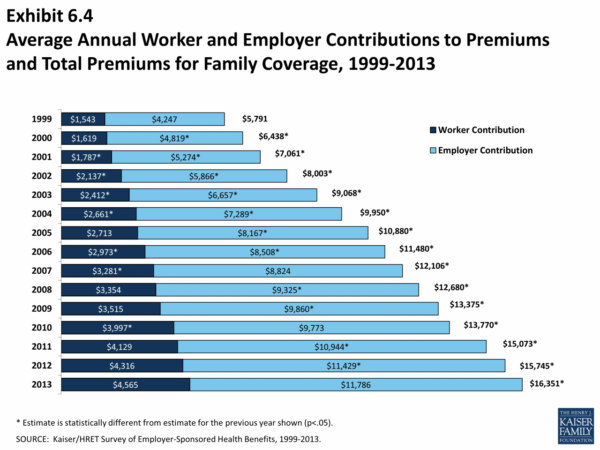
How much does private health insurance cost in Australia? This question is a crucial one for many Australians, as navigating the complex world of healthcare can be a daunting task. Private health insurance offers a valuable safety net, providing access to a wider range of medical services and potentially reducing out-of-pocket expenses. But understanding the cost factors and making an informed decision requires careful consideration.
This guide aims to demystify the intricacies of private health insurance in Australia, providing a comprehensive overview of the factors influencing costs, average premium ranges, government subsidies, and key considerations for choosing the right policy. Whether you’re a young individual starting out, a family with growing healthcare needs, or a retiree seeking peace of mind, understanding these aspects is essential for making informed choices about your health and financial well-being.
Understanding Private Health Insurance in Australia: How Much Does Private Health Insurance Cost In Australia
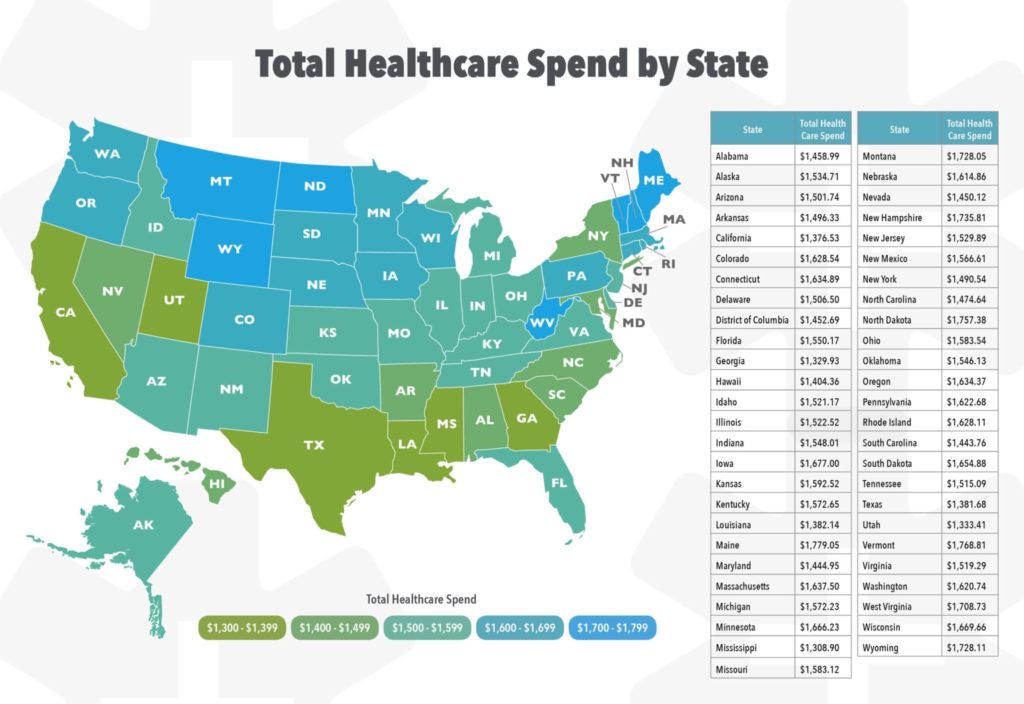
Private health insurance in Australia is a system that allows individuals to choose additional health coverage beyond the public Medicare system. It offers a range of benefits and options, and understanding its complexities is essential for making informed decisions.
Types of Private Health Insurance Policies, How much does private health insurance cost in australia
Private health insurance policies in Australia are categorized into different types, each offering a unique set of benefits and coverage. These policies can be broadly classified into hospital, extras, and combined policies.
- Hospital Cover: Hospital cover provides financial assistance for hospital stays, including surgery, accommodation, and medical care. This type of cover is essential for individuals who want to access private hospitals or have specific surgical procedures performed.
- Extras Cover: Extras cover provides reimbursement for a range of health services not covered by Medicare, such as dental, optical, physiotherapy, and alternative therapies. This type of cover can be customized to suit individual needs and preferences.
- Combined Cover: Combined cover combines both hospital and extras cover, providing comprehensive health insurance. This type of policy offers the most comprehensive coverage, but it also tends to be more expensive.
Benefits of Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance offers several benefits that can significantly enhance individuals’ healthcare experience. Some of the key advantages include:
- Access to Private Hospitals: Private health insurance allows individuals to choose private hospitals for their treatment, offering potentially shorter waiting times, more comfortable facilities, and a wider range of specialists.
- Choice of Specialists: With private health insurance, individuals can choose their own specialists, ensuring they receive treatment from the healthcare professionals they trust.
- Faster Treatment: Private health insurance can often lead to faster treatment times compared to the public system, especially for elective surgeries and non-urgent procedures.
- Wider Range of Treatments: Private health insurance may cover a wider range of treatments and services not available through Medicare, including alternative therapies and cosmetic procedures.
- Tax Benefits: Individuals with private health insurance may be eligible for tax rebates, reducing the overall cost of their premiums.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Private Health Insurance
The cost of private health insurance in Australia is influenced by a range of factors, including:
- Age: Younger individuals generally pay lower premiums than older individuals, as they are statistically less likely to require extensive healthcare services.
- Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions may face higher premiums, as they are considered a higher risk for insurance providers.
- Level of Cover: The level of cover chosen, including the type of policy (hospital, extras, or combined) and the specific benefits included, significantly affects the cost of premiums.
- Location: Premiums may vary depending on the location of residence, reflecting regional differences in healthcare costs and utilization.
- Lifestyle: Individuals with high-risk lifestyles, such as smokers or those who engage in extreme sports, may face higher premiums.
- Family Size: Premiums typically increase with family size, as more individuals are covered under the policy.
Last Recap
Navigating the world of private health insurance in Australia can be complex, but understanding the key factors influencing costs and making informed choices can lead to peace of mind and financial security. By carefully assessing your individual needs, comparing policies, and considering government subsidies, you can find a plan that aligns with your health goals and budget. Remember, investing in your health is an investment in your future.
User Queries
What are the different types of private health insurance policies available in Australia?
Australia offers a variety of private health insurance policies, including hospital cover, extras cover, and combined policies. Hospital cover provides coverage for inpatient care, while extras cover covers outpatient services like dental, physiotherapy, and optical. Combined policies offer both hospital and extras cover.
Can I get a discount on my private health insurance premiums?
Yes, several discounts and rebates are available for private health insurance premiums. These may include discounts for families, young adults, or those who have been with the same insurer for a long time. You can also get rebates from the government if you meet certain eligibility criteria.
What are the common out-of-pocket expenses associated with private health insurance?
Out-of-pocket expenses associated with private health insurance can include co-payments, gap fees, and excess payments. Co-payments are a fixed amount you pay for each service, while gap fees are the difference between what your insurer pays and the full cost of the service. Excess payments are a fixed amount you pay towards each claim.
How can I manage the costs of private health insurance?
Managing private health insurance costs involves comparing policies, considering discounts and rebates, and understanding out-of-pocket expenses. It’s also crucial to assess your individual needs and choose a policy that aligns with your budget and health goals.