
- Eligibility for Health Insurance
- Applying for Health Insurance
- Health Insurance Options
- Understanding Health Insurance Terms: Can I Apply For Health Insurance
- Navigating Health Insurance Coverage
- Health Insurance Costs and Budgeting
- Open Enrollment and Special Enrollment Periods
- Health Insurance Resources and Support
- Ultimate Conclusion
- Key Questions Answered
Can I apply for health insurance sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like a labyrinth, but understanding the basics and your options can empower you to make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
This guide will walk you through the process of applying for health insurance, exploring eligibility criteria, available plans, and crucial terms to understand. Whether you’re an individual seeking coverage, a family needing comprehensive protection, or an employer looking for options for your employees, this resource provides valuable insights to guide your journey.
Eligibility for Health Insurance
Eligibility for health insurance is determined by a variety of factors, including your age, residency, employment status, and pre-existing conditions. Understanding these factors can help you determine which plans you qualify for and what your options are.
Factors Determining Eligibility
Several factors influence your eligibility for health insurance.
- Age: Most health insurance plans are available to individuals of all ages, but some plans may have specific age requirements. For example, Medicare, the federal health insurance program for people aged 65 and older, is only available to those who meet certain age requirements.
- Residency: Health insurance plans are typically offered within specific geographic areas. You must reside in the coverage area to be eligible for a plan. For example, you cannot enroll in a health insurance plan offered in California if you live in New York.
- Employment Status: Your employment status can significantly impact your health insurance options. Many employers offer health insurance plans to their employees, but these plans are only available to those who work for the employer. If you are self-employed, you may be eligible for individual health insurance plans.
- Pre-Existing Conditions: In the United States, health insurance plans cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. However, some plans may have waiting periods before coverage for certain conditions takes effect. This means you might have to pay out-of-pocket for treatment for a pre-existing condition for a specified period before the plan covers it.
Common Eligibility Requirements
Here are some examples of common eligibility requirements for different types of health insurance plans:
- Employer-Sponsored Plans: Eligibility for employer-sponsored health insurance plans is usually determined by your employment status and the employer’s specific plan requirements. You must be an employee of the company offering the plan and meet any additional requirements set by the employer.
- Individual Health Insurance Plans: Individual health insurance plans are available to individuals who are not covered by an employer-sponsored plan. Eligibility for these plans typically depends on your residency, age, and income.
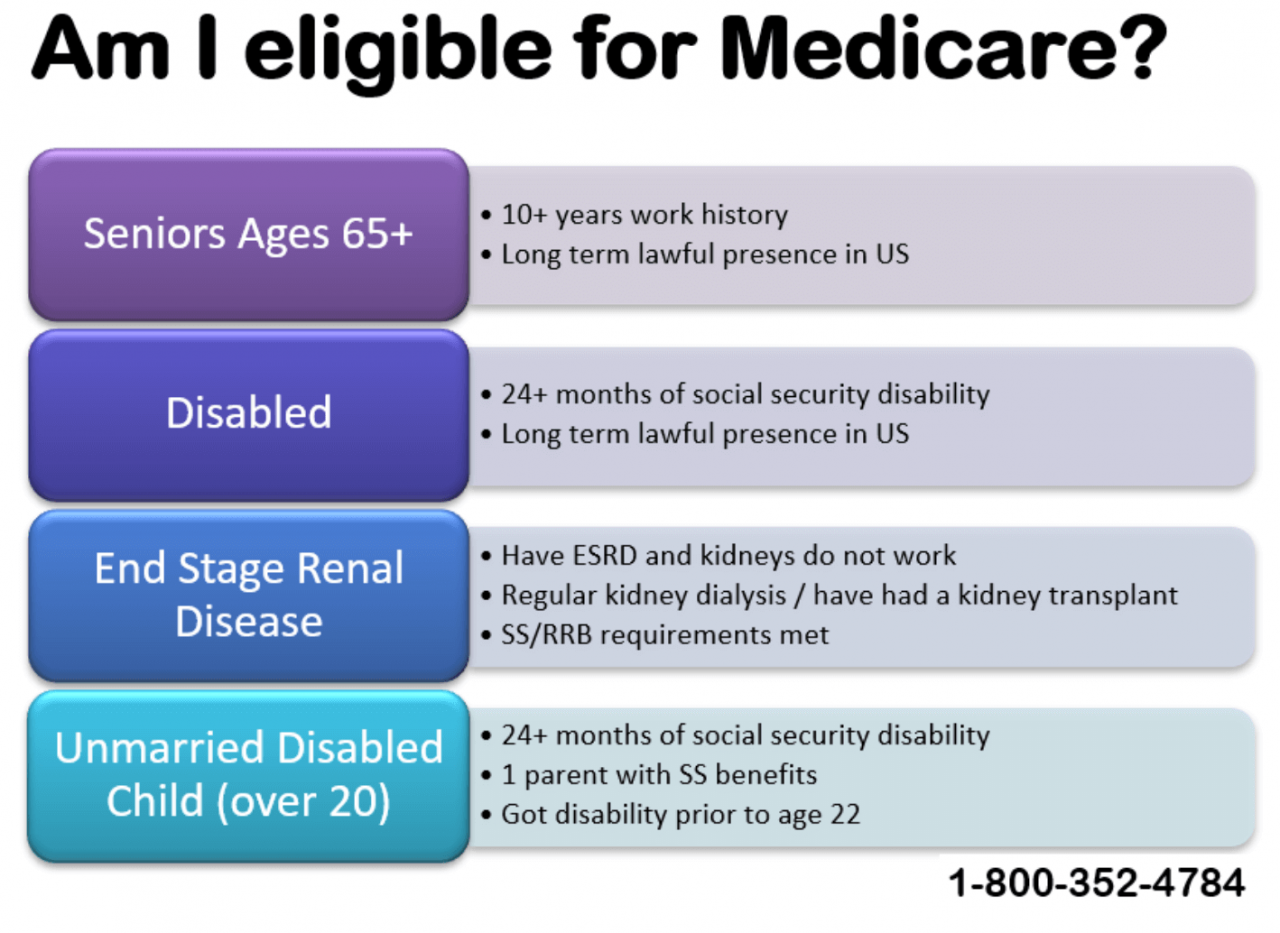
- Medicare: Medicare is a federal health insurance program available to individuals aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with certain disabilities.
- Medicaid: Medicaid is a state-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. Eligibility for Medicaid is determined by income and other factors, such as family size and disability status.
Eligibility Criteria for Major Health Insurance Providers
The following table Artikels the key eligibility criteria for major health insurance providers in the United States:
| Provider | Age | Residency | Employment Status | Pre-Existing Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue Cross Blue Shield | All ages | Specific geographic areas | Individuals and families | Covered |
| UnitedHealthcare | All ages | Specific geographic areas | Individuals and families | Covered |
| Aetna | All ages | Specific geographic areas | Individuals and families | Covered |
| Cigna | All ages | Specific geographic areas | Individuals and families | Covered |
Applying for Health Insurance
Applying for health insurance can seem overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. The process is straightforward, and many resources are available to help you navigate the steps.
Typical Application Process
The application process for health insurance typically involves providing personal information, health history, and coverage preferences. You can apply online, by phone, or through a broker or agent.
- Online Application: Many insurance companies have user-friendly online portals where you can submit your application. You’ll typically be asked to create an account and then provide your personal information, health history, and coverage preferences.
- Phone Application: You can also apply for health insurance by phone. You’ll be guided through the application process by a representative, who will ask you questions about your personal information, health history, and coverage preferences.
- Broker or Agent: A broker or agent can help you navigate the application process and find the best insurance plan for your needs. They can also assist you with filling out the application form and understanding the terms of your policy.
Required Documents
When applying for health insurance, you’ll typically need to provide the following documents:
- Proof of Identity: This can include your driver’s license, passport, or birth certificate.
- Social Security Number: Your Social Security number is required for the insurance company to verify your identity and eligibility for coverage.
- Proof of Residency: This can include a utility bill, bank statement, or lease agreement.
- Employment Information: If you’re employed, you’ll need to provide information about your employer, including your employer’s name and address.
- Income Information: You’ll need to provide information about your income, including your annual salary or wages.
- Health History: You’ll need to provide information about your health history, including any pre-existing conditions.
Completing an Application Form
The application form for health insurance typically includes the following sections:
- Personal Information: This section will ask for your name, address, phone number, date of birth, and Social Security number.
- Health History: This section will ask about your health history, including any pre-existing conditions, current medications, and past surgeries.
- Coverage Preferences: This section will ask about your coverage preferences, including the type of plan you’re interested in, the deductible you’re willing to pay, and the co-pay you’re comfortable with.
Step-by-Step Guide for Applying Online
Here’s a step-by-step guide for applying for health insurance online:
- Choose an Insurance Company: Research different insurance companies and compare their plans and rates.
- Visit the Company’s Website: Once you’ve chosen an insurance company, visit their website and click on the “Apply for Health Insurance” or “Get a Quote” button.
- Create an Account: You’ll typically need to create an account with the insurance company to start the application process.
- Fill Out the Application Form: The application form will ask for your personal information, health history, and coverage preferences.
- Upload Required Documents: You’ll need to upload copies of your required documents, such as your driver’s license, Social Security card, and proof of residency.
- Review and Submit: Carefully review your application form and ensure all information is accurate and complete. Once you’re satisfied, submit your application.
Health Insurance Options
Choosing the right health insurance plan can be overwhelming, but it’s crucial to understand the various options available to find the best fit for your needs and budget. Different plans offer different levels of coverage, benefits, and costs, so it’s important to carefully compare and contrast them before making a decision.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
There are several types of health insurance plans available, each catering to different needs and situations. The most common types include:
- Individual Health Insurance: Purchased by individuals directly from insurance companies, this option offers flexibility but can be expensive.
- Family Health Insurance: Covers multiple family members under one plan, offering cost savings compared to individual plans but requiring careful consideration of family needs and coverage requirements.
- Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance: Offered by employers as a benefit to employees, this type typically provides more affordable coverage but may have limited plan choices and potentially higher premiums for dependents.
- Government-Funded Programs: Public health insurance programs like Medicare (for individuals aged 65 and older) and Medicaid (for low-income individuals and families) provide essential coverage with varying eligibility criteria and benefits.
Comparing Health Insurance Plans
To make an informed decision, it’s essential to compare the key characteristics of different health insurance plans, including:
- Coverage: The range of medical services and treatments covered by the plan, including preventive care, hospitalization, prescription drugs, and mental health services.
- Premiums: The monthly payments you make for health insurance coverage. Premiums vary based on factors like age, location, health status, and plan type.
- Deductibles: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible typically means lower premiums, but you’ll pay more upfront for medical expenses.
- Copayments: Fixed amounts you pay for specific services, such as doctor visits or prescriptions, even after meeting your deductible.
Health Insurance Plan Features and Benefits
Different health insurance plans offer various features and benefits, influencing their overall value and suitability.
- Network: The group of doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers that are contracted with your insurance company. Staying within your network generally results in lower out-of-pocket costs.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: The plan’s coverage for prescription medications, including formularies (lists of covered drugs) and copayments.
- Mental Health Coverage: The availability and extent of coverage for mental health services, including therapy, medication, and inpatient care.
- Wellness Programs: Programs offered by insurance companies to encourage healthy habits and preventative care, potentially reducing healthcare costs in the long run.
Key Characteristics of Different Health Insurance Options
The following table summarizes the key characteristics of different health insurance options:
| Health Insurance Option | Coverage | Premiums | Deductibles | Copayments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Health Insurance | Wide range of plans with varying coverage levels | Typically higher than employer-sponsored plans | Variable, depending on plan | Variable, depending on plan |
| Family Health Insurance | Covers multiple family members under one plan | Higher than individual plans but often cheaper per person | Variable, depending on plan | Variable, depending on plan |
| Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance | Typically offers comprehensive coverage | Often lower than individual plans | Variable, depending on plan | Variable, depending on plan |
| Government-Funded Programs (Medicare/Medicaid) | Essential coverage for eligible individuals | Varying premiums and cost-sharing based on program and eligibility | Variable, depending on program | Variable, depending on program |
Understanding Health Insurance Terms: Can I Apply For Health Insurance
Navigating the world of health insurance can be confusing, especially with the numerous terms and concepts involved. Understanding these terms is crucial to making informed decisions about your coverage and managing your healthcare costs effectively.
Common Health Insurance Terms
To understand how health insurance works, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with common terminology. Here are some key terms you’ll encounter:
- Premium: The monthly or annual amount you pay to your insurance company for your health insurance policy. Think of it as a recurring payment for the coverage you’re receiving.
- Deductible: The amount you must pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services before your insurance coverage kicks in. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, you’ll pay the first $1,000 of your healthcare costs yourself. Once you’ve reached the deductible, your insurance will start covering the remaining costs.
- Copayment: A fixed amount you pay for a specific healthcare service, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription. Copayments are usually a set amount, regardless of the total cost of the service.
- Coinsurance: A percentage of the cost of healthcare services that you pay after your deductible has been met. For instance, if your coinsurance is 20%, you’ll pay 20% of the cost of covered services after your deductible is satisfied, and your insurance company will cover the remaining 80%.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The maximum amount you’ll have to pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services in a year. Once you’ve reached this limit, your insurance company will cover 100% of the remaining costs for the rest of the year.
Examples of How Terms Affect Healthcare Costs
Let’s illustrate how these terms can impact your healthcare expenses:
Imagine you have a health insurance plan with a $1,000 deductible, a $20 copayment for doctor’s visits, a 20% coinsurance, and an out-of-pocket maximum of $5,000.
You visit a doctor for a routine checkup. The cost of the visit is $150. Since your deductible is $1,000, you’ll pay the entire $150 out-of-pocket.
Now, let’s say you need a medical procedure that costs $5,000. After paying your $1,000 deductible, you’ll be responsible for 20% of the remaining $4,000, which is $800. Your insurance company will cover the remaining $3,200.
In this scenario, your total out-of-pocket costs for the year are $1,800 ($150 for the checkup + $1,000 deductible + $800 coinsurance).
If you were to have more extensive healthcare needs that year, your out-of-pocket costs would continue to rise until you reach your out-of-pocket maximum of $5,000. Once you hit that limit, your insurance would cover all remaining healthcare costs for the year.
Glossary of Key Health Insurance Terms
Here’s a quick glossary of key health insurance terms and their definitions:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Premium | The monthly or annual payment you make for your health insurance policy. |
| Deductible | The amount you must pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services before your insurance coverage begins. |
| Copayment | A fixed amount you pay for specific healthcare services, such as a doctor’s visit or prescription. |
| Coinsurance | A percentage of the cost of healthcare services that you pay after your deductible is met. |
| Out-of-Pocket Maximum | The maximum amount you’ll have to pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services in a year. |
| Benefits | The specific healthcare services covered by your insurance plan. |
| Network | A group of healthcare providers (doctors, hospitals, etc.) that have agreed to provide services at a discounted rate to members of your insurance plan. |
| Formulary | A list of prescription drugs covered by your insurance plan. |
Navigating Health Insurance Coverage
Once you have health insurance, understanding how to utilize its benefits is crucial. This includes recognizing coverage limitations, accessing healthcare providers within your network, and filing claims for reimbursement.
Understanding Coverage Limitations
Every health insurance plan has limitations. These can include:
- Pre-existing Conditions: Some plans may have restrictions on coverage for conditions you had before enrolling.
- Annual Limits: Plans may have limits on the total amount of coverage you can receive in a year.
- Co-pays and Deductibles: You may be required to pay a certain amount for each service you use (co-pay) or a set amount before your insurance starts covering costs (deductible).
- Network Restrictions: You may only be able to access healthcare providers within your plan’s network.
Accessing Healthcare Providers
To access healthcare providers within your network, you’ll typically need to:
- Contact your insurance company: Ask for a list of in-network doctors and hospitals.
- Use a provider directory: Most insurance companies have online directories where you can search for providers by specialty, location, and other criteria.
- Confirm with your provider: Before making an appointment, verify that the provider is in your network and accepts your insurance.
Filing Claims for Reimbursement, Can i apply for health insurance
When you receive healthcare services, you’ll need to file a claim with your insurance company to receive reimbursement.
- Gather your documentation: This typically includes your insurance card, a copy of the medical bill, and any other relevant paperwork.
- Submit your claim: You can file claims online, by mail, or by phone.
- Track your claim: Most insurance companies have online portals where you can check the status of your claim.
Common Healthcare Services Covered
Most health insurance plans cover essential healthcare services, including:
- Preventive care: This includes annual checkups, screenings, and vaccinations.
- Emergency care: Coverage for urgent medical situations.
- Hospitalization: Inpatient care, surgery, and other treatments provided in a hospital.
- Prescription drugs: Coverage for medications prescribed by a doctor.
- Mental health services: Therapy, counseling, and other mental health treatments.
Seeking Healthcare Services and Submitting Claims
The following flow chart illustrates the typical process of seeking healthcare services and submitting claims for reimbursement:
[Flowchart image description]
Seek Healthcare Services
- Identify Need: Determine if you need medical attention.
- Contact Provider: Choose an in-network provider and schedule an appointment.
- Receive Services: Obtain medical treatment or consultation.
Submit Claim for Reimbursement
- Gather Documentation: Collect insurance card, medical bills, and other relevant paperwork.
- File Claim: Submit claim online, by mail, or by phone.
- Track Claim: Monitor the status of your claim through the insurance company’s portal.
- Receive Payment: Insurance company processes the claim and reimburses you for covered services.
Health Insurance Costs and Budgeting
Understanding the cost of health insurance is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage. Several factors influence your health insurance premiums, and there are strategies you can use to minimize these costs.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
Several factors play a significant role in determining your health insurance premiums. These include:
- Age: Generally, older individuals tend to have higher premiums due to a greater likelihood of needing healthcare services.
- Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions often face higher premiums because they are considered higher risk.
- Coverage Level: Plans with comprehensive coverage, including extensive benefits and lower deductibles, typically have higher premiums compared to plans with limited coverage.
- Location: Premiums can vary depending on the geographical location, with higher costs often found in areas with a higher cost of living and denser populations.
Minimizing Health Insurance Costs
While health insurance costs can be significant, there are strategies to help you minimize expenses:
- Explore Different Plans: Compare premiums and benefits across various insurance providers and plans to find the most cost-effective option that meets your needs.
- Negotiate Rates: Consider negotiating with your insurance provider for a lower premium, especially if you have a good payment history or are willing to accept a higher deductible.
- Maximize Benefits: Utilize all available benefits and discounts offered by your insurance plan, such as preventive care services, wellness programs, and prescription drug discounts.
Average Annual Health Insurance Premiums
Here is a table outlining the estimated average annual premiums for various health insurance plans in the United States, based on data from the Kaiser Family Foundation:
| Plan Type | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| Individual Marketplace Plans | $5,100 |
| Employer-Sponsored Plans | $7,739 |
| Medicare Part B (Monthly Premium) | $170.10 |
Note: These premiums are estimates and may vary based on individual factors, such as age, health status, and location.
Open Enrollment and Special Enrollment Periods
Open enrollment and special enrollment periods are crucial times to apply for health insurance. These periods offer specific windows of opportunity to enroll in or change your health insurance plan. Understanding these periods is essential for securing the coverage you need.
Open Enrollment Periods
Open enrollment is a designated time frame when individuals can apply for health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace or directly from insurance companies. It is a standard period for everyone, regardless of life changes. During open enrollment, you can:
- Enroll in a health insurance plan for the first time.
- Change your existing health insurance plan.
- Drop your existing health insurance plan.
Special Enrollment Periods
Special enrollment periods are exceptions to the standard open enrollment period. These periods allow individuals to apply for health insurance outside the regular open enrollment window due to specific life events. These events include:
- Losing health insurance coverage due to job loss or a change in employment status.
- Getting married or divorced.
- Having a baby or adopting a child.
- Moving to a new state or county.
- Experiencing a change in income.
Open Enrollment and Special Enrollment Periods Timeline
| Period | Dates | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Open Enrollment | November 1 – January 15 | Standard period for applying for or changing health insurance plans. |
| Special Enrollment Period | Variable | Applies to individuals experiencing specific life events, allowing them to enroll in or change health insurance plans outside the open enrollment period. |
Health Insurance Resources and Support
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel overwhelming, but you don’t have to go it alone. There are numerous resources available to help you understand your options, apply for coverage, and find financial assistance.
Reputable Websites and Organizations
These websites and organizations offer valuable information and assistance regarding health insurance:
- HealthCare.gov: The official website for the Affordable Care Act (ACA), providing information on plans, eligibility, and enrollment.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): The federal agency responsible for administering Medicare and Medicaid, offering resources and information on both programs.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): A non-profit organization representing state insurance regulators, providing consumer information and resources on insurance topics, including health insurance.
- Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF): A non-profit organization that conducts research and provides information on health policy, including health insurance coverage and costs.
- Consumer Reports: A non-profit organization that provides independent testing and reviews of products and services, including health insurance plans.
Local Health Insurance Agencies and Government Programs
Local health insurance agencies and government programs can provide personalized assistance and guidance:
- State Insurance Departments: Each state has an insurance department that regulates insurance companies and provides consumer protection resources.
- Local Health Insurance Brokers: Independent insurance brokers can help you compare plans and find the best coverage for your needs.
- Community Health Centers: These centers offer affordable healthcare services and may provide assistance with applying for health insurance.
- Medicaid Offices: Each state has a Medicaid office that administers the program and can help you determine your eligibility.
Financial Assistance and Subsidies
The Affordable Care Act offers financial assistance to help individuals and families afford health insurance:
- Premium Tax Credits: These tax credits are available to individuals and families who meet certain income requirements and purchase insurance through the Marketplace. The credit reduces the monthly cost of your health insurance premiums.
- Cost-Sharing Reductions: These subsidies help lower the cost of deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance for individuals and families who qualify.
- Medicaid: A government-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families, providing comprehensive health coverage.
- CHIP (Children’s Health Insurance Program): A government-funded program that provides health insurance to children in families that meet certain income requirements.
Ultimate Conclusion

As you embark on your health insurance journey, remember that knowledge is power. Understanding the intricacies of eligibility, application processes, and plan options empowers you to make choices that align with your individual needs and financial situation. By taking the time to research, compare, and explore available resources, you can navigate the world of health insurance with confidence and find a plan that provides peace of mind and protects your health.
Key Questions Answered
How do I know if I qualify for government-funded health insurance?
Eligibility for government-funded programs like Medicare or Medicaid varies based on factors such as age, income, and disability status. You can visit the official websites of these programs or contact your local health insurance agency for specific eligibility requirements.
What happens if I have a pre-existing condition?
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits health insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. However, some plans may have limitations or waiting periods for certain conditions.
What are the best resources for finding affordable health insurance?
Websites like HealthCare.gov and your state’s health insurance marketplace offer comprehensive resources and tools to compare plans, estimate costs, and apply for financial assistance.





