- Eligibility for Medicare
- Medicare Coverage and Limitations
- Private Health Insurance
- Private Health Insurance for Permanent Residents
- Accessing Healthcare Services
- Government Subsidies and Incentives: Do Permanent Residents Need Private Health Insurance In Australia
- Ultimate Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Do permanent residents need private health insurance in Australia? This question is often pondered by individuals seeking a new life Down Under. While Medicare, Australia’s universal healthcare system, provides essential coverage, understanding its limitations and the role of private health insurance is crucial for navigating the healthcare landscape.
Permanent residents in Australia are eligible for Medicare, which covers a wide range of healthcare services. However, there are certain limitations to Medicare coverage, such as out-of-pocket expenses and waiting times for specialist consultations and elective surgeries. This is where private health insurance comes into play, offering additional benefits and potentially faster access to healthcare.
Eligibility for Medicare
Permanent residents in Australia are eligible for Medicare, the country’s universal healthcare system. This means they can access a wide range of essential medical services at a subsidized cost. However, there are specific criteria and waiting periods that permanent residents need to meet before they can access Medicare benefits.
Waiting Period for Medicare Benefits
Permanent residents must wait for a specific period before they can access Medicare benefits. This waiting period is designed to ensure that the healthcare system is not overwhelmed by newly arrived residents. The waiting period for accessing Medicare benefits is two months from the date of becoming a permanent resident. This waiting period applies to most Medicare benefits, including doctor’s visits, hospital stays, and some medications.
Requirements for Obtaining a Medicare Card, Do permanent residents need private health insurance in australia
To obtain a Medicare card, permanent residents must meet certain requirements. These requirements are:
- Proof of permanent residency status. This can be a permanent resident visa or a passport with a permanent resident stamp.
- A valid Australian address. This can be a residential address, a postal address, or a business address.
- A unique Medicare number. This number is assigned to each individual and is used to identify them when accessing Medicare services.
Permanent residents can apply for a Medicare card online, by phone, or in person at a Medicare office.
Medicare Coverage and Limitations
Medicare, Australia’s universal healthcare system, provides essential healthcare services to permanent residents. While it offers significant benefits, it’s crucial to understand its coverage limitations and potential out-of-pocket expenses.
Medicare Coverage for Permanent Residents
Medicare covers a wide range of healthcare services, including:
- Doctor consultations: Medicare covers a portion of the cost of consultations with general practitioners (GPs) and specialists.
- Hospital treatment: Medicare covers the cost of most hospital services, including inpatient care, surgeries, and emergency room visits.
- Diagnostic tests: Medicare covers a range of diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, X-rays, and ultrasounds.
- Mental health services: Medicare covers consultations with psychiatrists and psychologists.
- Prescription medications: Medicare provides a subsidy for a limited number of prescription medications.
Limitations of Medicare Coverage
Medicare is not a complete insurance plan and has limitations:
- Out-of-pocket expenses: Medicare does not cover all healthcare costs. Patients may have to pay a co-payment or gap fee for certain services. For example, there may be a gap between the Medicare rebate and the doctor’s fee.
- Waiting times: Depending on the service and location, there can be waiting times for elective surgeries and specialist appointments.
- Limited coverage for certain services: Medicare does not fully cover all healthcare services. For example, it may not cover alternative therapies, dental care, or some vision care.
Common Healthcare Services Not Fully Covered by Medicare
While Medicare provides substantial coverage, some healthcare services are not fully covered:
- Dental care: Medicare only covers a limited range of dental services, primarily for children and those with specific medical conditions. Most dental procedures require private health insurance or out-of-pocket payment.
- Physiotherapy: While Medicare provides a limited number of physiotherapy sessions, many patients require additional sessions for which they may need to pay out-of-pocket or use private health insurance.
- Optical care: Medicare covers a portion of the cost of eye tests and spectacles for children under 18. However, adults usually need to pay for most optical care out-of-pocket or through private health insurance.
- Alternative therapies: Medicare does not cover alternative therapies such as acupuncture, naturopathy, or homeopathy. These services are typically paid for out-of-pocket or through private health insurance.
Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance is an optional insurance policy in Australia that provides coverage for healthcare expenses not covered by Medicare, the public health insurance system. It offers a range of benefits, including access to private hospitals, shorter waiting times for elective surgeries, and coverage for a broader range of medical services.
Types of Private Health Insurance Policies
There are different types of private health insurance policies available in Australia, each with its own set of benefits and costs. The main types include:
- Hospital cover: This type of policy covers the costs of hospital stays, including accommodation, surgery, and other medical services. It is typically divided into different levels, with higher levels offering greater coverage and benefits.
- Extras cover: This policy covers the costs of medical services not covered by Medicare, such as dental, physiotherapy, and optical. It is often offered as an add-on to hospital cover, or as a standalone policy.
- Combined hospital and extras cover: This type of policy combines both hospital and extras cover, providing comprehensive coverage for a wide range of healthcare needs.
Benefits of Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance offers a number of benefits to policyholders, including:
- Access to private hospitals: Private health insurance provides access to private hospitals, which generally offer shorter waiting times for elective surgeries and a more comfortable environment.
- Shorter waiting times for elective surgeries: Private health insurance can significantly reduce waiting times for elective surgeries, allowing policyholders to receive treatment sooner.
- Coverage for a wider range of medical services: Private health insurance covers a wider range of medical services than Medicare, including dental, physiotherapy, and optical.
- Lower out-of-pocket expenses: Private health insurance can help reduce out-of-pocket expenses for healthcare, as it covers a portion of the costs.
- Tax benefits: Policyholders may be eligible for tax benefits for their private health insurance premiums.
Costs of Private Health Insurance
The cost of private health insurance varies depending on the type of policy, the level of cover, and the age and health of the policyholder.
- Premium costs: Private health insurance premiums are typically paid monthly or annually. The cost of premiums can vary significantly depending on the level of cover, the age of the policyholder, and the health of the policyholder.
- Excess payments: Some private health insurance policies have excess payments, which are the amount that the policyholder must pay towards the cost of their treatment before the insurance company starts paying. Excess payments can vary depending on the policy.
- Out-of-pocket expenses: Even with private health insurance, policyholders may still have to pay some out-of-pocket expenses for their healthcare, such as co-payments for services or for services not covered by their policy.
Private Health Insurance for Permanent Residents

While Medicare provides essential healthcare coverage for permanent residents in Australia, private health insurance can offer additional benefits and flexibility. Whether or not you need private health insurance as a permanent resident depends on several factors.
Factors Influencing the Need for Private Health Insurance
The decision to purchase private health insurance as a permanent resident involves weighing various factors, including your individual circumstances, health needs, and financial capabilities.
- Health Status and Pre-existing Conditions: If you have a pre-existing medical condition or require specialized healthcare, private health insurance can provide you with quicker access to treatments and specialists, potentially reducing waiting times.
- Desired Level of Healthcare: Private health insurance can offer access to private hospitals, a wider range of medical specialists, and potentially shorter waiting times for elective procedures.
- Financial Considerations: Private health insurance premiums can be a significant expense, so it’s crucial to assess your budget and compare different policies to find one that suits your needs and financial capabilities.
- Government Incentives: The Australian government offers incentives for individuals who take out private health insurance, such as tax rebates and discounts on premiums.
- Lifestyle and Family Needs: Your lifestyle and family needs can also influence your decision. For example, if you have a family with young children, you might consider private health insurance for additional coverage for their healthcare needs.
Situations Where Private Health Insurance May Be Beneficial
Private health insurance can be particularly beneficial for permanent residents in certain situations.
- Access to Private Hospitals: Private health insurance grants access to private hospitals, which generally offer shorter waiting times for elective procedures and a more personalized healthcare experience.
- Specialized Treatments and Procedures: Private health insurance can provide coverage for specialized treatments and procedures that may not be fully covered by Medicare.
- Dental and Optical Coverage: Private health insurance often includes dental and optical coverage, which are not covered by Medicare.
- Overseas Travel Coverage: Some private health insurance policies offer coverage for medical expenses incurred during overseas travel.
- Pre-existing Conditions: For individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, private health insurance can provide additional coverage and potentially faster access to treatment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance comes with both advantages and disadvantages, which you should consider before making a decision.
Advantages:
- Faster Access to Healthcare: Private health insurance can provide quicker access to medical specialists, treatments, and procedures compared to relying solely on Medicare.
- Choice of Healthcare Providers: Private health insurance allows you to choose from a wider range of healthcare providers, including private hospitals and specialists.
- Additional Coverage: Private health insurance often includes coverage for dental, optical, and other services not covered by Medicare.
- Government Incentives: The Australian government offers tax rebates and other incentives for individuals who hold private health insurance.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Private health insurance premiums can be a significant expense, especially for comprehensive policies.
- Waiting Periods: Some policies have waiting periods before certain benefits become available, such as for pre-existing conditions.
- Exclusions and Limitations: Private health insurance policies may have exclusions and limitations, so it’s crucial to carefully review the policy details before signing up.
Accessing Healthcare Services

As a permanent resident in Australia, you have access to a range of healthcare services, including those provided by Medicare and private health insurance. The process of accessing these services varies depending on whether you have private health insurance and the type of service you require.
Accessing Healthcare Services with Private Health Insurance
Having private health insurance in Australia can significantly enhance your access to healthcare services. It allows you to access a broader range of services, including specialist consultations, private hospitals, and elective surgeries, with potentially lower out-of-pocket costs.
Finding and Booking Appointments
To find and book appointments with healthcare providers, you can utilize the following methods:
- Private health insurance provider directory: Your private health insurance provider likely has a directory of healthcare providers within their network. This directory will often include details about the provider’s specializations, location, and contact information.
- Online booking platforms: Websites like HealthEngine or MyGov allow you to search for healthcare providers based on your location, specialization, and availability. These platforms often offer online booking options, making it convenient to schedule appointments.
- Word-of-mouth recommendations: Ask friends, family, or colleagues for recommendations on reputable healthcare providers in your area. This can provide valuable insights into the provider’s expertise and patient experience.
Accessing Healthcare Services without Private Health Insurance
Even without private health insurance, permanent residents in Australia can still access essential healthcare services through Medicare. Medicare covers a wide range of services, including GP visits, hospital admissions, and some essential medications.
Finding and Booking Appointments
To access healthcare services under Medicare, you can follow these steps:
- General Practitioner (GP): You can find a GP by searching online directories, such as the Australian Medical Association (AMA) website, or by asking for recommendations from friends or family. You can then contact the GP’s office to book an appointment.
- Public Hospitals: If you require emergency or specialized care, you can present yourself at a public hospital’s emergency department. You can also be referred to a public hospital by your GP for non-emergency procedures or consultations.
- Medicare-approved services: For certain services like physiotherapy or mental health counseling, you can search for Medicare-approved providers on the Medicare website or through online directories.
Cost Comparison
The table below Artikels the typical costs associated with accessing healthcare services with and without private health insurance in Australia:
| Service | With Private Health Insurance | Without Private Health Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| GP Consultation | Co-payment (usually $0-$50) | Medicare rebate (around $76.90) + gap payment (varies depending on the GP) |
| Hospital Admission | Private hospital cover (varies depending on policy) | Medicare rebate + out-of-pocket expenses (including co-payments and gap payments) |
| Elective Surgery | Private hospital cover (varies depending on policy) | Waiting list for public hospital (can be lengthy) + out-of-pocket expenses |
| Dental Care | Limited coverage (varies depending on policy) | Out-of-pocket expenses (can be substantial) |
| Mental Health Services | Limited coverage (varies depending on policy) | Medicare rebate + gap payment (varies depending on the provider) |
Note: The actual costs may vary depending on your specific health insurance policy, the provider’s fees, and other factors.
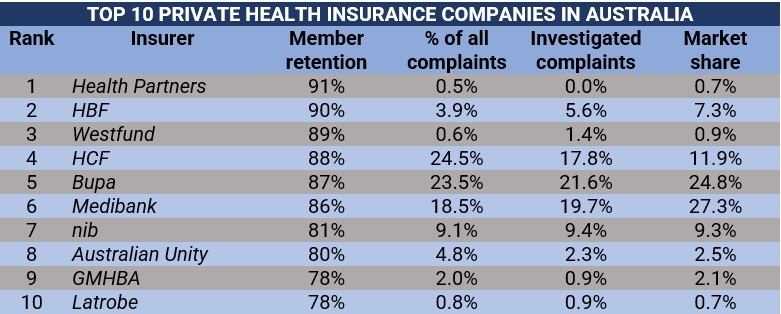
Government Subsidies and Incentives: Do Permanent Residents Need Private Health Insurance In Australia
The Australian government provides various subsidies and incentives to encourage Australians to take out private health insurance. These subsidies aim to make private health insurance more affordable and accessible, especially for those who are not covered by Medicare.
Eligibility for Government Subsidies
The eligibility criteria for receiving government subsidies for private health insurance are based on age, income, and family circumstances.
- Age: Individuals aged 30 years and over are eligible for government subsidies.
- Income: The amount of the subsidy is based on your taxable income. The higher your income, the smaller the subsidy you will receive.
- Family Circumstances: Individuals with a family, including dependants, may be eligible for higher subsidies.
Impact of Subsidies on Affordability
Government subsidies can significantly reduce the cost of private health insurance, making it more affordable for many Australians. The subsidies are calculated as a percentage of the premium, and the amount varies depending on the individual’s circumstances.
For example, a single person aged 35 with an annual taxable income of $80,000 may receive a government subsidy of around 20% of their premium.
Ultimate Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to purchase private health insurance as a permanent resident in Australia is a personal one, influenced by individual circumstances and priorities. Weighing the costs and benefits, considering the availability of government subsidies, and understanding the healthcare system’s complexities are essential steps in making an informed decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common benefits of private health insurance in Australia?
Private health insurance offers various benefits, including faster access to specialist consultations and elective surgeries, coverage for services not fully covered by Medicare, and potential tax rebates.
Is it mandatory for permanent residents to have private health insurance in Australia?
No, private health insurance is not mandatory for permanent residents in Australia. However, there are certain situations, such as accessing certain hospital services or receiving government subsidies, where having private health insurance can be advantageous.
How can I find the right private health insurance policy for me?
Several private health insurance providers operate in Australia. Comparing policies, considering your individual needs and budget, and seeking professional advice from a financial advisor can help you find the right policy.