmission lines, transformers, and other equipment for transporting electricity over long distances.
- Power distribution: Standards cover the distribution of electricity to consumers, including substations, cables, and distribution networks.
- Electrical installations: Standards ensure the safe and reliable installation of electrical systems in buildings, factories, and other facilities.
- Electrical equipment: Standards define safety, performance, and compatibility requirements for a wide range of electrical equipment, including appliances, lighting fixtures, and electronic devices.
Benefits of International Electricity Standards
Adopting international electricity standards offers a wide range of advantages, promoting efficiency, safety, and economic growth across various sectors. These standards provide a common framework for electrical equipment and systems, ensuring compatibility and interoperability, ultimately leading to a more interconnected and reliable global electrical infrastructure.
Interoperability and Compatibility
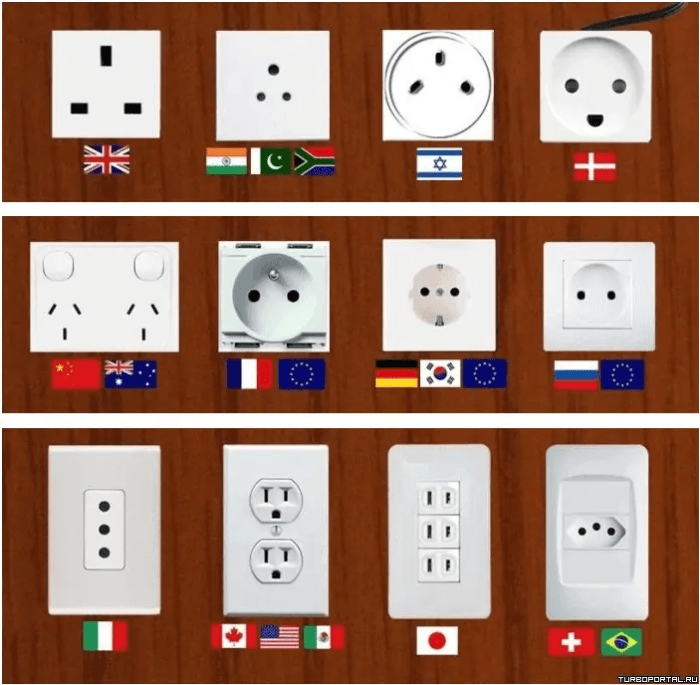
International electricity standards play a crucial role in ensuring the seamless integration of electrical equipment and systems from different manufacturers and regions. They establish common specifications for voltage, frequency, plugs, and sockets, allowing devices and appliances to operate without any compatibility issues. For instance, a laptop purchased in the United States can be used in Europe without requiring any modifications or adapters. This interoperability is essential for the smooth flow of electricity and the efficient operation of electrical systems.
Enhanced Safety
International electricity standards prioritize safety by setting minimum requirements for electrical equipment and systems. These standards cover various aspects, including insulation, wiring, and grounding, to minimize the risk of electrical shocks, fires, and other hazards. For example, the IEC 60320 standard defines the requirements for plugs and sockets, ensuring that they are designed to prevent accidental contact with live wires. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can produce safe products, and consumers can have peace of mind knowing that the electrical equipment they use meets international safety standards.
Reduced Costs
International electricity standards contribute to cost reduction in several ways. Firstly, they eliminate the need for manufacturers to develop and produce multiple versions of products for different markets, leading to economies of scale and lower production costs. Secondly, they facilitate the exchange of goods and services across borders, reducing transportation and logistics costs. Finally, they simplify the process of maintenance and repair, as standardized equipment and components are readily available worldwide.
Facilitating Trade and Promoting Economic Growth
International electricity standards are essential for promoting global trade and economic growth. They create a level playing field for manufacturers and suppliers, enabling them to access larger markets without facing trade barriers. This increased trade fosters competition, innovation, and economic development. Furthermore, standardized electrical systems facilitate the deployment of new technologies, such as renewable energy sources and smart grids, which are crucial for sustainable economic growth.
Benefits Across Sectors
| Sector | Benefits of International Electricity Standards |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Reduced production costs, improved product quality, increased global market access. |
| Energy | Enhanced grid reliability, increased energy efficiency, facilitated integration of renewable energy sources. |
| Transportation | Standardized charging infrastructure for electric vehicles, improved safety for electrified transportation systems. |
Challenges and Future Trends

The successful implementation and maintenance of international electricity standards face several challenges, and the emergence of new technologies further complicates the landscape. Examining these challenges and future trends is crucial for ensuring a reliable and sustainable global electricity system.
Challenges in Implementing and Maintaining International Electricity Standards
Implementing and maintaining international electricity standards pose various challenges, including:
- Coordination and Consensus Building: Achieving consensus among diverse stakeholders, including national regulatory bodies, industry players, and research institutions, is essential for successful standard development and adoption. The process requires extensive collaboration and compromise to ensure that standards are relevant, practical, and acceptable to all parties involved.
- Balancing Innovation and Standardization: The rapid pace of technological advancements in the electricity sector, such as the rise of renewable energy sources and smart grids, necessitates a delicate balance between promoting innovation and establishing standardized frameworks. Standards need to be flexible enough to accommodate emerging technologies while providing sufficient guidance and consistency.
- Ensuring Compatibility and Interoperability: International electricity standards are critical for ensuring compatibility and interoperability between different electricity systems and components. This is particularly important for cross-border electricity trade and the integration of distributed energy resources.
- Enforcing Compliance and Monitoring Implementation: Effective enforcement mechanisms are essential to ensure that standards are implemented consistently and that deviations are addressed promptly. This requires collaboration between national and international bodies and effective monitoring systems to track compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on International Electricity Standards
Emerging technologies, such as renewable energy and smart grids, have a significant impact on international electricity standards.
- Renewable Energy Integration: The increasing integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, necessitates new standards for grid interconnection, energy storage, and power electronics. These standards need to address the unique characteristics of renewable energy sources, such as their intermittency and variability.
- Smart Grid Technologies: Smart grids, which utilize advanced technologies for monitoring, control, and communication, require new standards for data exchange, cybersecurity, and interoperability. These standards need to ensure that smart grid systems can operate reliably and securely while promoting innovation and interconnectivity.
Future Trends in International Electricity Standards
The field of international electricity standards is constantly evolving to meet the challenges and opportunities of a changing energy landscape.
- Increased Focus on Sustainability: International electricity standards are expected to place greater emphasis on sustainability, promoting the use of renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, and carbon reduction. This will require the development of standards for energy storage, grid modernization, and the integration of distributed energy resources.
- Digitalization and Data Management: The increasing digitization of the electricity sector will require new standards for data exchange, cybersecurity, and interoperability. These standards will be essential for enabling the development of smart grids, distributed energy resources, and other digital technologies that can enhance grid efficiency and reliability.
- Harmonization and Convergence: There is a growing trend towards harmonization and convergence of international electricity standards. This will help to reduce technical barriers to trade, facilitate cross-border electricity flows, and promote global cooperation in the development of sustainable energy systems.
Case Studies
International electricity standards have proven to be instrumental in fostering global collaboration, enhancing safety, and promoting economic growth. The following case studies highlight the successful implementation of these standards across various industries and regions.
Successful Implementation of International Electricity Standards in the Renewable Energy Industry
International electricity standards have played a crucial role in the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies, particularly in the solar and wind power sectors. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed a comprehensive set of standards for photovoltaic (PV) systems, wind turbines, and related equipment, ensuring interoperability, safety, and performance. For instance, the IEC 61730 standard, which addresses the safety of PV systems, has been widely adopted by manufacturers and installers worldwide. This standardization has facilitated the seamless integration of PV systems into national grids, accelerating the transition towards renewable energy sources.
Impact of International Standards on the Electrical Infrastructure of a Developing Country
The adoption of international electricity standards has significantly contributed to the development of electrical infrastructure in emerging economies. In India, for example, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has aligned its national standards with IEC standards, leading to improved safety and reliability of electrical systems. The implementation of these standards has facilitated the expansion of the national grid, enhanced energy efficiency, and reduced the incidence of electrical accidents. The harmonization of standards has also attracted foreign investment in India’s power sector, promoting economic growth and development.
Comparative Analysis of International Electricity Standards Adoption and Economic Outcomes
| Country | Adoption of International Standards | Economic Outcomes |
|—|—|—|
| China | High | Rapid growth in renewable energy sector, increased exports of electrical equipment |
| Germany | High | World leader in renewable energy, strong manufacturing base in the electrical industry |
| Brazil | Moderate | Significant improvements in energy efficiency, increased access to electricity in rural areas |
| South Africa | Moderate | Challenges in implementing standards, but progress in upgrading electrical infrastructure |
| Nigeria | Low | Limited adoption of international standards, resulting in safety concerns and unreliable power supply |
This table illustrates the correlation between the adoption of international electricity standards and economic outcomes. Countries with a high level of adoption have generally experienced faster economic growth, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced competitiveness in the global market. Conversely, countries with low adoption rates often face challenges in developing their electrical infrastructure, leading to safety risks and unreliable power supply.
Summary

As technology continues to evolve, international electricity standards will remain at the forefront of innovation, facilitating the development of new energy solutions and ensuring a safe and reliable global energy ecosystem. By fostering collaboration and promoting interoperability, these standards will continue to power the world, connecting people and economies across the globe.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the difference between IEC, IEEE, and ANSI standards?
IEC is the International Electrotechnical Commission, IEEE is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, and ANSI is the American National Standards Institute. While they all develop electrical standards, IEC is a global organization, IEEE is primarily focused on North America, and ANSI is a U.S.-based organization.
How do international electricity standards impact consumer products?
International standards ensure that products like phones, laptops, and appliances can be used safely and reliably in different countries, promoting global trade and consumer confidence.
Are there any challenges in implementing international electricity standards?
Yes, challenges include ensuring harmonization across different regions, adapting to evolving technologies, and addressing the needs of developing countries.