Are 15 minute breaks required by law? This question is a common one for employees and employers alike, and the answer isn’t always straightforward. While federal law doesn’t explicitly mandate 15-minute breaks, it does establish a framework for break requirements through the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). These regulations aim to ensure employees have adequate rest and safety, leading to improved productivity and well-being.
The duration and frequency of breaks can vary depending on factors like the nature of the work, state laws, and company policies. Understanding the legal landscape surrounding breaks is crucial for both employees and employers to ensure compliance and maintain a positive work environment.
Legal Requirements for Breaks
In the United States, federal laws and regulations establish guidelines for breaks in the workplace, ensuring employee well-being and safety. These guidelines, primarily established by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), provide a framework for employers to follow. However, it is crucial to remember that state laws may impose additional requirements beyond these federal standards.
Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)
The FLSA, a federal law, is the primary source of guidance regarding breaks and meal periods. It Artikels minimum wage and overtime pay requirements, as well as standards for child labor. While the FLSA doesn’t mandate specific break requirements, it addresses break time in the context of calculating wages. The FLSA generally considers time spent on breaks as “work time” if it is unpaid and the employee is not “completely relieved from duty” during the break. This means that if an employee is required to remain on-site or perform tasks during a break, that time is considered work time and must be paid.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
OSHA’s primary focus is on workplace safety and health, not directly on break requirements. However, OSHA’s guidelines indirectly address breaks through the concept of “workplace safety.” OSHA regulations emphasize the importance of adequate rest and breaks for employees to maintain their physical and mental well-being. For example, OSHA guidelines suggest that employees engaged in physically demanding tasks or work in hazardous environments should have sufficient rest and breaks to prevent fatigue and accidents. While OSHA does not dictate specific break schedules, its guidelines highlight the significance of breaks in promoting a safe work environment.
State Laws
Many states have enacted laws that impose additional break requirements beyond the federal FLSA standards. These state laws can vary significantly in their scope and requirements. For example, some states require employers to provide paid breaks for nursing mothers, while others mandate specific break durations for employees working specific shifts. It is crucial for employers to be aware of the specific break requirements in their state and comply with both federal and state regulations.
Break Duration and Frequency
The duration and frequency of breaks are crucial aspects of employee well-being and legal compliance. Understanding the typical duration, legal implications, and frequency requirements is essential for employers to ensure they are providing adequate rest and meeting legal obligations.
Break Duration and Legal Implications
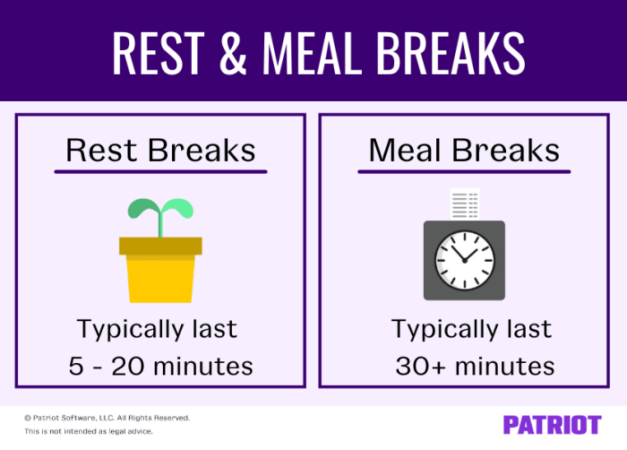
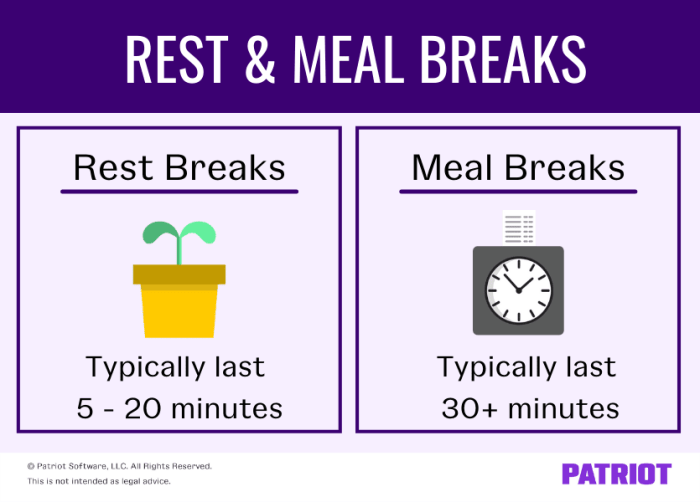
The duration of a break is typically 15 minutes, although this can vary depending on the industry and jurisdiction. This 15-minute duration is considered a “rest break” and is intended to allow employees to take a brief respite from work to rest, eat, or attend to personal needs.
Break Duration and Pay
A 15-minute break is generally considered an “unpaid” break. This means that employees are not required to be paid for this time. However, some states or jurisdictions may have laws that require employers to provide paid rest breaks, especially if the employee works a specific number of hours or performs certain types of tasks.
Frequency of Breaks
The frequency of breaks is determined by several factors, including the employee’s work hours, the type of work being performed, and the specific requirements of the jurisdiction.
- For example, in some states, employees who work more than a certain number of hours are required to take a specific number of breaks.
- Additionally, employees who perform physically demanding or mentally strenuous work may be required to take more frequent breaks to prevent fatigue and potential injury.
Break Requirements by Industry
Legal requirements for breaks can vary significantly across different industries.
- For instance, in retail, employees may be required to take a 15-minute break after working a certain number of hours, while in healthcare, employees may have more frequent breaks due to the demanding nature of their work.
- In manufacturing, employees may be required to take breaks at specific times to ensure safety and prevent accidents.
Employer Responsibilities

Employers have a legal obligation to provide employees with adequate breaks during their workday. These breaks are essential for employee health, safety, and productivity. The specific requirements for breaks vary depending on the state and industry. However, employers must comply with all applicable federal and state laws regarding break requirements.
Providing Breaks
Employers are legally obligated to provide employees with breaks under certain circumstances. For example, most states require employers to provide employees with a break after working a certain number of hours, typically after four or six hours of work. These breaks are usually unpaid and can be used for any purpose, such as eating, resting, or using the restroom.
Employers must also provide employees with breaks for specific tasks, such as breastfeeding or taking medication. These breaks may be paid or unpaid, depending on the circumstances.
Ensuring Suitable Break Areas
Employers are responsible for ensuring that employees have access to a suitable break area. This area should be clean, safe, and comfortable for employees to use. It should also be located in a place that is easily accessible to employees.
Employers must also provide employees with adequate facilities for breaks, such as restrooms, drinking water, and seating. These facilities should be maintained in a clean and sanitary condition.
Break Scheduling, Duration, and Location, Are 15 minute breaks required by law
The following table Artikels the employer’s responsibilities regarding break scheduling, duration, and location:
| Responsibility | Details |
|---|---|
| Break Scheduling | Employers must schedule breaks in a way that allows employees to take their breaks without disrupting their work. |
| Break Duration | Employers must ensure that employees have sufficient time to take their breaks. The minimum break duration is usually specified by state law. |
| Break Location | Employers must provide employees with a suitable break area that is clean, safe, and comfortable. |
Employee Rights and Considerations
Employees have the right to take breaks, as Artikeld by federal and state laws. These laws aim to ensure a safe and healthy work environment by providing employees with opportunities to rest, rehydrate, and prevent fatigue.
Consequences for Employers
Employers who fail to comply with break requirements can face legal consequences, including fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage. These consequences are a reminder of the importance of adhering to legal guidelines to protect employee well-being and avoid legal complications.
Exemptions from Break Requirements
While break requirements are generally applicable, some exceptions exist. For instance, employees working short shifts, typically defined as less than four hours, might be exempt from break requirements. However, employers should consult with their legal counsel to ensure compliance with specific state and federal regulations.
Common Break-Related Issues and Solutions
Employees may encounter various break-related issues, such as:
- Insufficient Break Time: Employees may not be given enough time to take breaks, particularly during busy periods. Solution: Employers should establish clear break policies and ensure employees have sufficient time to rest.
- Break Restrictions: Employers may impose limitations on when or where employees can take breaks, leading to inconvenience and frustration. Solution: Employers should provide reasonable break locations and times, considering the nature of the work and employee needs.
- Break Denial: Employees may be denied breaks due to workload pressure or staffing shortages. Solution: Employers should prioritize employee well-being and ensure that breaks are not sacrificed due to operational pressures.
Break Benefits and Impact

Providing regular breaks for employees is not merely a legal requirement but a strategic investment in their well-being and overall productivity. Breaks offer numerous benefits, ranging from improved employee performance to enhanced mental and physical health.
Benefits of Breaks
Breaks offer a multitude of benefits for both employees and employers. Here are some key advantages:
- Enhanced Productivity: Breaks allow employees to return to work refreshed and focused, leading to increased productivity and efficiency. Research indicates that short breaks can improve cognitive function and reduce mental fatigue, resulting in better performance.
- Reduced Fatigue: Prolonged periods of work without breaks can lead to fatigue, stress, and reduced concentration. Breaks provide an opportunity for employees to rest and recharge, minimizing the risk of burnout and errors.
- Improved Well-being: Breaks allow employees to engage in activities that promote their well-being, such as physical exercise, relaxation techniques, or social interaction. This can contribute to a healthier work-life balance and overall job satisfaction.
- Reduced Risk of Accidents: Fatigue can impair judgment and reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents in the workplace. Breaks help employees stay alert and focused, reducing the likelihood of safety incidents.
Impact of Inadequate Break Policies
Insufficient or poorly designed break policies can have a detrimental impact on employee morale and performance. Here are some potential consequences:
- Decreased Productivity: When employees are denied adequate breaks, they may experience fatigue, reduced concentration, and a decline in their ability to perform their tasks effectively.
- Increased Stress and Burnout: Lack of breaks can contribute to increased stress levels and burnout, leading to absenteeism, decreased engagement, and higher turnover rates.
- Reduced Job Satisfaction: Employees who feel undervalued and deprived of basic necessities, such as breaks, may experience decreased job satisfaction and motivation.
- Legal Issues: Failure to comply with legal requirements regarding breaks can lead to legal action and penalties.
Examples of Successful Break Policies
Several companies have successfully implemented break policies that benefit both employees and the organization. Here are some examples:
- Flexible Break Schedules: Some companies offer flexible break schedules, allowing employees to take breaks at times that best suit their individual needs and preferences. This can promote greater autonomy and employee satisfaction.
- Designated Break Areas: Companies can create designated break areas that are comfortable, inviting, and conducive to relaxation. These areas can include amenities such as comfortable seating, snacks, and beverages.
- Encouraging Breaks: Companies can actively encourage employees to take breaks by promoting the benefits of breaks and providing reminders. This can help to create a culture of prioritizing employee well-being.
Importance of Clear Communication
It is essential to establish a clear break policy that is communicated effectively to all employees. This policy should Artikel the following:
- Break Duration: Specify the minimum and maximum break durations allowed.
- Break Frequency: Define the frequency of breaks required, such as a 15-minute break every 2 hours.
- Break Procedures: Artikel the procedures for requesting and taking breaks, including notification requirements.
- Break Area: Indicate designated break areas and any restrictions or guidelines.
Conclusion: Are 15 Minute Breaks Required By Law
Navigating the legal requirements for breaks can seem complex, but understanding the basics is essential for both employees and employers. By ensuring compliance with federal and state laws, companies can foster a productive and safe work environment, while employees can advocate for their rights to appropriate rest and breaks. Remember, a well-defined break policy is not just a legal obligation but also a key factor in employee satisfaction, performance, and overall well-being.
Query Resolution
Are there any exceptions to the break requirements?
Yes, there are some exceptions. For example, employees who work short shifts or in certain exempt positions may not be subject to the same break requirements.
What if my employer doesn’t provide breaks?
If your employer fails to provide legally required breaks, you may have grounds to file a complaint with the Department of Labor or your state labor agency.
Can my employer require me to work during my break?
No, generally speaking, your employer cannot require you to work during a legally mandated break.