How expensive is health insurance? This question is a constant source of stress for individuals and families across the nation. The cost of healthcare continues to rise, making it increasingly difficult to afford essential medical coverage. This guide delves into the complex world of health insurance costs, exploring the factors that influence premiums, the various types of plans available, and strategies for reducing expenses.
From understanding the impact of age and health status to comparing individual and employer-sponsored plans, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of the landscape. We’ll also examine government programs and subsidies that aim to make health insurance more affordable, as well as practical tips for navigating the system and finding the best value for your needs.
Cost Comparison
Choosing between individual and employer-sponsored health insurance plans can be daunting. Understanding the cost differences and associated factors is crucial for making an informed decision.
Cost Differences, How expensive is health insurance
The cost of individual health insurance plans typically exceeds that of employer-sponsored plans. This disparity arises due to several contributing factors, including:
- Group Discounts: Employer-sponsored plans benefit from group discounts, as insurance companies offer lower premiums to larger groups of individuals.
- Subsidies: Individuals purchasing health insurance through the Marketplace may qualify for subsidies, reducing their out-of-pocket costs. Employer-sponsored plans typically don’t offer subsidies.
- Administrative Costs: Individual plans generally involve higher administrative costs compared to employer-sponsored plans.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
The decision between individual and employer-sponsored plans involves weighing potential benefits and drawbacks:
Individual Plans
- Flexibility: Individual plans offer greater flexibility in choosing plans and providers.
- Portability: Individuals can take their plan with them if they change jobs.
- Potential for Subsidies: Individuals may qualify for subsidies through the Marketplace.
- Higher Costs: Individual plans generally have higher premiums than employer-sponsored plans.
- Limited Network: Individual plans may have a more limited network of providers compared to employer-sponsored plans.
- Administrative Burden: Individuals are responsible for managing their own plans.
Employer-Sponsored Plans
- Lower Costs: Employer-sponsored plans typically have lower premiums than individual plans due to group discounts.
- Wider Network: Employer-sponsored plans often have a broader network of providers.
- Administrative Support: Employers typically provide administrative support for their plans.
- Limited Flexibility: Employer-sponsored plans may offer limited plan choices.
- Job Dependency: Coverage is tied to employment, potentially leading to disruptions in coverage if employment changes.
- No Subsidies: Employer-sponsored plans typically do not offer subsidies.
Government Programs and Subsidies
Government programs and subsidies play a significant role in making health insurance more affordable for many Americans. These programs are designed to provide financial assistance and coverage to individuals and families who might otherwise struggle to afford health insurance.
Medicare and Medicaid
Medicare and Medicaid are two major government-funded health insurance programs that provide coverage to millions of Americans.
- Medicare is a federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as younger people with certain disabilities.
- Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to low-income individuals and families, pregnant women, children, and people with disabilities.
Eligibility for these programs is based on factors such as age, income, and disability status.
- Medicare offers various coverage options, including hospital insurance (Part A), medical insurance (Part B), and prescription drug coverage (Part D).
- Medicaid coverage varies by state, but generally includes essential health benefits such as doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and mental health services.
Subsidies
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced subsidies to help individuals and families afford health insurance. These subsidies are available to those who purchase health insurance through the ACA Marketplace.
- The amount of the subsidy is based on income and family size.
- Subsidies can significantly reduce the cost of monthly premiums, making health insurance more affordable for many people.
“In 2022, an estimated 11.8 million people received subsidies through the ACA Marketplace.”
Strategies for Reducing Health Insurance Costs

Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like a maze, especially when it comes to keeping costs under control. Fortunately, several strategies can help you reduce your premiums and manage your overall healthcare expenses.
Choosing a Higher Deductible
Choosing a higher deductible can significantly reduce your monthly premium. A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible means you pay more upfront, but your monthly premiums will be lower. This strategy works best for individuals who are generally healthy and confident in their ability to manage smaller healthcare expenses.
Negotiating Rates
Many insurers are willing to negotiate rates, especially if you’re a loyal customer or if you’re considering switching providers. Be prepared to discuss your needs and budget, and be willing to shop around for the best rates.
Taking Advantage of Employer-Sponsored Plans
If your employer offers health insurance, it’s often a good idea to take advantage of it. Employer-sponsored plans typically have lower premiums than individual plans, and they often offer additional benefits like employer contributions and flexible spending accounts.
Exploring Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are tax-advantaged accounts that can be used to pay for healthcare expenses. HSAs are available to individuals with high-deductible health plans. The money you contribute to an HSA grows tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are also tax-free.
Utilizing Cost-Sharing Programs
Some insurers offer cost-sharing programs that can help you save money on healthcare expenses. These programs may provide discounts on prescription drugs, preventive care, or other services. Be sure to ask your insurer about any cost-sharing programs they offer.
Comparing Plans and Providers
Don’t be afraid to shop around for the best health insurance plan. Use online tools and resources to compare plans and providers based on your needs and budget. Consider factors such as coverage, premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs.
Seeking Assistance with Affordability
Several resources and organizations offer assistance with health insurance affordability. For example, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) provides subsidies to help individuals and families afford health insurance. Additionally, state and local organizations may offer programs to help with healthcare costs.
The Impact of Health Insurance Costs on Individuals and Families
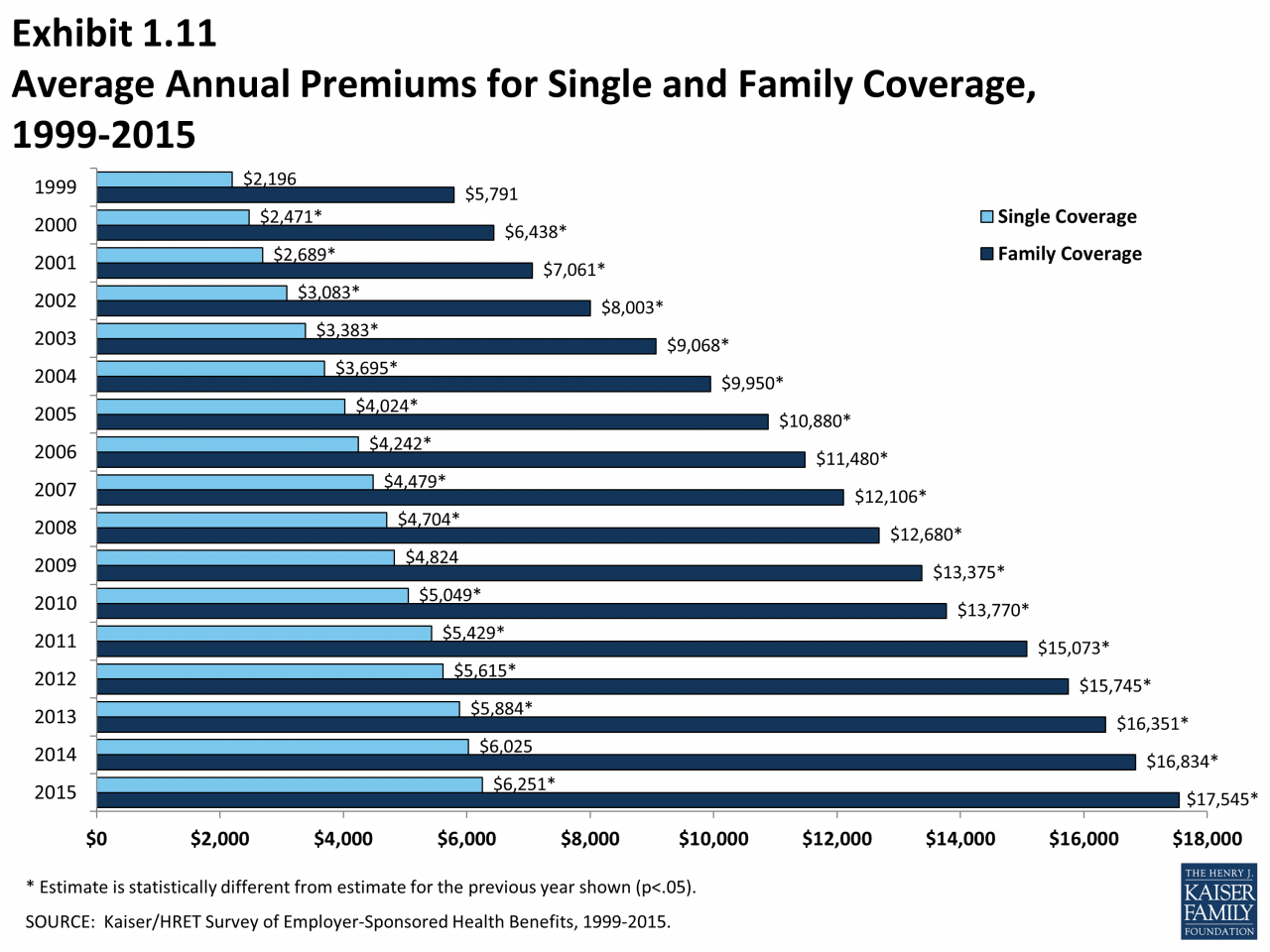
The cost of health insurance is a significant financial burden for many individuals and families, often impacting their financial well-being and access to essential healthcare services. Rising healthcare costs and insurance premiums have a direct impact on household budgets, leaving families with less disposable income for other necessities and savings.
The Financial Burden of Health Insurance Costs
High health insurance premiums can significantly strain household budgets, particularly for families with lower incomes. These costs can consume a large portion of disposable income, leaving less money for essential expenses like housing, food, transportation, and education. This financial strain can lead to difficult choices, forcing families to prioritize healthcare over other essential needs.
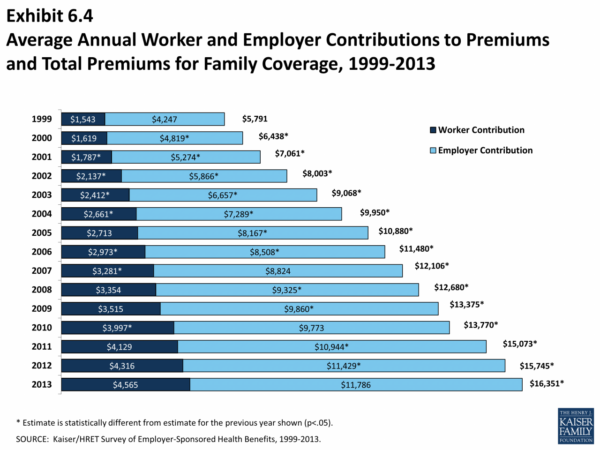
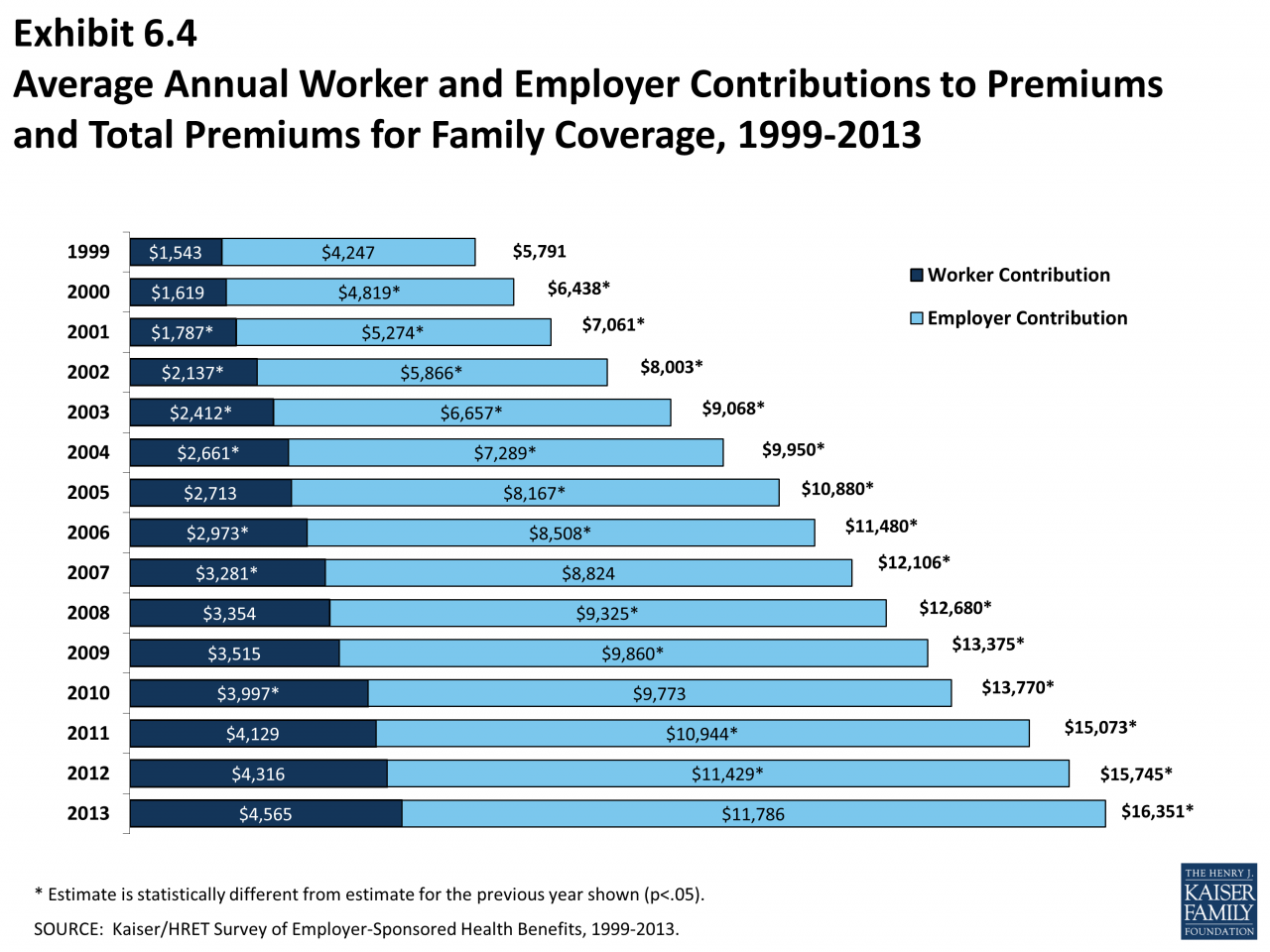
- A 2022 study by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that the average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance for a family of four was $22,221, with workers contributing an average of $5,714 per year.
- For individuals purchasing insurance through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces, premiums can vary significantly based on factors such as age, location, and health status. For example, in 2022, the average monthly premium for a silver plan in the ACA marketplace was $442, while the average monthly premium for a bronze plan was $263.
The Impact of High Premiums on Access to Healthcare
The rising cost of health insurance can also limit access to healthcare services. When individuals and families struggle to afford premiums, they may be forced to delay or forgo necessary medical care, leading to potentially serious health consequences.
- High deductibles and copayments can deter individuals from seeking preventive care or managing chronic conditions, leading to higher healthcare costs in the long run.
- The financial burden of healthcare costs can lead to medical debt, impacting credit scores and overall financial well-being.
- In some cases, individuals may be forced to choose between paying for essential needs and seeking medical attention, leading to delayed diagnoses and potentially preventable complications.
The Broader Societal Implications of Rising Healthcare Costs
The impact of rising healthcare costs extends beyond individual households. It has significant implications for the overall economy and society.
- Rising healthcare costs contribute to slower economic growth, as businesses face higher expenses and individuals have less disposable income to spend on goods and services.
- The high cost of healthcare can also strain the public sector, leading to budget deficits and potentially impacting funding for other essential services like education and infrastructure.
- The rising cost of healthcare can also lead to a widening gap in health outcomes between different socioeconomic groups, with those with lower incomes facing greater barriers to accessing quality care.
Ending Remarks
Ultimately, understanding how expensive health insurance is and the factors that influence its cost is crucial for making informed decisions about your healthcare. By exploring the different options available and employing cost-saving strategies, you can find a plan that meets your needs and fits within your budget. Remember, health insurance is an investment in your well-being, and with careful planning, you can secure the coverage you deserve without breaking the bank.
FAQ Compilation: How Expensive Is Health Insurance
How can I get health insurance if I’m unemployed?
You can explore options like individual health insurance plans, government programs like Medicaid, or subsidized plans through the Affordable Care Act marketplace.
What are the penalties for not having health insurance?
The Affordable Care Act requires most individuals to have health insurance. If you don’t have qualifying coverage, you may be subject to a tax penalty.
How often can I change my health insurance plan?
You can typically change your health insurance plan during open enrollment periods, which usually occur annually.