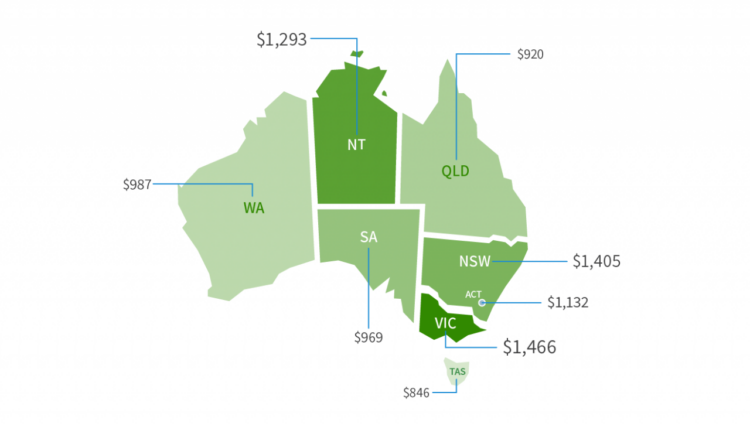
Insurance cost in Australia is a crucial consideration for individuals and families, as it impacts their financial well-being. The cost of insurance can vary significantly depending on a multitude of factors, including demographics, location, lifestyle, and the specific type of insurance needed. Understanding the key influences on insurance premiums is essential for making informed decisions and finding the best coverage at an affordable price.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of insurance costs in Australia, providing insights into the factors that shape premiums, the different types of insurance available, and strategies for reducing costs. We will delve into the role of government regulations, consumer protection laws, and emerging trends that are shaping the future of insurance pricing.
Insurance Cost Factors in Australia
Insurance premiums in Australia are influenced by a range of factors, reflecting the complexity of risk assessment and the need for a fair pricing system. Understanding these factors can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their insurance needs and manage their costs effectively.
Demographics
Demographics play a significant role in determining insurance premiums. Insurance companies analyze factors such as age, gender, and occupation to assess risk. For example, younger drivers are generally considered to be at a higher risk of accidents than older drivers, leading to higher premiums. Similarly, individuals in high-risk occupations, such as construction or mining, may face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of injuries or accidents.
Location
The location where an individual or business resides or operates also impacts insurance costs. Areas with higher crime rates, natural disaster risks, or traffic congestion can lead to higher premiums. For example, homes in areas prone to bushfires or floods may have higher insurance premiums to reflect the increased risk of damage.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle choices can also influence insurance premiums. For example, individuals who engage in high-risk activities, such as motorsports or extreme sports, may face higher premiums for personal accident or health insurance. Similarly, smokers or individuals with unhealthy lifestyles may face higher premiums for health insurance.
Risk Assessment
Insurance companies employ sophisticated risk assessment models to determine premiums. These models consider various factors, including:
- Claims history: Individuals with a history of claims may face higher premiums due to their increased risk profile.
- Credit score: A good credit score can indicate financial responsibility and may lead to lower premiums.
- Property value: For property insurance, the value of the property is a key factor in determining the premium.
- Safety features: Security systems, smoke detectors, and other safety features can reduce premiums by mitigating risk.
Specific Insurance Types
The factors influencing insurance costs vary depending on the type of insurance.
Home Insurance
- Location: As mentioned earlier, areas with higher crime rates or natural disaster risks will lead to higher premiums.
- Property value: The value of the home is directly proportional to the premium.
- Construction type: Homes built with fire-resistant materials may have lower premiums.
- Security features: Homes with security systems, smoke detectors, and other safety features can reduce premiums.
Car Insurance
- Age and driving experience: Younger and less experienced drivers generally face higher premiums.
- Vehicle type: High-performance or luxury vehicles tend to have higher premiums due to their higher repair costs.
- Driving history: Drivers with a history of accidents or traffic violations may face higher premiums.
- Location: Areas with higher traffic congestion or crime rates can lead to higher premiums.
Health Insurance
- Age and health: Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or older individuals may face higher premiums.
- Lifestyle: Smokers and individuals with unhealthy lifestyles may face higher premiums.
- Coverage level: Higher levels of coverage, such as private hospital cover, will lead to higher premiums.
Types of Insurance and Cost Comparisons: Insurance Cost In Australia
Insurance in Australia is a necessity for many individuals and businesses, offering protection against unexpected events. Understanding the different types of insurance available and their associated costs is crucial for making informed decisions.
Health Insurance, Insurance cost in australia
Health insurance in Australia provides coverage for medical expenses not covered by Medicare, the public health system. Private health insurance can include hospital, ambulance, and ancillary benefits such as dental and physiotherapy.
The cost of health insurance varies based on factors such as age, location, level of cover, and chosen provider.
On average, premiums for basic hospital cover can range from $50 to $100 per month, while comprehensive cover, including ancillary benefits, can cost upwards of $200 per month.
Car Insurance
Car insurance is mandatory in Australia and provides financial protection against damage to your vehicle, injuries to yourself or others, and legal liabilities arising from accidents.
The cost of car insurance is influenced by factors such as the type of vehicle, your driving history, location, and the level of cover you choose.
Comprehensive car insurance, covering damage to your vehicle and third-party liabilities, is generally more expensive than third-party property damage insurance, which only covers damage to other vehicles.
Home Insurance
Home insurance protects your property and belongings against various risks such as fire, theft, and natural disasters.
The cost of home insurance is determined by factors such as the value of your property, location, building materials, and the level of cover you choose.
Premiums for basic home insurance can start from around $50 per month, while comprehensive cover, including additional benefits like contents insurance, can cost upwards of $100 per month.
Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial support to your loved ones in the event of your death. It can help cover expenses such as funeral costs, mortgage repayments, and living expenses.
The cost of life insurance is influenced by factors such as your age, health, lifestyle, and the amount of cover you choose.
Premiums for term life insurance, which provides cover for a specific period, can range from $20 to $50 per month, while permanent life insurance, offering lifelong coverage, can be significantly more expensive.
Average Premiums for Different Insurance Types
| Insurance Type | Region | Average Premium (per month) |
|---|---|---|
| Health Insurance (Basic Hospital) | Sydney | $75 – $125 |
| Health Insurance (Comprehensive) | Melbourne | $150 – $250 |
| Car Insurance (Comprehensive) | Brisbane | $80 – $150 |
| Car Insurance (Third-Party Property Damage) | Perth | $50 – $100 |
| Home Insurance (Basic) | Adelaide | $60 – $110 |
| Home Insurance (Comprehensive) | Canberra | $120 – $200 |
| Life Insurance (Term) | Hobart | $30 – $60 |
| Life Insurance (Permanent) | Darwin | $100 – $250 |
Factors Affecting Insurance Cost Trends
Insurance costs in Australia are influenced by a complex interplay of economic, regulatory, technological, and social factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about their insurance needs and for insurers to effectively manage their pricing strategies.
Economic Factors
Economic factors, such as inflation and interest rates, significantly impact insurance costs. Inflation directly affects the cost of replacing or repairing insured assets, leading to higher premiums. Rising interest rates, on the other hand, can impact insurance costs in two ways:
- Increased cost of capital: Insurers need to borrow money to invest in their operations and cover claims. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, which is reflected in higher premiums.
- Reduced investment returns: Insurers invest premiums to generate returns that help offset claims costs. Higher interest rates can lead to lower investment returns, potentially forcing insurers to raise premiums to maintain profitability.
Regulatory Changes and Government Policies
Government regulations and policies play a significant role in shaping insurance costs.
- Changes in regulatory requirements: New regulations, such as those related to data privacy or consumer protection, can impose additional costs on insurers, which may be passed on to policyholders through higher premiums.
- Taxation policies: Government policies related to insurance taxation can influence the cost of insurance. For instance, changes in tax rates or deductions for insurance premiums can impact the overall cost for policyholders.
- Government subsidies and incentives: Government programs that provide subsidies or incentives for specific types of insurance, such as flood insurance or health insurance, can influence the cost of those insurance products.
Technological Advancements and Claims Data
Technological advancements have a significant impact on insurance costs.
- Data analytics: Advanced data analytics tools allow insurers to better understand risk profiles and pricing models, leading to more accurate and competitive pricing. For example, insurers can use data to identify factors that contribute to higher claims frequencies or severities, enabling them to adjust premiums accordingly.
- Automation and AI: The use of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in claims processing and risk assessment can improve efficiency and reduce operational costs. This can lead to lower premiums for policyholders.
- Telematics: Telematics devices, such as those used in car insurance, provide real-time data on driving behavior, allowing insurers to offer lower premiums to safer drivers.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the insurance industry are likely to continue shaping insurance costs in the future.
- Climate change: The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as floods and bushfires, are leading to higher claims costs, putting upward pressure on insurance premiums. For example, in Australia, insurers are increasingly incorporating climate change risks into their pricing models, particularly for properties located in areas prone to natural disasters.
- Cybersecurity: Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, leading to higher insurance costs for businesses and individuals. As cyber threats evolve, insurers are developing new products and coverage options to address these risks, potentially leading to higher premiums for those seeking protection.
- Shared economy: The rise of the shared economy, such as ride-sharing and home-sharing platforms, is creating new insurance challenges. Insurers are adapting their products and pricing models to address these emerging risks, potentially leading to changes in insurance costs for individuals and businesses operating in the shared economy.
Strategies for Reducing Insurance Costs

In Australia, insurance costs can be a significant expense. However, there are several strategies you can implement to lower your premiums and ensure you are getting the best value for your money.
Increasing Deductibles
Increasing your deductible can be a simple and effective way to reduce your insurance premiums. Your deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance policy starts covering the remaining costs. By raising your deductible, you agree to take on more financial responsibility in the event of a claim, which signals to insurers that you are less likely to file a claim. This, in turn, lowers your premiums. However, it is important to choose a deductible that you can comfortably afford in case of an unexpected event.
Bundling Insurance Policies
Bundling your insurance policies with the same provider can lead to significant savings. Insurance companies often offer discounts for customers who combine multiple policies, such as home, car, and health insurance, under one umbrella. This is because bundling reduces administrative costs for insurers, allowing them to pass on the savings to you. When you bundle, you are also more likely to remain a loyal customer, which further benefits the insurance company.
Negotiating with Providers
Don’t be afraid to negotiate with your insurance provider. If you have been a loyal customer with a good claims history, you may be eligible for a discount. You can also try negotiating a lower premium by comparing quotes from different providers and highlighting the benefits of your business to the insurer.
Maintaining a Good Credit Score and Driving Record
A good credit score and driving record can significantly impact your insurance premiums. Insurance companies often use credit scores to assess your risk, and a higher score can lead to lower premiums. Similarly, a clean driving record with no accidents or violations demonstrates responsible driving behavior, making you a less risky customer.
Shopping Around for Competitive Insurance Quotes
The insurance market is competitive, and it pays to shop around for the best rates. Online comparison websites and insurance brokers can help you quickly compare quotes from multiple providers. Be sure to provide accurate information when requesting quotes to ensure you receive accurate pricing.
Government Initiatives and Consumer Protection

The Australian government plays a crucial role in regulating the insurance industry to ensure fair and transparent practices, protect consumers, and promote affordability. This involves setting standards, enforcing consumer protection laws, and promoting initiatives that increase transparency and accessibility.
Consumer Protection Laws and Regulations
The Australian government has implemented several consumer protection laws and regulations to safeguard consumers’ rights and interests in the insurance market. These laws are designed to ensure fair and transparent pricing practices, protect consumers from unfair or deceptive conduct, and provide avenues for redress in case of disputes.
- The Australian Consumer Law (ACL) is a comprehensive piece of legislation that applies to all insurance products and services. It prohibits unfair or misleading representations, ensures that insurance contracts are clear and understandable, and provides consumers with the right to cancel certain contracts within a specified period.
- The Insurance Contracts Act 1984 (ICA) sets out specific rules governing insurance contracts, including provisions related to disclosure requirements, policy terms, and the process for resolving disputes. It also establishes the Australian Financial Complaints Authority (AFCA), an independent body that handles complaints related to insurance products and services.
- The Privacy Act 1988 governs the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information by insurance companies. It ensures that consumers have control over their personal information and that it is used ethically and responsibly.
Initiatives for Transparency and Affordability
The Australian government has implemented several initiatives to promote transparency and affordability in the insurance market. These initiatives aim to empower consumers by providing them with more information about insurance products and services, enabling them to make informed decisions and compare prices effectively.
- The Insurance Comparison Website (ICW), operated by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), allows consumers to compare insurance quotes from different providers online. This platform promotes competition and helps consumers find the best deals.
- The Insurance Council of Australia (ICA), an industry body, has developed a number of initiatives to improve transparency and consumer understanding of insurance products. These initiatives include the development of standardized product disclosure statements and the provision of online resources and tools for consumers.
- The Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS), an independent body, provides free and impartial dispute resolution services for consumers who have complaints about insurance products and services.
Government Programs and Subsidies
The Australian government offers several programs and subsidies to assist consumers with insurance costs. These programs target specific groups or situations, such as low-income earners, people with disabilities, or those affected by natural disasters.
- The National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) provides funding for disability support services, including insurance products. The NDIS can help individuals with disabilities access affordable insurance coverage for their specific needs.
- The Natural Disaster Relief and Recovery Arrangements (NDRRA) provides financial assistance to individuals and communities affected by natural disasters, including insurance-related costs. The NDRRA can help individuals recover from the financial impact of natural disasters and rebuild their lives.
- The Commonwealth Seniors Health Card (CSHC) provides access to discounted health care services, including some insurance products. The CSHC can help seniors access affordable insurance coverage and reduce their overall health care costs.
Final Review
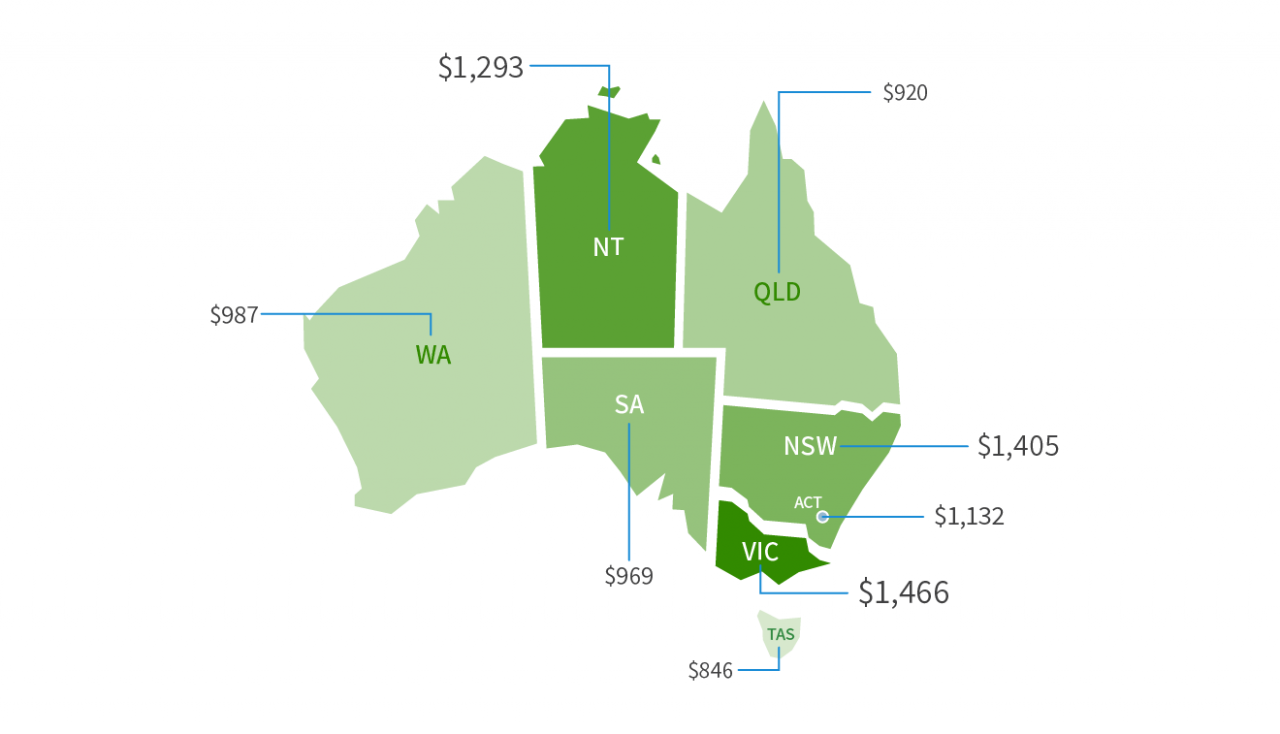
Navigating the complexities of insurance costs in Australia can be daunting, but by understanding the factors that influence premiums, comparing different providers, and implementing cost-saving strategies, individuals can secure the necessary coverage without breaking the bank. By staying informed about government initiatives and consumer protection laws, consumers can ensure they are treated fairly and receive the best possible value for their insurance investments.
FAQ Insights
What are the most common types of insurance in Australia?
The most common types of insurance in Australia include health insurance, car insurance, home insurance, and life insurance.
How can I compare insurance quotes from different providers?
You can use online comparison websites, contact insurance brokers, or directly contact insurance providers to obtain quotes. Ensure you compare similar coverage levels and features before making a decision.
Are there any government subsidies available for insurance costs?
Yes, the Australian government offers various subsidies and programs to assist individuals with insurance costs, particularly for health insurance. You can check with the government or a financial advisor for more information.