- Introduction to Private Health Insurance in Australia
- Tax Deductibility of Private Health Insurance Premiums
- Tax Deductible Components of Private Health Insurance
- Tax Deductible Expenses for Private Health Insurance
- Impact of Tax Deductions on Private Health Insurance
- Additional Considerations for Tax Deductibility: Is Private Health Insurance Tax Deductible In Australia
- Resources and Further Information
- Wrap-Up
- FAQ Corner
Is private health insurance tax deductible in Australia? This is a question many Australians ask, especially as healthcare costs continue to rise. Navigating the complex world of private health insurance can be challenging, but understanding the tax implications is crucial for making informed decisions.
Private health insurance offers a range of benefits, from covering hospital costs to providing access to a wider range of medical services. But how much does it really cost? Knowing whether you can claim tax deductions for your premiums can significantly impact your overall out-of-pocket expenses.
Introduction to Private Health Insurance in Australia
Private health insurance is a crucial aspect of the Australian healthcare system, offering individuals and families access to a broader range of medical services and potentially shorter waiting times. It acts as a supplementary layer to the public Medicare system, providing additional benefits and choices.
Understanding the different types of private health insurance available is essential for making informed decisions about coverage.
Types of Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance in Australia encompasses a range of options, each tailored to specific needs and budgets. The most common types include:
- Hospital cover: This type of insurance covers the cost of hospital stays, including surgery, accommodation, and other related expenses. Hospital cover is further categorized into different levels, with higher levels offering more comprehensive coverage.
- Extras cover: This type of insurance covers a wide range of medical expenses outside of hospital stays, such as dental, optical, physiotherapy, and alternative therapies. Extras cover can be tailored to individual needs, with different levels of coverage available.
- Combined cover: This option combines both hospital and extras cover, providing comprehensive protection for a range of medical expenses.
Benefits of Private Health Insurance
Choosing private health insurance offers several benefits, including:
- Faster access to treatment: Private health insurance can often reduce waiting times for elective surgery and other medical procedures, compared to relying solely on the public Medicare system.
- Choice of specialists and hospitals: Private health insurance allows individuals to choose from a wider range of specialists and hospitals, including private facilities.
- Coverage for a wider range of services: Private health insurance covers a broader range of medical services, including dental, optical, and physiotherapy, which are not fully covered by Medicare.
- Potential tax benefits: Depending on your income and the type of private health insurance you have, you may be eligible for tax rebates or discounts.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Private Health Insurance
The cost of private health insurance is influenced by several factors, including:
- Age: Younger individuals typically pay lower premiums than older individuals, as they are generally considered to be at lower risk of needing medical care.
- Level of cover: The cost of private health insurance increases with the level of cover chosen, with higher levels of cover offering more comprehensive protection.
- Health status: Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions may pay higher premiums, as they are considered to be at higher risk of needing medical care.
- Location: The cost of private health insurance can vary depending on your location, as different regions may have different healthcare costs.
- Lifestyle factors: Factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and weight can influence the cost of private health insurance.
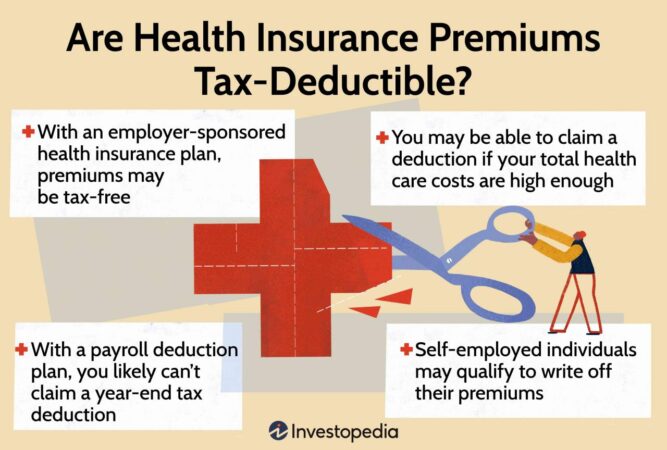
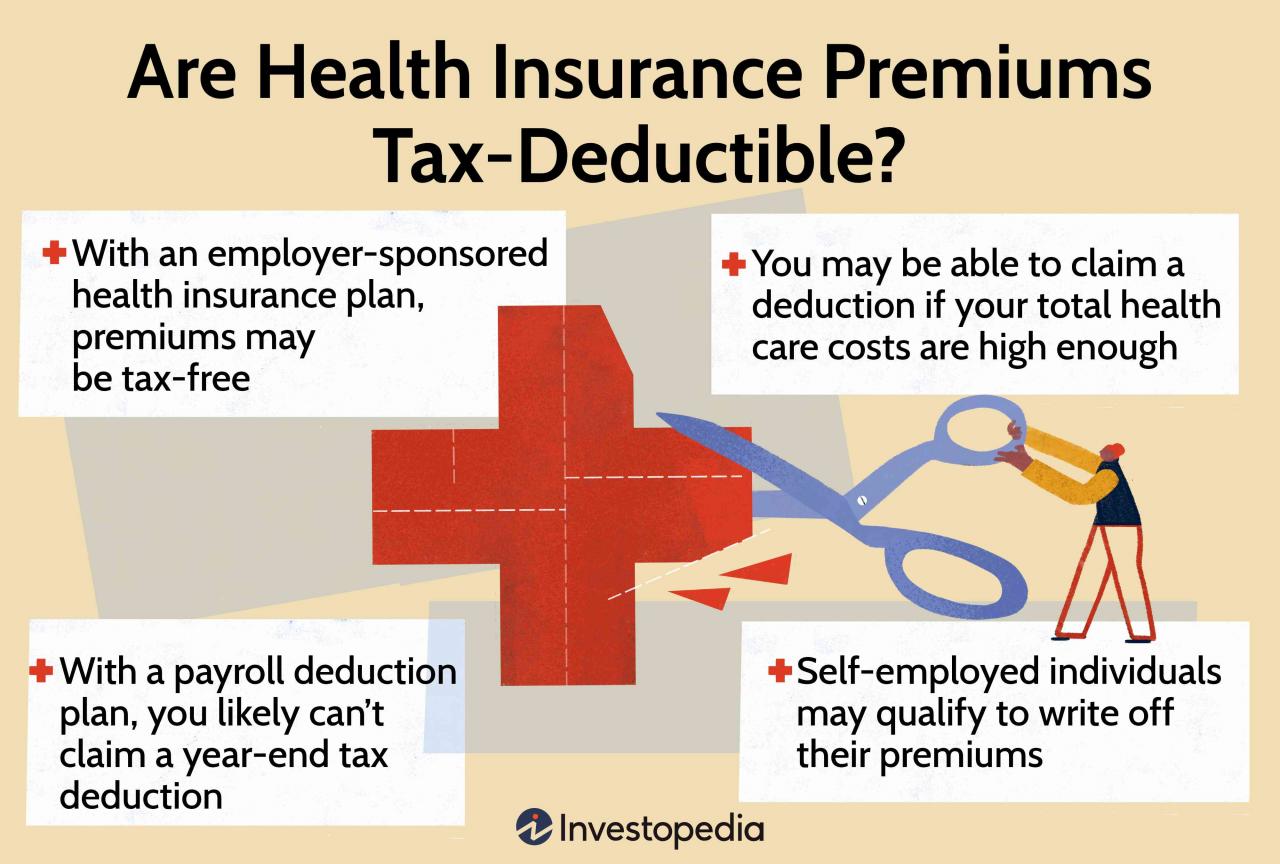
Tax Deductibility of Private Health Insurance Premiums
In Australia, the tax system provides some incentives for individuals to take out private health insurance. This is achieved through tax deductions, which can reduce your taxable income and ultimately lower your tax liability.
Tax Deductible Private Health Insurance Premiums
The tax deductibility of private health insurance premiums depends on specific criteria. To claim a tax deduction for your private health insurance premiums, you must meet the following conditions:
- You must be a resident of Australia.
- You must be 65 years of age or older.
- You must be receiving a government pension or allowance, such as the Age Pension, Disability Support Pension, or Carer Payment.
- You must have a “Lifetime Health Cover” (LHC) loading on your private health insurance policy. This loading is applied to policies taken out after a certain age, and it increases the premium cost. It’s designed to encourage people to take out private health insurance earlier in life.
Types of Private Health Insurance Premiums Tax Deductible
The types of private health insurance premiums that are tax deductible are:
- Premiums for hospital cover.
- Premiums for ancillary cover, such as dental, optical, and physiotherapy.
- Premiums for ambulance cover.
Limitations and Restrictions
There are some limitations and restrictions on the tax deductibility of private health insurance premiums:
- The tax deduction is only available for the portion of your premium that covers hospital and ancillary cover. Premiums for ambulance cover are not tax deductible.
- The tax deduction is limited to the amount of your premium that exceeds a certain threshold. This threshold is reviewed annually by the Australian government and is indexed to inflation. For the 2023-24 financial year, the threshold is $1,740 for singles and $3,480 for couples.
- You can only claim a tax deduction for private health insurance premiums if you have paid them during the financial year. You cannot claim a tax deduction for premiums paid in a previous financial year.
For example, if your total private health insurance premium for the 2023-24 financial year is $2,500, and the threshold for singles is $1,740, you can only claim a tax deduction for $760 (the amount exceeding the threshold).
Tax Deductible Components of Private Health Insurance

You can claim tax deductions for certain components of your private health insurance premiums, which can help reduce your tax liability. These components are generally categorized as hospital and ancillary cover.
Hospital and Ancillary Cover Deductibility
The deductibility of hospital and ancillary cover premiums depends on your age and whether you are claiming the private health insurance rebate.
- Individuals aged 30 or over who claim the private health insurance rebate can claim a tax deduction for their hospital and ancillary cover premiums.
- Individuals aged under 30 can only claim a tax deduction for their hospital and ancillary cover premiums if they have a “Lifetime Health Cover” (LHC) loading applied to their premiums. The LHC loading is a penalty applied to individuals who take out private health insurance after the age of 30. This loading can be reduced or removed if you hold continuous private health insurance for a certain period.
To claim a tax deduction for hospital and ancillary cover, you need to meet specific criteria:
- You must be a resident of Australia.
- You must have paid the premiums yourself. This means you cannot claim a deduction for premiums paid by your employer or someone else.
- You must have held the private health insurance policy for the entire financial year. If you cancel your policy during the year, you can only claim a deduction for the premiums you paid up to the date of cancellation.
- You must have a valid policy with a registered private health insurer.
Extras Cover Deductibility, Is private health insurance tax deductible in australia
Extras cover, which covers things like dental, physiotherapy, and optical expenses, is generally not tax deductible. However, there are some exceptions:
- Individuals with a pre-existing condition may be able to claim a tax deduction for extras cover premiums if they meet specific criteria. This is usually only applicable if the extras cover is specifically designed to cover the pre-existing condition.
- Individuals who are self-employed may be able to claim a tax deduction for extras cover premiums as a business expense if they can demonstrate that the cover is necessary for their work.
Tax Deductible Expenses for Private Health Insurance
Beyond the premiums you pay, certain expenses related to your private health insurance can be claimed as tax deductions in Australia. These deductions can help reduce your overall tax liability, making private health insurance even more affordable.
Expenses Deductible for Private Health Insurance
The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) allows deductions for various expenses associated with private health insurance. Here’s a table outlining the eligible expenses, criteria, and maximum deductible amounts:
| Expense Type | Eligibility Criteria | Maximum Deductible Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Private Health Insurance Premiums | Must be a resident of Australia and hold a private health insurance policy. | No maximum limit. |
| Out-of-Pocket Medical Expenses | Expenses not covered by your private health insurance, such as:
|
No maximum limit, but must exceed a threshold of $2,200 per individual or $4,400 per family. |
| Overseas Medical Expenses | Expenses incurred for medical treatment received overseas, if your policy covers it. | No maximum limit. |
Impact of Tax Deductions on Private Health Insurance
Tax deductions play a significant role in making private health insurance more affordable for Australians. By reducing your taxable income, tax deductions effectively lower the overall cost of your health insurance premiums.
Impact of Tax Deductions on the Overall Cost
Tax deductions directly reduce the amount of tax you pay. The amount of the deduction depends on your individual circumstances, including your income and the type of health insurance policy you hold. The lower your taxable income, the greater the impact of the tax deduction.
Comparison of Costs with and Without Tax Deductions
To illustrate the impact of tax deductions, consider a hypothetical example:
Scenario: An individual with an annual taxable income of $80,000 pays a $2,000 annual premium for private health insurance. Assuming a marginal tax rate of 32.5%, the tax deduction would be $650 (32.5% of $2,000). This means the individual would effectively pay only $1,350 for their health insurance after the tax deduction.
Table:
| Scenario | Premium | Tax Deduction | Effective Cost |
|—|—|—|—|
| With Tax Deduction | $2,000 | $650 | $1,350 |
| Without Tax Deduction | $2,000 | $0 | $2,000 |
This example highlights how tax deductions can significantly reduce the cost of private health insurance. The effective cost of the insurance is lower for individuals who can claim tax deductions.
Making Private Health Insurance More Affordable
Tax deductions can make private health insurance more affordable in the following ways:
* Reduced Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Tax deductions lower the actual cost of health insurance, leaving more money in your pocket for other expenses.
* Increased Affordability: Tax deductions make private health insurance more accessible to a wider range of individuals, particularly those with lower incomes.
* Incentive for Health Coverage: The availability of tax deductions encourages individuals to take out private health insurance, contributing to a healthier and more sustainable healthcare system.
Additional Considerations for Tax Deductibility: Is Private Health Insurance Tax Deductible In Australia
There are a few additional factors to consider when determining the tax deductibility of your private health insurance premiums. These factors can impact the amount of tax deductions you are eligible for, so it’s important to understand them thoroughly.
Changes in Income or Health Status
Changes in your income or health status can significantly affect your eligibility for tax deductions on your private health insurance premiums. If your income falls below a certain threshold, you may no longer be eligible for the full tax rebate, or any rebate at all. Similarly, if your health status changes and you require more extensive health cover, you may be able to claim a higher tax deduction. It’s essential to review your policy and tax situation regularly to ensure you’re claiming all the deductions you’re entitled to.
Maximizing Tax Deductions
To maximize your tax deductions for private health insurance, you can consider the following strategies:
- Choose the right level of cover: Selecting a policy that aligns with your individual needs and circumstances can help you optimize your tax deductions. For example, if you have a pre-existing medical condition, you may want to consider a policy that provides comprehensive coverage for your specific needs.
- Review your policy regularly: As your health and financial situation change, it’s crucial to review your private health insurance policy to ensure it still meets your requirements and provides the most favorable tax deductions.
- Keep accurate records: Maintain meticulous records of your private health insurance premiums and any related expenses, such as out-of-pocket medical costs. This will help you substantiate your claims for tax deductions.
- Seek professional advice: Consulting a financial advisor or tax professional can provide valuable insights into maximizing your tax deductions for private health insurance. They can help you understand the intricacies of the tax system and identify any potential opportunities to minimize your tax liability.
Resources and Further Information
It’s crucial to have access to accurate and up-to-date information when navigating the complexities of tax deductions for private health insurance. This section provides a comprehensive guide to relevant resources, contact details, and key terms for your understanding.
Official Government Websites
Official government websites are your primary source for reliable and comprehensive information about tax deductions for private health insurance. These websites offer detailed guidelines, eligibility criteria, and current legislation.
- Australian Taxation Office (ATO): The ATO website is the most comprehensive resource for information about tax deductions in Australia. It provides detailed information on the eligibility criteria, documentation requirements, and claiming procedures for private health insurance deductions. You can find relevant information on the ATO website, including a dedicated section on private health insurance, tax guides, and frequently asked questions.
- Department of Health: This website provides information about private health insurance in Australia, including policies, benefits, and costs. You can find details about the Private Health Insurance Act 1973, which governs the industry.
Financial Advisors
Seeking advice from qualified financial advisors can provide personalized guidance and ensure you make informed decisions regarding your private health insurance and tax deductions.
- Financial Planning Association of Australia (FPA): The FPA website provides a directory of certified financial planners across Australia. You can search for advisors specializing in tax planning and private health insurance.
- Association of Financial Advisers (AFA): The AFA also provides a directory of certified financial advisors who can offer expert advice on tax deductions and financial planning.
Key Terms and Definitions
Understanding key terms is crucial for navigating tax deductions for private health insurance. Here’s a list of common terms and their definitions.
- Private Health Insurance: A type of insurance that covers medical expenses, including hospital and ancillary benefits.
- Tax Deductible: Expenses that can be claimed as deductions on your income tax return, reducing your taxable income.
- Medicare Levy Surcharge (MLS): An additional tax levied on higher-income earners who do not have private health insurance.
- Lifetime Health Cover (LHC): A loading applied to private health insurance premiums for individuals who take out cover after a certain age.
Wrap-Up

Understanding the tax deductibility of private health insurance premiums is essential for maximizing your financial benefits. By carefully considering the conditions, types of cover, and eligible expenses, you can potentially reduce your tax liability and make private health insurance more affordable. Remember, consulting with a qualified financial advisor can help you navigate the complexities of tax deductions and make informed decisions about your health insurance choices.
FAQ Corner
What are the main types of private health insurance in Australia?
The main types include hospital cover, ancillary cover (extras), and combined hospital and ancillary cover. Hospital cover provides financial assistance for hospital stays and procedures, while ancillary cover covers services like dental, physiotherapy, and optical care. Combined cover offers both hospital and ancillary benefits.
Are all private health insurance premiums tax deductible?
No, not all premiums are tax deductible. You must meet specific eligibility criteria, such as being a resident of Australia and having a valid policy. The deductibility also depends on the type of cover and the specific expenses incurred.
How do I claim tax deductions for my private health insurance premiums?
You can claim deductions when you lodge your annual tax return. You’ll need to provide evidence of your premium payments and other eligible expenses. The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) website has detailed information and resources to guide you through the process.