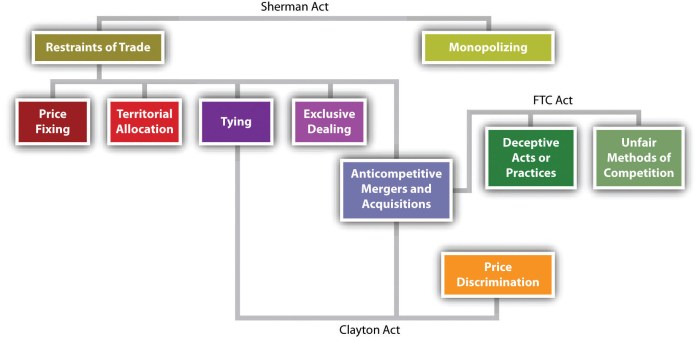
What are antitrust laws? They are a set of rules designed to prevent monopolies and promote fair competition in the marketplace. These laws are essential for ensuring that consumers have access to a wide range of choices and that businesses operate in a fair and transparent manner. The history of antitrust laws dates back to the late 19th century, a time when powerful monopolies were stifling innovation and harming consumers. The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890, the first federal antitrust law, was passed to address these concerns.
Antitrust laws cover a wide range of business practices, including price fixing, market allocation, and predatory pricing. They also regulate mergers and acquisitions to prevent the creation of monopolies. The enforcement of antitrust laws is crucial for maintaining a healthy and competitive economy. It involves identifying and addressing anti-competitive behavior, ensuring that consumers are not being exploited, and promoting innovation and economic growth.
Antitrust Laws in the Digital Age

The rapid rise of the digital economy has brought about significant changes in how businesses operate and compete. The internet and mobile technologies have enabled the emergence of new digital platforms and business models, posing unique challenges to traditional antitrust laws designed for the industrial age. This section explores the unique challenges posed by digital markets to antitrust laws, discusses the evolving nature of antitrust enforcement in the digital economy, and examines specific antitrust concerns related to different digital industries.
Challenges Posed by Digital Markets
The digital economy presents several unique challenges to antitrust laws. One key challenge is the prevalence of network effects, where the value of a product or service increases as more users join the platform. This can lead to the emergence of dominant platforms with significant market power, making it difficult for new entrants to compete. Another challenge is the difficulty in defining relevant markets in the digital age. Traditional market definitions based on physical goods and services may not adequately capture the dynamic nature of digital markets, where products and services are constantly evolving and blurring the lines between different industries.
Furthermore, the vast amounts of data collected by digital platforms raise concerns about potential anticompetitive practices. These platforms can use their data to identify and target competitors, potentially hindering their growth. Moreover, the global nature of digital markets makes it difficult for national antitrust authorities to effectively regulate cross-border activities.
Evolving Antitrust Enforcement in the Digital Economy
Antitrust enforcement agencies worldwide are grappling with the challenges posed by the digital economy. They are increasingly recognizing the need for new approaches to address the unique characteristics of digital markets.
One key area of focus is the regulation of platform dominance. Antitrust authorities are scrutinizing the practices of large digital platforms, such as search engines, social media companies, and e-commerce marketplaces, to ensure they do not engage in anticompetitive behavior. This includes examining practices such as self-preferencing, where platforms favor their own products or services over those of competitors, and data collection and usage that could stifle competition.
Another area of focus is the regulation of mergers and acquisitions in the digital economy. Antitrust authorities are paying close attention to the potential impact of mergers on competition in digital markets, particularly those involving companies with significant market power.
Antitrust Concerns in Specific Digital Industries
| Digital Industry | Antitrust Concerns | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Search Engines | Self-preferencing, data collection and usage, exclusionary practices | Google’s alleged favoring of its own products and services in search results, data collection and usage for targeted advertising, exclusionary practices against competitors |
| Social Media | Network effects, data collection and usage, anticompetitive acquisitions | Facebook’s dominance in social media, data collection and usage for targeted advertising, acquisitions of potential competitors such as Instagram and WhatsApp |
| E-commerce | Market power, data collection and usage, self-preferencing | Amazon’s dominance in e-commerce, data collection and usage for targeted advertising, self-preferencing of its own products and services |
| Mobile App Stores | Gatekeeper power, app distribution restrictions, pricing practices | Apple and Google’s control over app distribution on their mobile operating systems, restrictions on app development and distribution, high commission fees for app developers |
The Impact of Antitrust Laws on Consumers

Antitrust laws are crucial for protecting consumers from unfair business practices and promoting a competitive marketplace. These laws ensure that consumers have access to a wide range of choices at fair prices, fostering innovation and economic growth.
The Relationship Between Antitrust Laws and Consumer Choice
Antitrust laws play a vital role in ensuring consumer choice by preventing monopolies and other anti-competitive practices. When companies have too much market power, they can dictate prices, limit product variety, and reduce the quality of goods and services. This can lead to consumers having fewer options and paying higher prices. Antitrust laws aim to prevent this by promoting competition and ensuring that consumers have a wide range of choices.
Examples of How Antitrust Laws Have Benefited Consumers, What are antitrust laws
Antitrust laws have had a significant impact on consumer welfare, protecting them from unfair business practices and promoting a more competitive marketplace. Here are some examples:
- In the 1980s, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) investigated and ultimately blocked the proposed merger of AT&T and T-Mobile. This merger would have created a dominant player in the wireless telecommunications market, potentially leading to higher prices and fewer choices for consumers. The DOJ’s action ensured that the wireless market remained competitive, benefiting consumers with lower prices and more choices.
- In the 2000s, the DOJ sued Microsoft for anti-competitive practices related to its Windows operating system. The lawsuit alleged that Microsoft used its dominant market position to stifle competition and harm consumers. The settlement of the lawsuit required Microsoft to make changes to its business practices, including providing more choices for consumers and promoting interoperability between its products and those of its competitors. This action resulted in a more competitive market for software and benefited consumers with lower prices and more choices.
- In recent years, the DOJ and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) have investigated the potential anti-competitive practices of large technology companies, such as Google, Amazon, and Facebook. These investigations have focused on concerns about these companies using their dominant market positions to stifle competition and harm consumers. The outcome of these investigations will have a significant impact on the future of the digital economy and the choices available to consumers.
Global Perspectives on Antitrust Laws
Antitrust laws, also known as competition laws, are designed to promote fair competition and prevent monopolies in the marketplace. While the core principles of antitrust law are generally similar across the globe, the specific rules and enforcement mechanisms can vary significantly from country to country. This variation reflects differences in economic and political contexts, cultural values, and historical experiences.
Comparison of Antitrust Laws Across Countries
The differences in antitrust laws across countries can be observed in several key areas, including:
- Merger Control: The thresholds for triggering merger reviews, the types of mergers subject to scrutiny, and the standards for approving or blocking mergers can vary widely. For example, the European Union (EU) has a more stringent approach to merger control than the United States, often blocking mergers that would be allowed in the U.S. due to concerns about market dominance.
- Anti-Competitive Practices: The specific types of anti-competitive practices prohibited by law can differ. For instance, some countries have laws specifically targeting predatory pricing, while others focus more on cartels and price-fixing. The EU, for example, has a broad prohibition on “abuse of dominance” by firms with market power, which encompasses a wide range of practices, including predatory pricing, tying, and bundling.
- Enforcement Mechanisms: The agencies responsible for enforcing antitrust laws and the penalties for violations can vary significantly. In the U.S., the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ) share enforcement responsibility, while in other countries, a single agency might handle antitrust matters. The range of penalties can include fines, injunctions, and even criminal charges.
Challenges of International Cooperation in Antitrust Enforcement
International cooperation in antitrust enforcement presents several challenges:
- Jurisdictional Issues: Determining which country has jurisdiction over a particular antitrust case can be complex, especially in cases involving multinational companies operating in multiple markets. This can lead to jurisdictional disputes and potential conflicts between different enforcement agencies.
- Differences in Laws and Enforcement Practices: The differences in antitrust laws and enforcement practices across countries can make it difficult to coordinate investigations and prosecutions. This can hinder the ability of agencies to effectively address cross-border anti-competitive conduct.
- Confidentiality and Data Sharing: Sharing sensitive information and evidence between agencies can be challenging due to concerns about confidentiality and data protection. This can limit the ability of agencies to fully investigate and prosecute cross-border antitrust cases.
Examples of Global Antitrust Issues and Their Resolutions
There have been several notable instances of international cooperation in antitrust enforcement:
- The Airline Cartel Case (2006-2010): In 2006, antitrust authorities in the U.S., EU, and other countries launched investigations into allegations of price-fixing and other anti-competitive practices by major airlines. The investigations resulted in significant fines for several airlines, including British Airways, Lufthansa, and Air France-KLM.
- The Google Search Case (2010-2017): The EU Commission investigated Google for alleged anti-competitive practices related to its search engine and advertising services. In 2017, the Commission fined Google €2.42 billion for abusing its dominant position in the search market. This case highlighted the challenges of regulating large technology companies with global reach.
Ultimate Conclusion
Antitrust laws play a critical role in safeguarding fair competition and protecting consumers. By preventing monopolies and fostering a level playing field, these laws ensure that businesses compete on merit, leading to lower prices, higher quality goods and services, and a more dynamic economy. The digital age has brought new challenges to antitrust enforcement, as companies operate in global markets and leverage vast amounts of data. However, the core principles of antitrust law remain relevant, and policymakers are constantly adapting these principles to address the evolving challenges of the modern economy. As technology continues to advance and markets become increasingly interconnected, antitrust laws will continue to be essential for promoting a fair and competitive marketplace that benefits consumers and businesses alike.
Common Queries: What Are Antitrust Laws
How do antitrust laws impact innovation?
Antitrust laws can actually promote innovation by preventing monopolies from stifling competition. When companies have to compete, they are more likely to invest in research and development to create new products and services. This can lead to a more dynamic and innovative economy.
What are some examples of antitrust violations?
Examples of antitrust violations include price fixing, market allocation, and predatory pricing. Price fixing occurs when companies agree to set prices at a certain level, often artificially high. Market allocation involves companies dividing up a market among themselves, eliminating competition. Predatory pricing occurs when a company sets prices below cost to drive competitors out of business.
Who enforces antitrust laws?
In the United States, antitrust laws are enforced by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ). These agencies investigate potential violations, bring lawsuits, and issue cease and desist orders.
How can I report an antitrust violation?
You can report an antitrust violation to the FTC or the DOJ. You can also contact your state attorney general’s office, as many states have their own antitrust laws.