- Introduction to Australian Insurance
- Types of Insurance in Australia
- Regulatory Framework of Insurance in Australia
- Obtaining Insurance in Australia
- Making a Claim
- Common Insurance Issues in Australia
- Future Trends in Australian Insurance
- Conclusive Thoughts: How Insurance Works In Australia
- Query Resolution
How insurance works in Australia sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Insurance in Australia is a vital aspect of financial planning, providing a safety net against unexpected events and safeguarding individuals and businesses from significant financial losses. From the fundamental concepts of risk transfer and pooling to the diverse types of insurance available, this guide will delve into the intricate world of Australian insurance.
Understanding the regulatory framework, the process of obtaining insurance, and how to make a claim are crucial for navigating this complex landscape. This comprehensive overview will explore the various aspects of insurance in Australia, including the key players, regulations, and trends shaping the future of this essential industry.
Introduction to Australian Insurance

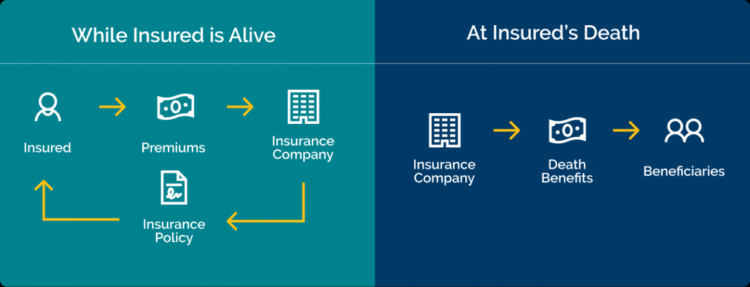
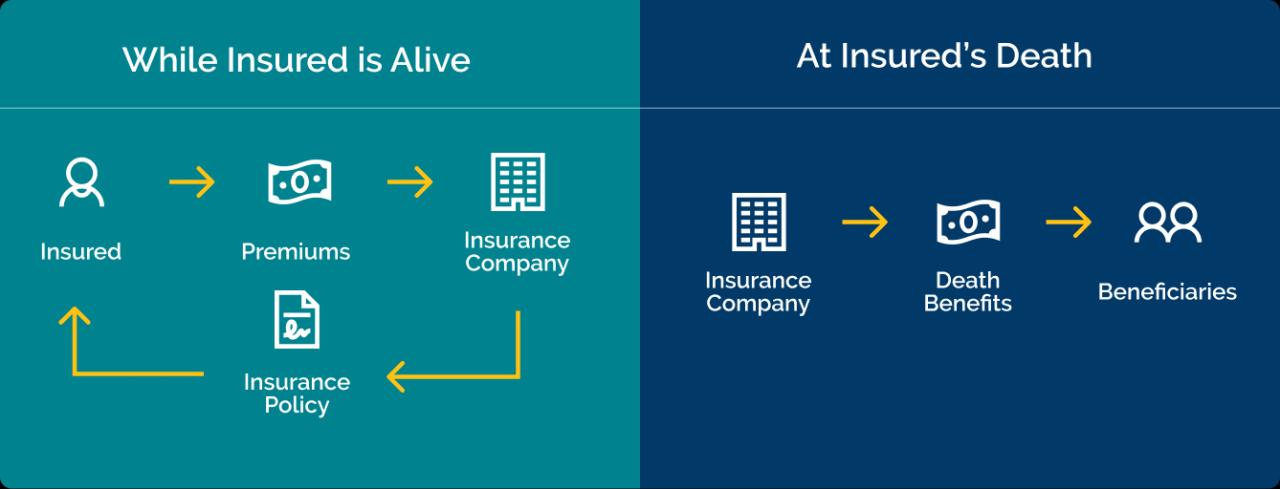
Insurance is an essential part of Australian life, providing financial protection against unexpected events. It works by transferring the risk of financial loss from individuals to insurance companies, who pool together the premiums paid by many policyholders to cover potential claims.
Risk Transfer and Pooling
The fundamental principles of insurance are risk transfer and pooling. Risk transfer refers to the process of shifting the financial burden of a potential loss from the insured individual to the insurer. Pooling involves combining the premiums paid by a large group of policyholders to create a fund that can be used to cover claims. This spreads the risk of financial loss across the entire pool, reducing the financial impact on any one individual.
Historical Development of Insurance in Australia
Insurance has a long history in Australia, dating back to the early days of European settlement. The first insurance companies were established in the 19th century, initially focusing on marine insurance. Over time, the industry expanded to offer a wide range of insurance products, including life, health, property, and motor vehicle insurance. The development of insurance in Australia has been shaped by factors such as economic growth, technological advancements, and changes in societal needs.
Types of Insurance in Australia

Australia offers a wide range of insurance products to cater to diverse needs, from protecting your health and finances to safeguarding your assets. Understanding the various types of insurance available can help you make informed decisions about your financial security and peace of mind.
Life Insurance, How insurance works in australia
Life insurance provides financial protection to your loved ones in the event of your death. It pays out a lump sum benefit to your beneficiaries, which can help them cover expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and living costs.
- Term Life Insurance: This type of life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, usually 10 to 30 years. It is typically more affordable than permanent life insurance but does not build cash value.
- Permanent Life Insurance: This type of life insurance provides lifelong coverage and can accumulate cash value, which you can borrow against or withdraw.
- Total and Permanent Disability (TPD) Insurance: This insurance provides a lump sum payment if you become totally and permanently disabled, preventing you from working.
Health Insurance
Health insurance helps cover the costs of medical treatment and healthcare services. It can provide access to private hospitals, shorter waiting times for procedures, and cover some out-of-pocket expenses.
- Private Health Insurance: This type of insurance offers coverage for a range of medical expenses, including hospital stays, surgery, and some outpatient services. It can be purchased as a standalone policy or as an add-on to your existing life insurance.
- Medicare: This is Australia’s universal healthcare system, providing subsidized access to essential medical services, including hospital care, doctor visits, and some medications.
Property Insurance
Property insurance protects your assets against various risks, such as fire, theft, and natural disasters. It can cover the cost of repairs or replacement, as well as loss of income if your property is damaged or destroyed.
- Home Insurance: This insurance covers your home and its contents against various risks, including fire, theft, and natural disasters.
- Contents Insurance: This insurance covers your personal belongings, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing, against loss or damage.
- Landlord Insurance: This insurance is designed for landlords, covering their investment property against risks such as damage, vacancy, and liability.
Motor Vehicle Insurance
Motor vehicle insurance protects you and your vehicle in the event of an accident or other incident. It can cover the cost of repairs, medical expenses, and legal fees.
- Compulsory Third Party (CTP) Insurance: This insurance is mandatory in all Australian states and territories, covering your liability to others in the event of an accident.
- Third Party Property (TPP) Insurance: This insurance covers damage to other people’s property if you are at fault in an accident.
- Comprehensive Car Insurance: This insurance provides the most comprehensive coverage, including damage to your own vehicle, as well as third-party liability.
Other Types of Insurance
In addition to the main categories of insurance, there are other types of insurance available in Australia, such as:
- Travel Insurance: This insurance provides protection for unexpected events while you are traveling, such as medical emergencies, lost luggage, and travel delays.
- Income Protection Insurance: This insurance provides a regular income payment if you are unable to work due to illness or injury.
- Business Insurance: This insurance covers various risks associated with running a business, such as property damage, liability, and business interruption.
Regulatory Framework of Insurance in Australia
The Australian insurance industry is governed by a comprehensive regulatory framework designed to ensure its stability, fairness, and consumer protection. The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the insurance industry, ensuring its compliance with regulations and safeguarding the interests of policyholders.
Role of APRA in Insurance Regulation
APRA is an independent statutory authority responsible for prudential regulation of the Australian financial services industry, including insurance. APRA’s primary objective is to maintain the stability and integrity of the financial system by setting prudential standards for insurers, monitoring their financial health, and taking necessary actions to mitigate risks. APRA’s key responsibilities in insurance regulation include:
- Setting prudential standards for insurers, including capital adequacy requirements, risk management frameworks, and governance practices.
- Monitoring the financial health of insurers through regular reporting and on-site inspections.
- Intervening in the affairs of insurers that are deemed to be at risk of failing, including taking steps to restore their financial stability or placing them under administration.
- Promoting consumer protection by ensuring that insurers are compliant with relevant legislation and regulations.
Key Legislation and Regulations Governing Insurance in Australia
The insurance industry in Australia is subject to a range of legislation and regulations, including:
- Insurance Act 1973: This Act provides the overarching framework for the insurance industry, setting out the legal requirements for insurers, brokers, and policyholders. It also covers topics such as insurance contracts, disclosure obligations, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Corporations Act 2001: This Act applies to insurers that are registered as corporations. It sets out the requirements for corporate governance, financial reporting, and disclosure of information to investors.
- Privacy Act 1988: This Act protects the privacy of personal information held by insurers, requiring them to comply with principles such as collection, use, and disclosure of personal information.
- Australian Consumer Law: This law, which is a combination of the Competition and Consumer Act 2010 and the Fair Trading Act 1987, applies to all businesses in Australia, including insurers. It sets out consumer protection provisions, including unfair contract terms, misleading and deceptive conduct, and product safety.
- APRA Prudential Standards: These standards provide detailed guidance on prudential requirements for insurers, covering areas such as capital adequacy, risk management, and governance.
Consumer Protection Measures in Place for Insurance Holders
The Australian government has implemented various measures to protect consumers in the insurance industry. These include:
- Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS): The FOS is an independent body that provides free and impartial dispute resolution services for consumers who have complaints about financial services, including insurance.
- Australian Financial Complaints Authority (AFCA): AFCA is a national, independent dispute resolution scheme for consumers who have complaints about financial products and services, including insurance.
- Insurance Council of Australia (ICA): The ICA is a non-profit industry body that represents insurers in Australia. It promotes ethical practices, provides consumer information, and facilitates dispute resolution.
- Product Disclosure Statements (PDS): Insurers are required to provide PDSs to consumers before they purchase insurance policies. These documents contain detailed information about the policy’s terms and conditions, benefits, exclusions, and risks.
- Cooling-off periods: Consumers are generally entitled to a cooling-off period of 14 days after they purchase an insurance policy, during which time they can cancel the policy without penalty.
- Right to a fair and reasonable premium: Consumers have the right to expect that their insurance premiums are fair and reasonable, taking into account factors such as their risk profile and the coverage provided.
- Right to access to information: Consumers have the right to access information about their insurance policies, including their policy documents, claims history, and premium calculations.
Obtaining Insurance in Australia
In Australia, securing insurance involves a straightforward process, often conducted online or through an insurance broker.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums in Australia are determined by various factors, reflecting the risk associated with each individual or property.
- Age: Younger individuals generally pay lower premiums, as they are statistically less likely to make claims. As individuals age, premiums may increase due to higher risk factors.
- Health: For health insurance, pre-existing conditions and overall health status significantly influence premium costs. Individuals with chronic illnesses or higher risk profiles may face higher premiums.
- Risk Profile: This encompasses factors such as driving history, occupation, and location. For example, individuals living in areas prone to natural disasters may pay higher premiums for home insurance.
- Claims History: Individuals with a history of making claims may face higher premiums, as insurers perceive them as higher risk.
Comparison of Insurance Providers and Their Offerings
The Australian insurance market is competitive, with numerous providers offering a wide range of products. It is essential to compare different providers and their offerings before making a decision.
- Price: Compare premiums across different providers to find the most affordable option. However, remember that the cheapest option may not always be the best. Consider the coverage offered and the provider’s reputation.
- Coverage: Carefully review the policy documents to understand the scope of coverage provided by each provider. Ensure the coverage meets your specific needs and requirements.
- Customer Service: Research the provider’s reputation for customer service. Look for reviews and testimonials from other customers to gauge their experience.
- Claims Process: Understand the provider’s claims process and how easy it is to make a claim. Consider the provider’s track record for processing claims efficiently and fairly.
Making a Claim
Making a claim with your insurance provider is a crucial step when an insured event occurs. This process involves notifying your insurer, providing necessary documentation, and following their instructions to receive compensation for your losses.
Claim Process
The process of making an insurance claim in Australia typically involves these steps:
- Contact your insurer: Immediately contact your insurer to report the incident. This can be done through phone, email, or online portals, depending on the insurer’s preferred methods.
- Provide initial details: During the initial contact, you will need to provide basic information about the incident, including the date, time, location, and nature of the event.
- Submit a claim form: Your insurer will provide you with a claim form, which you need to complete and submit with supporting documentation.
- Claim assessment: The insurer will assess your claim, reviewing the documentation and potentially conducting an investigation.
- Claim approval or denial: Based on the assessment, the insurer will decide whether to approve or deny your claim. If approved, you will receive compensation for your losses.
Required Documentation
The specific documentation required for an insurance claim varies depending on the type of insurance and the nature of the incident. However, some common documents include:
- Policy documents: This includes your insurance policy, which Artikels the terms and conditions of your coverage.
- Proof of loss: This could include police reports, medical reports, repair estimates, or other documentation supporting your claim.
- Personal identification: You will need to provide proof of identity, such as a driver’s license or passport.
- Financial records: Depending on the claim, you may need to provide financial records, such as bank statements or invoices.
Factors Influencing Claim Processing and Payout
Several factors can influence the claim processing time and the amount of compensation you receive. These include:
- Policy coverage: The terms and conditions of your insurance policy will determine what events are covered and the limits of coverage.
- Claim validity: The insurer will assess the validity of your claim, ensuring it meets the policy requirements and that the event is covered.
- Documentation quality: Providing accurate and complete documentation can expedite the claim processing and increase the chances of approval.
- Insurer’s assessment: The insurer’s assessment of the claim, including any investigations, will influence the final payout.
- Pre-existing conditions: In some cases, pre-existing conditions or prior claims can affect the claim processing and payout.
Common Insurance Issues in Australia
Insurance, while essential for safeguarding against unforeseen events, can also present challenges for individuals and businesses in Australia. Understanding common issues and implementing effective mitigation strategies is crucial for navigating the complexities of insurance in the Australian context.
Underinsurance
Underinsurance occurs when the sum insured on a policy is insufficient to cover the full replacement value of the insured asset in the event of a loss. This can have significant financial implications for policyholders, as they may have to bear a portion of the loss out of their own pocket.
- Impact: Underinsurance can lead to substantial financial hardship, particularly in the event of a major loss, such as a house fire or a natural disaster. Policyholders may find themselves unable to fully rebuild or replace their property or assets, leaving them with a significant financial burden.
- Mitigation: Regular reviews of insurance policies to ensure adequate coverage are essential. Factors like inflation, property renovations, and market fluctuations can impact the value of assets over time. Seeking professional advice from a qualified insurance broker can help determine the appropriate sum insured for individual needs.
Claims Disputes
Disputes regarding insurance claims can arise from various factors, including disagreements over the extent of coverage, the value of the loss, or the interpretation of policy terms. These disputes can be time-consuming, stressful, and costly for policyholders.
- Impact: Claim disputes can delay the settlement process, leaving policyholders in a state of uncertainty and financial strain. The process of resolving disputes can be complex and involve legal fees, potentially further increasing the financial burden.
- Mitigation: Careful consideration of policy terms and conditions, clear communication with insurers, and thorough documentation of claims are crucial for avoiding disputes. In the event of a dispute, seeking independent legal advice can help navigate the complexities and protect policyholder rights.
Exclusions and Limitations
Insurance policies often contain exclusions and limitations that restrict coverage for certain events, circumstances, or types of losses. These clauses can be complex and difficult to understand, potentially leading to unexpected financial burdens for policyholders.
- Impact: Exclusions and limitations can significantly reduce the scope of coverage, leaving policyholders vulnerable to unforeseen financial risks. For instance, a policy may exclude coverage for certain types of natural disasters or pre-existing conditions.
- Mitigation: Thoroughly reviewing policy documents and seeking clarification from insurers regarding exclusions and limitations is essential. Understanding these aspects before purchasing a policy can help avoid surprises and ensure appropriate coverage for individual needs.
Fraud and Misrepresentation
Insurance fraud, including false claims or misrepresentation of information during the application process, can have serious consequences for both policyholders and the insurance industry.
- Impact: Fraudulent claims can inflate premiums for all policyholders, while misrepresentation can lead to policy cancellation or denial of claims. Individuals found guilty of insurance fraud may face legal penalties, including fines and imprisonment.
- Mitigation: Honesty and transparency are crucial in dealing with insurance matters. Providing accurate information during the application process and reporting claims truthfully are essential for maintaining the integrity of the insurance system.
Rising Premiums
Insurance premiums can fluctuate due to factors such as increased claims costs, economic conditions, and regulatory changes. Rising premiums can pose a financial challenge for policyholders, particularly those on fixed incomes.
- Impact: Higher premiums can strain household budgets and force individuals to make difficult choices regarding their insurance coverage. It can also discourage individuals from seeking necessary insurance protection due to affordability concerns.
- Mitigation: Exploring different insurance providers, comparing quotes, and considering policy options with higher deductibles can help mitigate the impact of rising premiums. Maintaining a good driving record and taking preventive measures to reduce risks can also influence premium rates.
Future Trends in Australian Insurance
The Australian insurance landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory shifts. These trends are shaping the future of insurance, creating opportunities for innovation and growth.
Impact of Technology
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the insurance industry, driving efficiency, improving customer experience, and creating new opportunities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming insurance processes, from risk assessment and underwriting to claims processing and fraud detection. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are enhancing customer service, providing instant support and personalized solutions.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of connected devices is enabling insurers to gather real-time data on policyholders’ behavior and risk profiles. This data can be used to personalize premiums, provide tailored advice, and offer preventive measures. For example, telematics devices in vehicles can track driving behavior, allowing insurers to offer discounts for safe driving.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology is creating opportunities for greater transparency and efficiency in insurance processes. It can streamline claims processing, improve data security, and facilitate peer-to-peer insurance models.
- Big Data Analytics: Insurers are leveraging big data analytics to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, risk factors, and market trends. This data-driven approach enables them to develop more accurate pricing models, offer personalized products, and improve risk management.
Emerging Trends
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of insurance in Australia.
- Insurtech: The rise of insurtech startups is disrupting traditional insurance models, offering innovative solutions and digital-first experiences. Insurtech companies are leveraging technology to provide faster, more efficient, and personalized insurance services.
- Personalized Insurance: Consumers are increasingly demanding personalized insurance solutions tailored to their specific needs and risk profiles. Insurers are responding by offering flexible policies and pricing models based on individual data and behavior.
- Sustainable Insurance: Growing concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability are driving the development of sustainable insurance products. Insurers are offering policies that cover risks associated with climate change and encourage sustainable practices.
- Digital Distribution: The increasing use of digital channels for insurance distribution is changing the way consumers purchase and manage their policies. Insurers are investing in online platforms and mobile apps to provide seamless and convenient customer experiences.
Predictions for the Future
The Australian insurance industry is expected to continue evolving, driven by the trends discussed above.
- Increased Automation: AI and other technologies will continue to automate insurance processes, reducing manual tasks and improving efficiency.
- Personalized and Data-Driven Products: Insurers will offer more personalized and data-driven products, tailored to individual customer needs and risk profiles.
- Growing Importance of Insurtech: Insurtech startups will continue to disrupt the traditional insurance industry, offering innovative solutions and challenging established players.
- Greater Focus on Sustainability: Sustainable insurance products and practices will become increasingly important as concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability grow.
- Shift Towards Digital Channels: Consumers will increasingly rely on digital channels for insurance purchases, claims management, and customer service.
Conclusive Thoughts: How Insurance Works In Australia
Insurance in Australia is a dynamic and ever-evolving field. As technology continues to transform the industry, individuals and businesses can expect to see new innovations and solutions emerging. By staying informed about the latest trends and developments, Australians can make informed decisions about their insurance needs and secure their financial well-being.
Query Resolution
What are the main types of insurance available in Australia?
Australia offers a wide range of insurance types, including life insurance, health insurance, home insurance, car insurance, and business insurance, among others.
How do I choose the right insurance provider?
It’s essential to compare quotes from different insurance providers, consider their reputation, coverage options, and customer service.
What are the factors that influence insurance premiums?
Factors such as age, health, risk profile, location, and the type and amount of coverage all contribute to determining insurance premiums.
What happens if I need to make a claim?
You’ll need to contact your insurance provider, provide the necessary documentation, and follow their claim process. The time it takes to process and pay out a claim can vary depending on the specific circumstances.