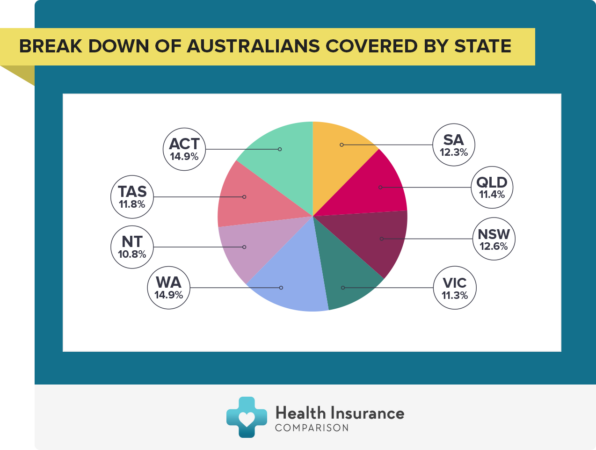
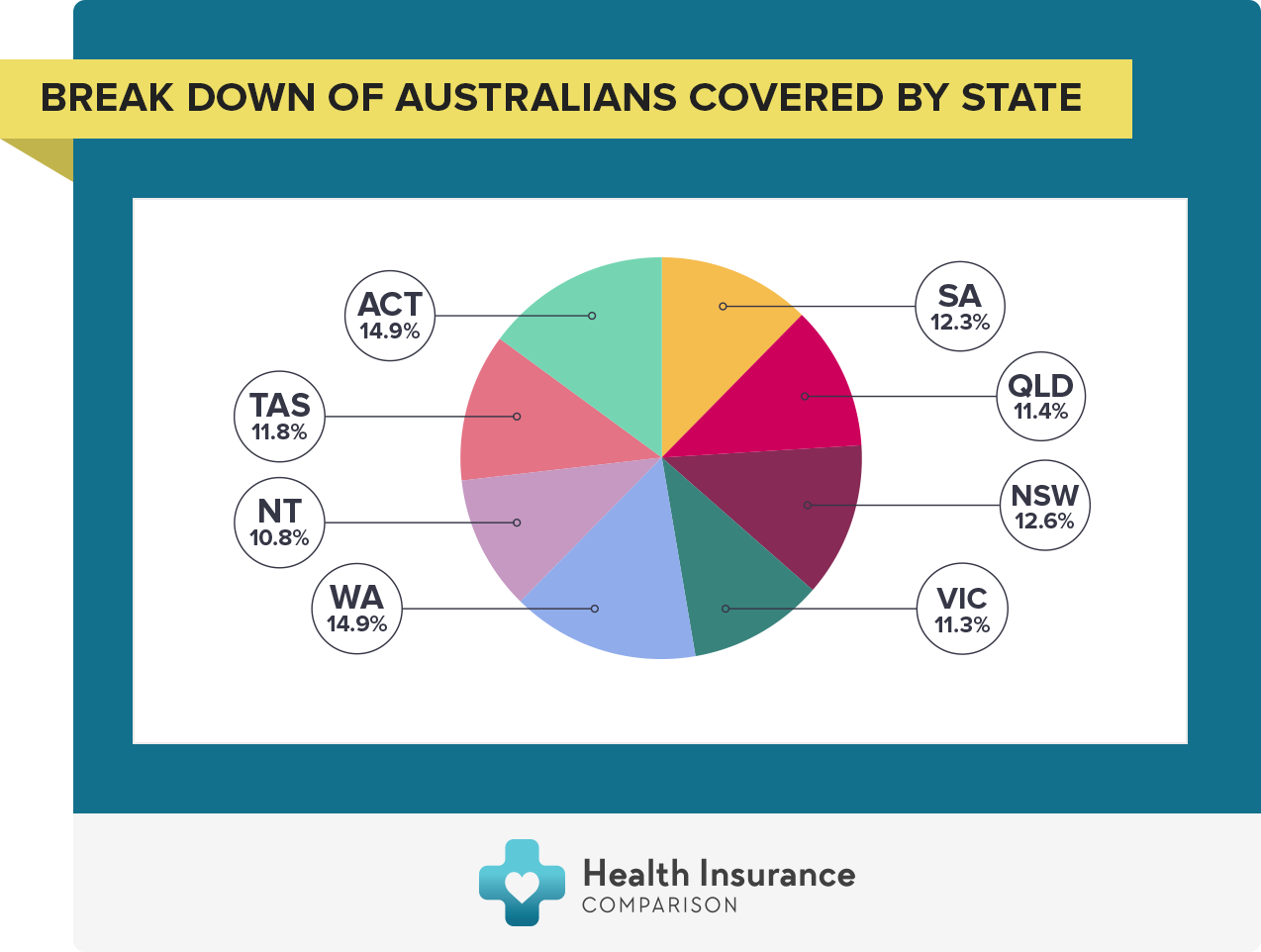
- Overview of Australian Health Insurance
- Types of Private Health Insurance
- Hospital Cover
- Extras Cover
- Choosing the Right Health Insurance
- Health Insurance Rebates and Incentives
- Health Insurance Costs and Premiums: Types Of Health Insurance In Australia
- Managing Your Health Insurance
- Summary
- Detailed FAQs
Types of health insurance in Australia play a crucial role in navigating the healthcare system, offering a range of options to complement the public Medicare scheme. Understanding the different types of private health insurance available is essential for individuals and families seeking to enhance their healthcare coverage and access to medical services.
This guide delves into the complexities of private health insurance in Australia, exploring the various policy types, coverage levels, and factors influencing costs. From hospital cover to extras cover, we provide a comprehensive overview to empower you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your health insurance needs.
Overview of Australian Health Insurance
Australia has a unique healthcare system that combines universal public healthcare with a private health insurance market. This system aims to provide access to healthcare for all Australians while allowing individuals to choose additional coverage through private insurance.
Medicare
Medicare is Australia’s universal healthcare system, funded through taxes. It provides essential healthcare services, including:
- Doctor’s consultations
- Hospital stays
- Some medications
- Some diagnostic tests
Medicare covers most basic healthcare needs, but it has limitations. For example, it may not cover all medical expenses, such as private hospital rooms, dental care, or physiotherapy.
Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance provides additional coverage beyond what Medicare offers. It is a voluntary system where individuals choose the level of coverage they need and can afford. Private health insurance policies can cover:
- Private hospital rooms
- Dental care
- Physiotherapy
- Other medical expenses not covered by Medicare
Private health insurance providers in Australia are regulated by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA). They offer a range of policies with different levels of coverage and premiums.
Factors Influencing the Need for Private Health Insurance
Several factors can influence an individual’s decision to purchase private health insurance, including:
- Access to Private Hospitals: Private health insurance provides access to private hospitals, offering shorter waiting times for elective surgeries and potentially more comfortable facilities.
- Coverage for Specific Medical Needs: Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or specific healthcare requirements might opt for private insurance to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Financial Protection: Private health insurance can help protect against high out-of-pocket medical expenses, especially for procedures or treatments not fully covered by Medicare.
- Government Incentives: The Australian government offers various incentives to encourage people to take out private health insurance, including tax rebates and subsidies.
Types of Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance in Australia offers a range of policies designed to cater to diverse needs and budgets. Understanding the different types of policies and their coverage can help you make an informed decision about the best option for your individual circumstances.
Types of Private Health Insurance Policies
Private health insurance policies in Australia can be broadly categorized into three main types:
- Hospital Cover: This type of policy covers the costs of hospital treatment, including accommodation, surgery, and other medical procedures performed in a public or private hospital.
- Extras Cover: Extras cover provides financial assistance for a wide range of medical services and treatments not typically covered by Medicare, such as dental, optical, physiotherapy, and alternative therapies.
- Combined Hospital and Extras Cover: This comprehensive policy combines the benefits of both hospital and extras cover, offering a complete package of healthcare protection.
Comparing Private Health Insurance Policies
The following table compares the coverage and benefits of each type of private health insurance policy:
| Policy Type | Coverage | Benefits | Cost Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Cover | Covers hospital treatment, including accommodation, surgery, and medical procedures. |
|
|
| Extras Cover | Covers medical services and treatments not covered by Medicare, such as dental, optical, physiotherapy, and alternative therapies. |
|
|
| Combined Hospital and Extras Cover | Covers both hospital treatment and a range of extras services. |
|
|
Hospital Cover

Hospital cover is a vital component of private health insurance in Australia, providing financial protection against the costs of hospital treatment. It offers coverage for various medical procedures, including surgeries, inpatient care, and other related services.
Levels of Hospital Cover
Private health insurers offer different levels of hospital cover to cater to diverse needs and budgets. The three primary levels are:
- Basic
- Mid-level
- Comprehensive
The level of cover chosen directly impacts the range of hospital services and procedures covered, as well as the associated premiums.
Benefits of Different Hospital Cover Levels
The benefits associated with each hospital cover level vary significantly.
Basic Hospital Cover
Basic hospital cover provides the most limited coverage and typically includes:
- Public hospital waiting list accommodation
- Some surgical procedures
- Limited coverage for certain medical conditions
Mid-Level Hospital Cover
Mid-level hospital cover offers a broader range of benefits compared to basic cover, including:
- Access to private hospital accommodation
- A wider selection of surgical procedures
- Coverage for a greater variety of medical conditions
Comprehensive Hospital Cover
Comprehensive hospital cover provides the most extensive coverage, including:
- Full access to private hospital accommodation and services
- Coverage for a wide range of surgical procedures
- Comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical conditions
Implications of Choosing a Hospital Cover Level
The choice of hospital cover level has significant implications for individuals and families.
Financial Considerations
- Basic hospital cover typically has the lowest premiums, while comprehensive cover has the highest.
- The cost of premiums can vary significantly depending on factors such as age, health status, and the insurer.
Health Needs
- Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions may require a higher level of cover to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Those who anticipate needing extensive hospital care in the future may benefit from comprehensive cover.
Lifestyle Considerations
- Individuals with active lifestyles or those who engage in high-risk activities may prefer a higher level of cover for potential injuries or illnesses.
- Families with young children may consider comprehensive cover to ensure access to specialized pediatric care.
Extras Cover
Extras cover is a type of private health insurance that helps you pay for a range of health services not covered by Medicare, such as dental, optical, and physiotherapy. While Medicare covers essential healthcare services, it doesn’t cover the costs of many common health services, like dental check-ups, eye tests, or physiotherapy treatments. This is where extras cover comes in, offering a valuable way to supplement your health insurance.
Examples of Common Extras Cover Benefits
Extras cover can provide financial assistance for a wide range of health services, including:
- Dental: This can cover costs for dental check-ups, cleaning, fillings, and more. Some policies might also offer coverage for more extensive procedures like crowns, bridges, or dentures.
- Optical: This can help cover the cost of eye exams, glasses, and contact lenses. Some policies might offer coverage for specific types of lenses or frames.
- Physiotherapy: This can cover the cost of physiotherapy sessions for various conditions, including injuries, back pain, and rehabilitation.
- Chiropractic: This can cover the cost of chiropractic treatments for musculoskeletal issues.
- Massage Therapy: This can cover the cost of massage therapy sessions for various reasons, including stress relief, muscle tension, and pain management.
- Hearing Aids: This can cover the cost of hearing aids and related services.
- Podiatry: This can cover the cost of podiatry services for foot and ankle problems.
- Psychology: This can cover the cost of psychological assessments and therapy sessions.
- Alternative Therapies: Some extras cover policies might offer coverage for alternative therapies like acupuncture, naturopathy, and homeopathy.
How Extras Cover Complements Medicare and Hospital Cover
Extras cover complements Medicare and hospital cover by providing financial assistance for a range of health services that are not covered by these programs.
- Medicare: Medicare provides essential healthcare services like hospital stays, doctor visits, and some medications, but it doesn’t cover the costs of many common health services like dental check-ups, eye tests, or physiotherapy treatments.
- Hospital Cover: Hospital cover helps pay for the costs of hospital stays, but it doesn’t cover the costs of outpatient services like dental, optical, or physiotherapy.
Extras cover fills this gap by providing financial assistance for these services, allowing you to access them without having to pay the full cost out of pocket.
Choosing the Right Health Insurance
Choosing the right private health insurance policy can be a daunting task, but it’s crucial to make an informed decision that meets your individual needs and budget. There are many factors to consider, and taking the time to research and compare options will help you find the best policy for your circumstances.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Private Health Insurance Policy
It’s essential to consider several factors before settling on a policy. These factors will help you narrow down your choices and ensure you’re getting the best value for your money.
- Your Health Needs: Consider your current health status, any pre-existing conditions, and your likelihood of needing hospital care in the future. If you have specific health concerns, ensure the policy covers those treatments.
- Your Budget: Private health insurance premiums can vary significantly depending on the level of cover, age, and other factors. Set a realistic budget and compare policies within your price range.
- Your Lifestyle: Your lifestyle and hobbies can influence your insurance needs. If you’re an active person, you may need a policy that covers sports injuries or physiotherapy. Similarly, if you travel frequently, consider policies with overseas cover.
- Your Family Situation: If you have a family, you’ll need a policy that covers all members. Some policies offer family discounts, so it’s worth comparing these options.
- Your Location: The availability of hospitals and specialists in your area can affect your choice of policy. Ensure the policy you choose provides coverage at hospitals and clinics in your local area.
Comparing Quotes and Benefits from Different Insurers
Once you’ve considered these factors, it’s time to start comparing quotes and benefits from different insurers. This is crucial to ensure you’re getting the best value for your money.
- Use a Comparison Website: Comparison websites allow you to quickly and easily compare quotes from multiple insurers side-by-side. This makes it easy to see which policies offer the best value for your needs.
- Read the Policy Documents: Don’t just rely on the information provided on comparison websites. Carefully read the policy documents to understand the specific benefits and exclusions of each policy.
- Consider the Excess: The excess is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in. Policies with lower excesses generally have higher premiums. Choose an excess that balances your budget with your risk tolerance.
- Look for Value-Added Benefits: Some insurers offer additional benefits, such as discounts on health products or services. These benefits can add value to your policy and make it more attractive.
Flowchart for Choosing the Right Health Insurance Policy
The following flowchart Artikels the steps involved in choosing the right private health insurance policy:
“Remember, choosing the right private health insurance policy is a personal decision. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. Take the time to research and compare options to find the best policy for your individual needs and budget.”
Health Insurance Rebates and Incentives
The Australian government recognizes the importance of private health insurance and offers a system of rebates and incentives to encourage Australians to take up coverage. These programs aim to make health insurance more affordable and accessible, ultimately promoting a healthier population.
Government Health Insurance Rebates
The government’s health insurance rebate system is a significant financial incentive for Australians considering private health insurance. It provides a direct financial contribution towards the cost of your premiums, making coverage more affordable. The rebate is calculated based on your income and the level of cover you choose, with higher rebates available for lower-income earners and those with comprehensive policies.
- Income-Based Rebates: The amount of the rebate you receive is based on your income, with lower-income earners receiving a higher rebate. This ensures that individuals and families with limited financial resources can access private health insurance.
- Level of Cover: The rebate also depends on the level of cover you choose. Comprehensive policies, offering broader coverage, generally attract higher rebates compared to basic policies.
- Lifetime Health Cover Loading: This is an additional premium charged for individuals who take up private health insurance after a certain age. It is designed to encourage younger Australians to take up coverage earlier in life, ensuring a sustainable health insurance system. However, the government offers a loading reduction scheme for those who take up private health insurance before they turn 31. This makes private health insurance more attractive to younger Australians, encouraging them to plan for their future health needs.
Other Incentives for Private Health Insurance
Beyond the government rebate, there are additional incentives available to encourage Australians to take up private health insurance. These include:
- Medicare Levy Surcharge: Individuals with higher incomes who do not have private health insurance are required to pay an additional surcharge on their Medicare levy. This encourages those with the financial capacity to contribute to the health system by taking up private health insurance.
- Tax Deductible Premiums: You can claim a tax deduction for your private health insurance premiums. This further reduces the cost of coverage and can be particularly beneficial for individuals and families in higher tax brackets.
- Private Health Insurance Rebate: This rebate is a direct payment from the government towards your private health insurance premiums, further reducing the cost of coverage. The amount of the rebate is calculated based on your age and the level of cover you choose.
Health Insurance Costs and Premiums: Types Of Health Insurance In Australia
Private health insurance premiums are the monthly or annual fees you pay for your coverage. The cost of these premiums can vary significantly depending on a number of factors, including your age, health status, and the type of policy you choose.
Factors Influencing Premium Costs
The cost of your private health insurance premiums is influenced by several factors. These factors are considered by insurers when calculating your premium.
- Age: Younger people generally pay lower premiums than older people, as they are statistically less likely to require expensive medical treatment.
- Health Status: People with pre-existing medical conditions may pay higher premiums than those in good health. Insurers consider the risk of you needing to claim on your policy, and higher-risk individuals generally pay more.
- Policy Type: The type of policy you choose, including the level of hospital cover and extras cover, will also affect your premium. More comprehensive policies with higher levels of cover will typically cost more.
- Location: Where you live can also influence your premium. Insurers may charge different premiums based on the cost of healthcare in different areas.
- Lifestyle: Your lifestyle choices, such as smoking or engaging in risky activities, can also impact your premium.
Age and Health Status
The relationship between age, health status, and premium costs is complex.
- Age: As you age, your risk of needing medical treatment increases, leading to higher premiums.
- Health Status: People with pre-existing conditions may pay higher premiums as they are considered a higher risk to insurers. For example, someone with diabetes may face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of needing diabetes-related healthcare services.
Premium Structures of Different Insurers
Different insurers have different premium structures. Some insurers may offer lower premiums for younger people, while others may have more competitive rates for people with pre-existing conditions.
- Loading: Some insurers may add a loading to your premium if you have a pre-existing condition. This loading is a percentage increase to your premium based on the risk associated with your condition.
- Discounts: Insurers may offer discounts for things like healthy lifestyle choices, family memberships, or if you’re a member of a particular group, such as a professional association.
Managing Your Health Insurance
Having private health insurance in Australia is a smart decision for your health and financial well-being. But it’s not enough to just have a policy; you need to manage it effectively to get the most out of your coverage. This involves understanding your policy, making claims, staying informed about changes, and taking advantage of available resources.
Understanding Your Policy
It’s crucial to thoroughly understand the details of your private health insurance policy. This ensures you know what benefits you have, what is covered, and what limitations or exclusions apply. Familiarizing yourself with the policy document, including the product disclosure statement (PDS), is the first step.
- Review the PDS: This document provides a comprehensive overview of your policy, including the benefits, exclusions, waiting periods, and premium details. It’s essential to read it carefully and keep it for reference.
- Understand Your Cover: Identify the specific types of cover you have, such as hospital, extras, or ambulance cover. This will help you understand what services are included and what you are entitled to claim for.
- Check Waiting Periods: Some benefits, like certain surgical procedures, may have waiting periods before you can claim. Ensure you understand these waiting periods to avoid surprises when you need to access care.
- Be Aware of Exclusions: Every policy has exclusions, which are services or treatments not covered. Familiarize yourself with these to avoid unnecessary claims or disappointment.
Making Claims
When you need to use your health insurance, making a claim is a straightforward process. However, it’s essential to understand the steps involved and gather the necessary documentation.
- Know Your Claim Process: Your insurer will provide you with a claims process Artikeld in your policy documents or on their website. Understand the steps involved and the required documentation.
- Gather Necessary Information: This typically includes details of the service, the provider’s details, and your policy number. You may also need to provide receipts or invoices.
- Submit Your Claim: You can usually submit claims online, by phone, or by mail. Follow your insurer’s instructions carefully and ensure all required information is included.
- Track Your Claim: Most insurers provide online portals or apps where you can track the progress of your claim. This helps you stay informed and ensure it’s processed promptly.
Staying Informed
Health insurance policies can change, and it’s crucial to stay updated on any modifications to your coverage. This includes changes to benefits, premiums, or exclusions.
- Review Policy Updates: Your insurer will notify you of any policy changes, usually by mail, email, or through online updates. Make sure you review these updates carefully and understand the implications.
- Check for Rebates and Incentives: The Australian government offers rebates and incentives for private health insurance. Stay informed about these programs to maximize your benefits.
- Monitor Your Premium: Premiums can fluctuate based on various factors, such as your age, health status, and changes to the policy. Monitor your premiums and consider adjusting your cover if necessary.
Accessing Benefits, Types of health insurance in australia
Your private health insurance provides access to a range of benefits, including hospital cover, extras cover, and other services. To maximize these benefits, it’s essential to understand how to access them.
- Hospital Cover: This covers the costs of inpatient treatment in a private hospital. When you need hospital care, choose a hospital that participates in your insurer’s network to ensure coverage.
- Extras Cover: This covers the costs of a variety of services, such as dental, optical, physiotherapy, and alternative therapies. Check your policy for the specific extras benefits included.
- Other Benefits: Some policies may offer additional benefits, such as ambulance cover or travel insurance. Familiarize yourself with these benefits and how to access them.
Summary
Navigating the world of Australian health insurance can seem daunting, but with a clear understanding of the available options and the factors influencing costs, you can make informed choices that align with your individual circumstances and healthcare priorities. Remember to compare quotes, consider your health needs, and leverage the benefits of the government’s rebate system to maximize your health insurance value.
Detailed FAQs
What is the difference between Medicare and private health insurance?
Medicare is Australia’s universal public health insurance scheme, providing essential healthcare services. Private health insurance supplements Medicare, offering additional coverage for services not fully covered by Medicare, such as private hospital rooms and elective surgeries.
How do I choose the right type of health insurance?
Consider your health needs, budget, and coverage priorities. Factor in the cost of premiums, benefits offered, and any potential government rebates. Consult with a health insurance broker or compare quotes online to find the policy that best suits your individual circumstances.
What are the benefits of having private health insurance?
Private health insurance provides access to a wider range of healthcare services, including private hospital rooms, shorter wait times for elective surgeries, and coverage for extras such as dental and physiotherapy.