How to write a comparative case study for laws is a valuable skill for legal scholars and practitioners. This method of research allows for a deeper understanding of legal principles and their application by comparing and contrasting different cases from various jurisdictions, historical periods, or thematic contexts. By examining these similarities and differences, we gain valuable insights into the evolution and interpretation of the law.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the process of writing a comparative case study for laws, from choosing relevant cases to presenting your findings in a clear and persuasive manner. We will explore each stage of the research process, offering practical tips and strategies to ensure your study is well-structured, informative, and impactful.
Understanding Comparative Case Studies
Comparative case studies are a valuable tool in legal research, allowing for the analysis and comparison of legal systems, doctrines, or practices across different jurisdictions or time periods. They provide a deeper understanding of the complexities and nuances of legal issues, fostering critical analysis and informed decision-making.
Comparative case studies offer numerous benefits in legal research. By examining how similar legal issues are addressed in different contexts, researchers can gain insights into the strengths and weaknesses of various legal systems, identify potential areas for improvement, and develop more effective legal solutions. Additionally, comparative case studies contribute to the development of legal theory by challenging existing assumptions and fostering cross-cultural understanding.
Types of Comparative Case Studies
Comparative case studies can be categorized based on their scope and focus. Here are some common types:
- Cross-Jurisdictional Studies: These studies compare legal systems, doctrines, or practices across different jurisdictions, such as comparing the application of criminal law in the United States and the United Kingdom. For example, a cross-jurisdictional study could examine how different jurisdictions address the issue of hate speech, analyzing the legal frameworks, case law, and societal perspectives in each jurisdiction.
- Historical Studies: These studies examine how legal systems, doctrines, or practices have evolved over time within a specific jurisdiction. For instance, a historical study could trace the development of property law in England from the medieval period to the present day, analyzing the impact of historical events and social changes on the legal framework.
- Thematic Studies: These studies focus on a specific legal issue or theme and compare how it is addressed in different jurisdictions or time periods. For example, a thematic study could explore the concept of legal personhood, examining how different legal systems define and grant personhood to entities like corporations, animals, or artificial intelligence.
Choosing Case Studies
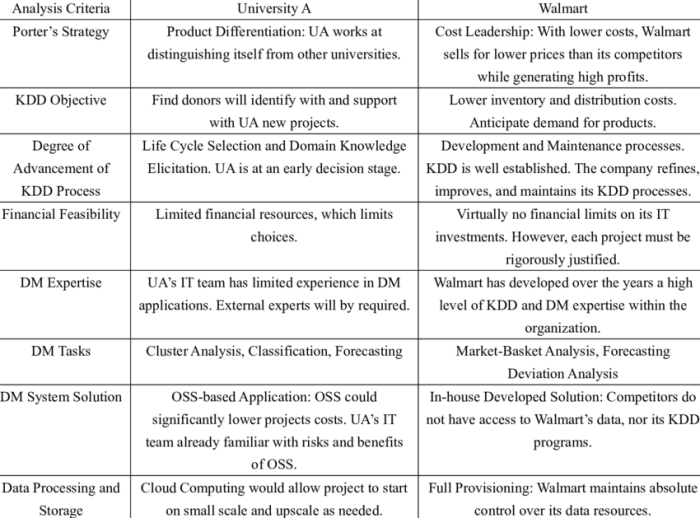
The selection of case studies is crucial for a successful comparative analysis. The chosen cases should be relevant to the research question and provide valuable insights for comparison. Careful consideration of the legal context and historical background of each case is essential for understanding the nuances and complexities of the legal issues at hand.
Identifying Relevant Legal Cases or Scenarios for Comparison
The first step in choosing case studies is to identify relevant legal cases or scenarios for comparison. This involves considering the research question and identifying the key legal issues that will be explored in the comparative analysis. For example, if the research question focuses on the evolution of privacy law in different jurisdictions, the chosen cases should involve legal disputes related to privacy rights and the different approaches taken by courts or legislatures in various jurisdictions.
Criteria for Selecting Comparable Cases
Once relevant cases have been identified, it is important to select cases that are comparable and provide valuable insights. This involves considering several criteria:
- Similarities in Legal Framework: The cases should share a similar legal framework, such as common law or civil law systems. This ensures that the comparison is meaningful and that the legal issues are being addressed within a similar context.
- Comparable Facts: The cases should involve comparable facts and circumstances. This helps to isolate the legal issues and ensure that the comparison is based on similar situations.
- Different Legal Outcomes: The cases should have different legal outcomes. This provides a basis for comparison and allows for an analysis of the reasons behind the different outcomes.
- Relevance to Research Question: The cases should be relevant to the research question and provide insights into the legal issues being explored.
Importance of Considering the Legal Context and Historical Background
It is important to consider the legal context and historical background of each case to understand the nuances and complexities of the legal issues at hand. This includes factors such as:
- Historical Development of the Law: The historical development of the law in each jurisdiction can influence the interpretation and application of legal principles.
- Cultural and Social Context: The cultural and social context of each jurisdiction can influence the development and application of legal rules.
- Political Influences: Political influences can also play a role in shaping legal outcomes.
By carefully considering these factors, researchers can select case studies that are relevant, comparable, and provide valuable insights for a comparative analysis.
Developing Research Questions
Crafting clear and specific research questions is crucial for guiding your comparative case study analysis. These questions act as a compass, directing your investigation and ensuring a focused and meaningful examination of the chosen cases.
Relationship Between Research Questions and Chosen Cases, How to write a comparative case study for laws
Research questions should be directly related to the chosen cases. The cases should be relevant to the research questions and provide sufficient data to answer them. It is important to select cases that offer a diverse range of perspectives and allow for meaningful comparisons.
- Example: If your research question focuses on the effectiveness of different legal frameworks in regulating online platforms, you might choose cases that examine the regulatory approaches of the European Union, the United States, and China. These cases would provide a range of perspectives on the issue and allow for comparisons across different legal systems.
Ensuring Answerability of Research Questions
It is essential to ensure that the research questions are answerable through the chosen cases. The cases should provide enough data and information to address the research questions effectively.
- Example: If your research question investigates the impact of legal reforms on public perception of the judiciary, you would need cases that provide data on public opinion before and after the reforms. Cases without such data would not be suitable for answering the research question.
Analyzing the Cases
This section delves into the core of your comparative case study by examining the legal frameworks and relevant laws applicable to each case. It then compares and contrasts the legal arguments, court decisions, and outcomes, identifying key differences and similarities in the legal principles and application of law. This analysis will illuminate the strengths and weaknesses of each legal system and provide insights into the evolution of legal principles.
Legal Frameworks and Relevant Laws
This examines the legal frameworks and relevant laws applicable to each case. This involves identifying the relevant jurisdictions, the applicable laws, and the legal principles that underpin these laws. For example, if the cases involve contract law, you would need to identify the relevant contract law principles in each jurisdiction and how these principles are applied in practice.
- Identify the jurisdictions where the cases arose.
- Identify the relevant laws, statutes, and regulations applicable to each case.
- Analyze the legal principles underlying the relevant laws.
- Provide examples of how these legal principles are applied in each case.
Comparison of Legal Arguments, Court Decisions, and Outcomes
This focuses on comparing and contrasting the legal arguments, court decisions, and outcomes of the chosen cases. It involves analyzing the arguments presented by the parties involved, the reasoning used by the courts in reaching their decisions, and the ultimate outcome of each case.
- Summarize the legal arguments presented by the parties in each case.
- Analyze the reasoning used by the courts in reaching their decisions.
- Compare and contrast the court decisions and outcomes in each case.
- Identify any key differences or similarities in the legal arguments, court decisions, and outcomes.
Identifying Key Differences and Similarities
This focuses on identifying key differences and similarities in the legal principles and application of law in the chosen cases. This involves identifying areas where the legal systems differ in their approach to similar legal issues and areas where they converge in their application of legal principles.
- Identify key differences in the legal principles and application of law in the chosen cases.
- Identify key similarities in the legal principles and application of law in the chosen cases.
- Explain the reasons for these differences and similarities.
- Discuss the implications of these differences and similarities for the development of law.
Structuring the Comparative Case Study

Once you have chosen your cases and developed your research questions, the next step is to structure your comparative case study. A well-structured case study will make your analysis clear, concise, and easy to follow.
A typical structure for a comparative case study includes the following sections:
Introduction
The introduction should provide an overview of the research topic, the purpose of the study, and the research questions. It should also introduce the chosen cases and briefly explain why they were selected.
Case Descriptions
This section should provide detailed descriptions of the chosen cases, including relevant background information, legal context, and key facts. This section should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be organized in a way that allows for easy comparison between the cases.
Comparative Analysis
This is the heart of the comparative case study. Here, you will analyze the cases in relation to your research questions. You should compare and contrast the cases, identifying similarities and differences in their legal context, key facts, and outcomes. You should also provide evidence to support your claims, drawing on relevant legal sources, scholarly articles, and other credible sources.
Discussion
This section provides an opportunity to discuss the findings of your comparative analysis. You should discuss the implications of your findings, including the limitations of your study. You should also consider the broader context of your findings and their potential impact on legal practice and policy.
Conclusion
The conclusion should summarize the main findings of your comparative case study and reiterate the answers to your research questions. It should also provide a brief overview of the implications of your findings and potential areas for further research.
Table of Comparison
A table comparing and contrasting the key aspects of the chosen cases can be a valuable tool for organizing and presenting your analysis. The table should include columns for each case and rows for the key aspects you are comparing.
Here is an example of a table that could be used to compare two cases:
| Aspect | Case 1 | Case 2 |
|—|—|—|
| Legal Context | | |
| Key Facts | | |
| Outcome | | |
For example, if you are comparing two cases involving freedom of speech, the table could include columns for each case and rows for the type of speech involved, the legal context, the arguments made by the parties, and the outcome of the case.
Providing Evidence
When you are making claims about the cases, it is important to provide evidence to support your claims. This evidence can come from a variety of sources, including:
* Legal citations: You should cite relevant case law, statutes, and other legal sources to support your claims.
* Scholarly articles: Articles from academic journals can provide valuable insights into the legal issues at hand.
* Other credible sources: You can also use other credible sources, such as government reports, news articles, and legal commentaries, to support your claims.
When you cite your sources, you should use a consistent citation style, such as the Bluebook or the Chicago Manual of Style.
Example
Imagine you are conducting a comparative case study on the right to privacy in the context of social media. You have chosen two cases: *Doe v. Facebook*, a case involving a user’s right to privacy in the context of Facebook’s data collection practices, and *Smith v. Twitter*, a case involving a user’s right to privacy in the context of Twitter’s use of user data for targeted advertising.
In your comparative analysis, you could compare and contrast the legal context, the key facts, and the outcomes of the two cases. For example, you could discuss the different privacy laws that were applied in each case, the different arguments made by the parties, and the different rulings issued by the courts.
You could also use a table to compare and contrast the key aspects of the two cases. For example, the table could include columns for each case and rows for the type of data involved, the legal basis for the user’s claim, and the outcome of the case.
By providing evidence to support your claims, you can ensure that your analysis is credible and persuasive.
Presenting the Findings
After meticulously analyzing the chosen cases, the next step is to present the findings in a clear and concise manner. This section focuses on summarizing the key takeaways from the comparative analysis, discussing their implications for legal practice and policy, and suggesting recommendations based on the insights gained.
Summarizing Key Findings and Conclusions
The comparative analysis reveals significant similarities and differences between the chosen cases. This section summarizes the key findings and conclusions drawn from the analysis.
- [Finding 1]: Describe the first key finding and its significance in the context of the comparative analysis. This could involve identifying common patterns, contrasting approaches, or highlighting specific areas of divergence between the cases. Provide supporting evidence from the analysis to substantiate the finding.
- [Finding 2]: Present the second key finding and its implications for the research question. Explain how this finding contributes to the overall understanding of the legal issue being investigated. Offer concrete examples from the cases to illustrate the finding.
- [Finding 3]: Discuss the third key finding and its relevance to the broader legal context. Explain how this finding connects to existing legal principles, theories, or practices. Provide relevant legal precedents or scholarly literature to support the finding.
Implications for Legal Practice and Policy
The findings of the comparative case study have important implications for legal practice and policy. This section explores the potential impact of the findings on various stakeholders, including legal professionals, policymakers, and the public.
- [Implication 1]: Explain how the findings suggest potential changes or adjustments in legal practice. Provide specific examples of how legal professionals could adapt their approach or strategies based on the insights gained from the comparative analysis.
- [Implication 2]: Discuss the implications of the findings for policy development. Explain how the findings could inform the creation of new laws, regulations, or policies. Provide examples of specific policy recommendations based on the analysis.
- [Implication 3]: Explore the broader societal implications of the findings. Explain how the findings could impact public perception, social norms, or the administration of justice. Provide examples of how the findings could influence public discourse or policy debates.
Recommendations
Based on the findings and their implications, the comparative case study offers recommendations for legal practice and policy. This section presents specific suggestions for improving legal frameworks, enhancing legal processes, or addressing identified challenges.
- [Recommendation 1]: Provide a specific recommendation based on the findings. Explain the rationale behind the recommendation and how it could contribute to improving legal practice or policy. Provide concrete examples of how the recommendation could be implemented.
- [Recommendation 2]: Present a second recommendation, building upon the findings of the comparative analysis. Explain the expected benefits of implementing this recommendation and address potential challenges or limitations. Provide relevant examples to illustrate the recommendation’s application.
- [Recommendation 3]: Offer a third recommendation, drawing upon the insights gained from the comparative analysis. Explain the potential impact of this recommendation on legal practice, policy, or broader societal issues. Provide concrete examples of how the recommendation could be implemented and its potential effects.
Conclusion
By carefully selecting and analyzing relevant cases, formulating clear research questions, and structuring your study in a logical and persuasive manner, you can create a comparative case study that not only deepens your understanding of the law but also contributes valuable insights to the legal field. Whether you are a student, a lawyer, or a researcher, mastering the art of writing a comparative case study for laws will equip you with the skills to effectively analyze and communicate legal knowledge.
Essential FAQs: How To Write A Comparative Case Study For Laws
What are some examples of comparative case studies in law?
Examples include comparing the application of the right to free speech in different countries, analyzing how different legal systems handle issues like intellectual property, or examining the evolution of a specific legal doctrine over time.
How do I find relevant cases for my comparative case study?
You can start by searching legal databases, reviewing scholarly articles, consulting with experts in the field, and exploring case law summaries and digests.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a comparative case study?
Common mistakes include failing to clearly define your research questions, neglecting to provide sufficient context for the cases, and overlooking potential biases in your analysis.
How can I ensure my comparative case study is well-written and persuasive?
Use clear and concise language, organize your thoughts logically, provide strong evidence to support your claims, and carefully consider the audience for your study.