Imagine a world without electricity. It’s hard to fathom, isn’t it? But this invisible force, powering our homes, businesses, and everything in between, relies on a complex system of rules and regulations. The electricity market, a vast network of generators, retailers, and consumers, operates under a carefully crafted framework that ensures the efficient and reliable delivery of power.
These rules are more than just bureaucratic hurdles. They are the foundation upon which the entire electricity market stands, dictating everything from how prices are set to how energy is generated and distributed. From the perspective of the average consumer, understanding these rules can empower you to make informed choices about your energy consumption and potentially save money.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
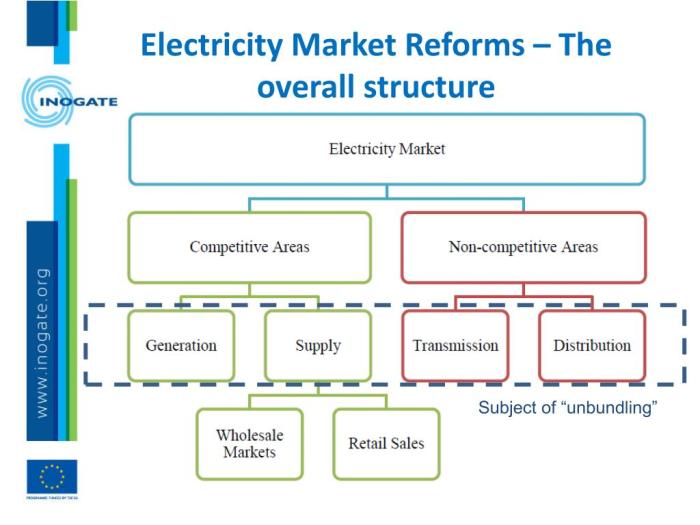
The electricity market is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, policy changes, and evolving consumer preferences. These trends are shaping the future of electricity markets, requiring adjustments to existing rules and regulations.
Impact of Renewable Energy Integration
The increasing integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is significantly impacting electricity market rules. The intermittent nature of these resources poses challenges for grid stability and balancing supply and demand.
- Market Design: Electricity markets are evolving to accommodate the variability of renewable energy. This includes mechanisms like real-time pricing, capacity markets, and renewable energy certificates (RECs) to incentivize and manage renewable energy integration.
- Grid Modernization: Integrating large amounts of renewable energy requires significant upgrades to the electricity grid, including smart grids, advanced metering infrastructure, and energy storage solutions.
- Policy Frameworks: Governments are implementing policies to promote renewable energy development, such as renewable portfolio standards (RPS) and feed-in tariffs (FITs), which influence market rules and incentives.
Role of Distributed Generation and Energy Storage
The rise of distributed generation (DG), such as rooftop solar panels and small-scale wind turbines, is decentralizing electricity production and creating new opportunities for consumers to become prosumers (both producers and consumers). Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro, are playing a crucial role in managing the intermittency of renewable energy sources and improving grid reliability.
- Market Structures: The emergence of DG and energy storage is challenging traditional market structures, leading to the development of new market designs that facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading and community energy systems.
- Demand Response: DG and energy storage enable demand response programs, where consumers can adjust their electricity consumption based on price signals or grid needs, enhancing grid flexibility and efficiency.
- Market Segmentation: The growth of DG and energy storage is creating new market segments, such as the retail energy market, where consumers have more choices for electricity providers and energy services.
Impact of New Technologies
Emerging technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are poised to revolutionize electricity markets, impacting market rules, operations, and consumer behavior.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and security in electricity markets, enabling peer-to-peer energy trading, tracking renewable energy certificates, and simplifying energy transactions.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms can optimize grid operations, improve forecasting accuracy, enhance demand response programs, and personalize energy consumption for individual consumers.
- Internet of Things: IoT devices can connect energy systems and consumers, enabling real-time data collection, demand response programs, and automated energy management.
Final Review
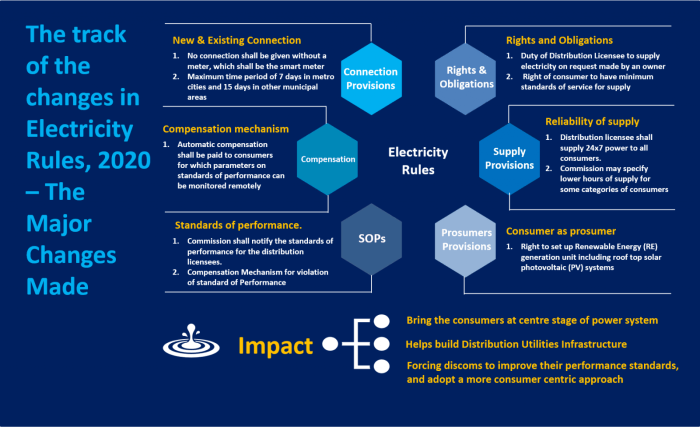
The electricity market is a dynamic ecosystem, constantly evolving with advancements in technology and shifting energy demands. The rules governing this market are crucial for ensuring fair competition, transparency, and the reliable flow of energy. As we move towards a future powered by renewable sources and smart grids, the role of these regulations will only become more important. By understanding the intricacies of the electricity market and the rules that shape it, we can work towards a more sustainable and efficient energy future.
Quick FAQs
How do electricity market rules affect the price I pay for electricity?
Electricity market rules influence prices by setting guidelines for how energy is generated, traded, and distributed. Factors like competition, market power, and regulatory policies all play a role in determining the final price you pay.
What are some of the challenges facing the electricity market today?
The electricity market faces challenges like integrating renewable energy sources, managing grid stability, and addressing climate change concerns. Balancing these competing priorities requires careful consideration of market rules and regulations.
What are some of the emerging trends in electricity market rules?
Emerging trends include the integration of distributed generation, the rise of smart grids, and the adoption of blockchain technology for energy trading. These trends will likely lead to changes in market rules and regulations.