Can t afford health insurance – Can’t afford health insurance? You’re not alone. The rising cost of healthcare in the United States is a major concern for millions of Americans. This issue is not just about numbers; it’s about real people struggling to access the care they need. This article explores the factors driving this crisis, the impact on individuals and families, and potential solutions to make healthcare more affordable.
From soaring prescription drug prices to the increasing cost of medical procedures, the cost of healthcare has been steadily rising for decades. This rise is fueled by a complex interplay of factors, including technological advancements, administrative inefficiencies, and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases. As healthcare costs continue to climb, many Americans are finding it increasingly difficult to afford the coverage they need.
The Rising Cost of Healthcare

The cost of healthcare in the United States has been steadily increasing for decades, posing a significant challenge to individuals and families. This upward trend has raised concerns about affordability and accessibility, prompting discussions about the factors contributing to this phenomenon.
Factors Contributing to Rising Healthcare Costs
The rising cost of healthcare in the United States is a complex issue influenced by various factors.
- Administrative Costs: The US healthcare system is highly complex, with a significant portion of spending allocated to administrative tasks such as billing, insurance processing, and paperwork. This administrative burden contributes to the overall cost of healthcare.
- Technology Advancements: While technological advancements in medicine have led to improved treatments and diagnostics, they also come with higher costs. New technologies require investments in infrastructure, training, and maintenance, adding to the overall healthcare expenditure.
- Aging Population: The United States is experiencing an aging population, with a growing number of individuals over 65 years old. This demographic shift leads to increased demand for healthcare services, including chronic disease management and long-term care, contributing to higher costs.
- Prescription Drug Costs: The cost of prescription drugs has been rising steadily, driven by factors such as research and development costs, patent protection, and marketing expenses. The high cost of prescription drugs is a significant contributor to the overall healthcare expenditure.
- Defensive Medicine: Physicians may order more tests and procedures than necessary to protect themselves from potential lawsuits. This practice, known as defensive medicine, adds to the cost of healthcare without necessarily improving patient outcomes.
- Lack of Price Transparency: The lack of price transparency in healthcare makes it difficult for patients to compare costs and make informed decisions about their care. This opaqueness can lead to higher prices and less competition in the market.
Impact of Inflation on Healthcare Costs
Inflation has a significant impact on healthcare costs, making it more challenging for individuals and families to afford necessary medical care.
- Increased Costs of Supplies and Services: Inflation drives up the cost of medical supplies, equipment, and services, directly impacting the overall healthcare expenditure.
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of individuals, making it harder to afford healthcare expenses even if their incomes remain unchanged.
- Higher Insurance Premiums: Insurance companies often adjust their premiums to reflect rising healthcare costs, leading to higher out-of-pocket expenses for individuals.
Cost of Healthcare in the United States Compared to Other Developed Nations
The United States spends significantly more on healthcare than other developed nations, yet its health outcomes are not consistently better.
- Higher Spending per Capita: The US spends more on healthcare per capita than any other developed country, according to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Lower Life Expectancy: Despite higher healthcare spending, the United States has a lower life expectancy than many other developed nations, indicating potential inefficiencies in the healthcare system.
- Higher Rates of Chronic Diseases: The US has higher rates of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity compared to other developed countries, contributing to higher healthcare costs.
Understanding Health Insurance Options
Navigating the world of health insurance can be confusing, especially when you’re on a tight budget. There are numerous plans available, each with its own set of benefits, costs, and limitations. Understanding these options is crucial to making an informed decision about the right coverage for your needs and budget.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
There are several common types of health insurance plans, each with its own set of features and costs. Understanding these differences can help you choose a plan that best suits your individual circumstances.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs typically offer lower premiums than other plans, but they require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the HMO network. You must get referrals from your PCP to see specialists. HMOs generally have lower out-of-pocket costs than other plans, but they offer limited coverage for care received outside the network.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to see any doctor or specialist within the PPO network without a referral. PPOs typically have higher premiums than HMOs, but they offer more coverage for out-of-network care.
- High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs): HDHPs have lower premiums than traditional plans, but they have a higher deductible. This means you pay a larger amount out-of-pocket before the insurance kicks in. HDHPs are often coupled with a Health Savings Account (HSA), which allows you to save pre-tax dollars for medical expenses.
Comparing Plan Benefits and Drawbacks
The best type of health insurance plan for you depends on your individual needs and circumstances. Here’s a comparison of the benefits and drawbacks of each type of plan, with an emphasis on affordability:
| Plan Type | Benefits | Drawbacks | Affordability |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | Lower premiums, lower out-of-pocket costs, good for preventive care | Limited network, need referrals, limited out-of-network coverage | Generally affordable, but may not cover all needs |
| PPO | More flexibility, wider network, more out-of-network coverage | Higher premiums, higher out-of-pocket costs | May be less affordable than HMOs, but offers more flexibility |
| HDHP | Lower premiums, tax-advantaged savings account (HSA) | Higher deductible, high out-of-pocket costs until deductible is met | Potentially affordable with HSA contributions, but may require significant upfront costs |
Government-Sponsored Programs
Government-sponsored programs like Medicare and Medicaid provide health insurance coverage to specific populations.
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for people aged 65 and older, as well as individuals with certain disabilities.
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to low-income individuals and families.
These programs can be essential for individuals who might not be able to afford private health insurance.
The Impact of Unaffordable Healthcare
The inability to afford healthcare has far-reaching consequences, affecting individuals, families, and communities. It creates a vicious cycle of poor health, financial instability, and limited opportunities.
Real-Life Stories of Healthcare Struggles
The impact of unaffordable healthcare is not just a statistic; it is a reality for millions of people. Stories of individuals and families struggling to access essential medical care are commonplace.
- A single mother working two minimum wage jobs cannot afford health insurance for herself and her child. When her child develops a chronic illness, she is forced to choose between paying rent and medical bills, putting her family at risk of homelessness.
- A young man with a pre-existing condition is denied coverage by insurance companies, leaving him with limited options for treatment and facing mounting medical debt.
- A senior citizen on a fixed income struggles to afford prescription drugs, forcing her to choose between filling her prescriptions and buying groceries.
Consequences of Delaying or Forgoing Medical Treatment
When people cannot afford healthcare, they often delay or forgo necessary medical treatment, leading to serious consequences.
- Exacerbation of Existing Conditions: Delaying treatment for chronic conditions like diabetes, asthma, or heart disease can lead to complications, hospitalizations, and even death.
- Emergent Situations: Avoiding routine checkups and preventive care can result in conditions being diagnosed at later stages, when treatment is more complex and expensive. This can lead to emergency room visits and hospitalizations, which are often significantly more costly.
- Missed Work and Productivity: Untreated health conditions can impact an individual’s ability to work, leading to lost wages and decreased productivity.
Health and Financial Risks of Lacking Health Insurance
The lack of health insurance can have significant health and financial risks for individuals and families.
- Medical Debt: Uninsured individuals are often left with substantial medical bills, which can lead to bankruptcy, foreclosure, and other financial hardships.
- Limited Access to Care: Without insurance, individuals may face difficulty finding doctors and hospitals willing to provide care, particularly for specialized treatments.
- Preventive Care Gaps: Insurance often covers preventive services, such as screenings and vaccinations, which can help identify and prevent health problems. Without insurance, these services may be inaccessible, increasing the risk of developing serious health issues.
Solutions and Strategies for Affordability
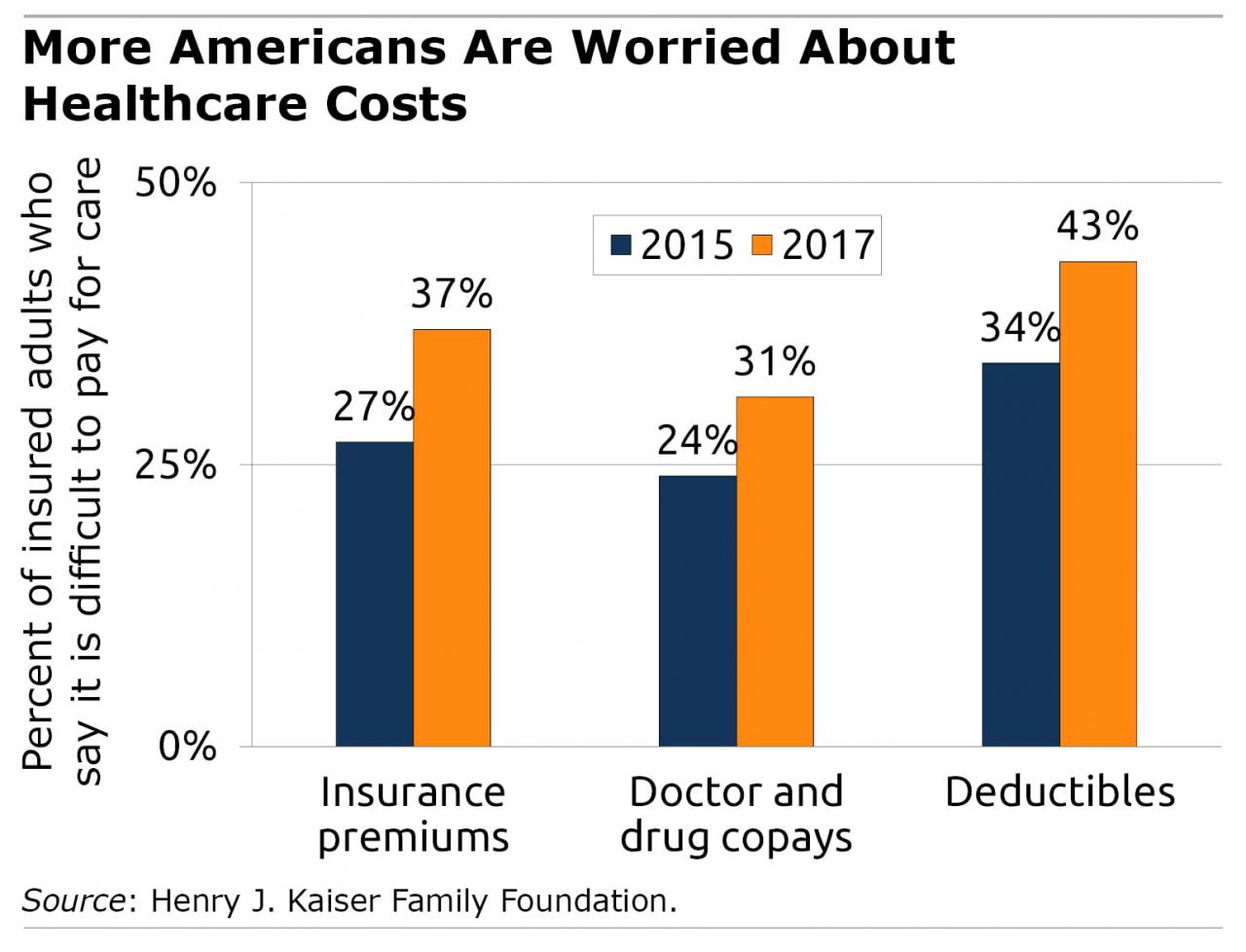
The high cost of healthcare is a significant concern for many Americans, leading to financial strain and delayed or forgone care. Fortunately, various solutions and strategies exist to address affordability, aiming to make healthcare more accessible and manageable. These solutions involve a multi-pronged approach, encompassing government initiatives, individual actions, and employer involvement.
Government Initiatives to Lower Costs, Can t afford health insurance
Government initiatives play a crucial role in addressing healthcare affordability. These initiatives aim to control costs, expand access, and provide financial assistance to individuals and families.
- Negotiating Drug Prices: The government can leverage its purchasing power to negotiate lower prices for prescription drugs, particularly for commonly used medications. This can significantly reduce healthcare costs for individuals and families.
- Expanding Access to Generic Medications: Encouraging the use of generic medications, which are typically significantly cheaper than brand-name drugs, can save individuals and the healthcare system substantial amounts of money. This can be achieved through various measures, such as streamlining the approval process for generic drugs and promoting public awareness of their efficacy and safety.
- Increasing Government Subsidies: Expanding government subsidies for healthcare, such as those offered through programs like Medicaid and the Affordable Care Act (ACA), can help individuals and families afford health insurance premiums and out-of-pocket costs. This can ensure that essential healthcare services are accessible to all, regardless of income level.
Individual Strategies for Managing Healthcare Costs
Individuals can take proactive steps to manage their healthcare costs and make informed decisions about their health.
- Utilizing Preventive Care: Engaging in preventive care, such as regular checkups, screenings, and vaccinations, can help individuals identify health issues early, preventing potential complications and costly treatments later. Preventive care is often covered by insurance plans, making it a cost-effective way to manage health.
- Seeking Affordable Healthcare Providers: Individuals can research and choose affordable healthcare providers, such as community health centers or clinics that offer sliding-scale fees based on income. Additionally, utilizing telehealth services, which offer virtual consultations and remote monitoring, can be a cost-effective alternative to traditional in-person care.
- Negotiating Medical Bills: Individuals can negotiate medical bills with healthcare providers and insurance companies. This may involve seeking a payment plan, appealing denied claims, or negotiating a lower price for services. It is important to be prepared with relevant documentation and to understand the terms of insurance coverage.
Employer Involvement in Affordable Health Insurance
Employers play a vital role in ensuring their employees have access to affordable health insurance.
- Offering Affordable Health Insurance Plans: Employers can offer affordable health insurance plans to their employees, potentially contributing a significant portion of the premium costs. This can help employees manage healthcare expenses and attract and retain talent.
- Promoting Health and Wellness Programs: Employers can promote health and wellness programs to their employees, encouraging healthy habits and reducing the likelihood of developing chronic health conditions. These programs can include fitness classes, nutrition counseling, and smoking cessation support, ultimately reducing healthcare costs for both employees and employers.
The Importance of Advocacy and Policy Change
The rising cost of healthcare is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. While individual efforts to manage healthcare expenses are important, systemic change is necessary to make healthcare affordable for everyone. Advocating for policy changes that address the root causes of high healthcare costs is crucial to ensure a more equitable and accessible healthcare system.
Key Stakeholders in Healthcare Policy
Various stakeholders play a significant role in shaping healthcare policy, each with their own perspectives and interests. Understanding these perspectives is essential for effective advocacy.
- Government Agencies: Federal and state agencies, such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and state health departments, are responsible for administering healthcare programs, setting regulations, and allocating funding. They have a direct impact on healthcare affordability through programs like Medicaid and Medicare.
- Healthcare Providers: Hospitals, clinics, doctors, and other healthcare providers are directly involved in delivering care. Their costs, including staffing, technology, and infrastructure, influence overall healthcare expenses. Advocacy efforts should consider the challenges faced by providers in delivering quality care while managing costs.
- Insurance Companies: Private insurance companies play a critical role in providing health coverage. Their pricing models, network design, and administrative costs impact affordability. Advocacy efforts should address concerns regarding insurance company practices that contribute to high premiums and limited access to care.
- Pharmaceutical Companies: Drug manufacturers develop and market medications, and their pricing practices significantly influence healthcare costs. Advocacy should address concerns regarding high drug prices and explore solutions to make essential medications more affordable.
- Consumer Advocacy Groups: Organizations dedicated to protecting the rights and interests of consumers, including those with limited access to healthcare, play a vital role in advocating for policy changes that promote affordability and access.
Potential Policy Solutions
Advocacy efforts should focus on promoting policy solutions that address the root causes of healthcare affordability challenges.
- Expanding Access to Medicaid: Medicaid is a government-funded health insurance program for low-income individuals and families. Expanding eligibility criteria for Medicaid would provide coverage to more people who are currently uninsured or underinsured, improving access to affordable care.
- Creating a Public Option for Health Insurance: A public option would provide a government-run health insurance plan that competes with private insurance companies. This would increase competition and potentially drive down costs for consumers.
- Reforming the Healthcare System: Systemic changes, such as negotiating drug prices, controlling administrative costs, and promoting preventive care, could significantly impact healthcare affordability. Advocacy should focus on implementing reforms that reduce unnecessary spending and improve efficiency.
- Addressing Social Determinants of Health: Factors like poverty, lack of education, and limited access to healthy food and housing contribute to poor health outcomes and higher healthcare costs. Advocacy should address these social determinants of health to create a more equitable healthcare system.
Closing Summary: Can T Afford Health Insurance

The inability to afford health insurance has far-reaching consequences. It can lead to delayed or forgone medical care, resulting in poorer health outcomes and increased financial burdens. Ultimately, addressing the affordability crisis requires a multifaceted approach that involves both individual strategies and policy changes. By advocating for reforms that promote cost transparency, expand access to affordable coverage, and incentivize preventive care, we can work towards a healthcare system that is accessible and affordable for all.
Expert Answers
What are some common reasons why people can’t afford health insurance?
High premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs can make health insurance unaffordable for many. Individuals with low incomes or unstable employment may also struggle to afford coverage.
What are some resources available for people who can’t afford health insurance?
Government-sponsored programs like Medicaid and the Affordable Care Act marketplace offer subsidies and financial assistance to make coverage more affordable. Some states also have their own programs to help low-income residents access healthcare.
What are some strategies for managing healthcare costs?
Negotiate medical bills, utilize preventive care, seek affordable healthcare providers, and consider generic medications to help control costs. It’s also important to understand your insurance plan and benefits.





