What are the universal laws? This question has captivated thinkers and philosophers for centuries, driving them to explore the underlying principles that govern the universe and our place within it. From the ancient Greeks to modern scientists, the search for universal laws has fueled countless discoveries and debates, shaping our understanding of the world and our place in it.
This exploration delves into various perspectives on universal laws, examining their existence, their influence, and their implications. We will navigate through philosophical schools of thought, scientific principles, ethical frameworks, and artistic representations to gain a comprehensive understanding of this profound concept.
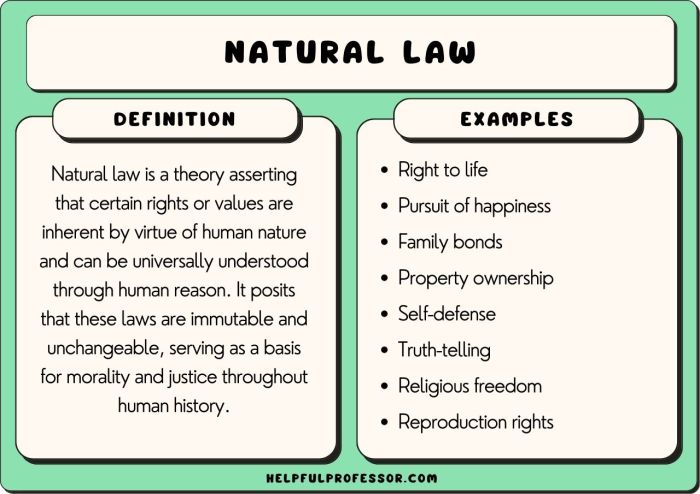
Ethical and Moral Frameworks

Universal laws and ethical principles are deeply intertwined, with the former often serving as a foundation for the latter. Universal laws, by their nature, aim to establish a framework for orderly and just societies, while ethical principles provide guidance for individual conduct and moral decision-making.
The Relationship Between Universal Laws and Ethical Principles
Ethical principles are often informed by universal laws, as these laws reflect societal values and norms. For instance, the universal law against murder is rooted in the ethical principle of respect for human life. This principle, in turn, informs various ethical frameworks, shaping how individuals approach moral dilemmas.
Ethical Frameworks and Universal Laws
Different ethical frameworks offer distinct perspectives on the relationship between universal laws and individual action.
- Utilitarianism: This framework emphasizes maximizing overall happiness and well-being. It suggests that actions are morally right if they produce the greatest good for the greatest number of people. Utilitarianism can support universal laws that promote societal welfare, even if they may infringe upon individual rights in certain situations. For example, a utilitarian might argue that mandatory vaccination laws, while limiting individual autonomy, are justified if they prevent the spread of a deadly disease and protect public health.
- Deontology: This framework emphasizes duty and moral obligation. It suggests that actions are morally right if they adhere to universal moral principles, regardless of their consequences. Deontology places a strong emphasis on respecting individual rights and upholding universal laws that protect those rights. For instance, a deontologist might argue that even if lying could lead to a positive outcome, it is morally wrong because it violates the universal principle of truthfulness.
Applying Universal Laws in Ethical Decision-Making, What are the universal laws
Consider a hypothetical scenario where a doctor discovers a patient has a contagious disease that poses a risk to public health. The universal law in this jurisdiction mandates reporting such diseases to the authorities. However, the patient has requested confidentiality, fearing social stigma. The doctor must now weigh the ethical implications of their actions, considering the universal law, the patient’s rights, and the potential harm to the community.
Conclusion

As we conclude our journey through the vast landscape of universal laws, we are left with a sense of wonder and a renewed appreciation for the complexity and interconnectedness of the universe. The quest for universal truth remains a constant endeavor, one that drives us to explore, question, and strive for a deeper understanding of the world around us. While definitive answers may remain elusive, the pursuit itself offers invaluable insights and a profound sense of purpose.
FAQ Guide: What Are The Universal Laws
Are universal laws absolute and unchanging?
The concept of absolute and unchanging universal laws is a complex one. While some laws, like those in physics, appear to be consistent across different scales and systems, others, like those in ethics, are subject to interpretation and cultural context. It is important to consider the limitations and potential evolution of universal laws.
What is the difference between universal laws and cultural norms?
Universal laws are often seen as overarching principles that apply to all individuals and societies, while cultural norms are specific rules and customs that vary from one culture to another. Universal laws may provide a foundation for ethical behavior, while cultural norms shape specific social practices and expectations.
Do universal laws apply to all living things?
While some fundamental laws of physics and chemistry apply to all matter, including living organisms, the concept of universal laws in the context of life and behavior is more complex. Evolutionary processes and individual adaptations introduce variations that challenge the idea of universally applicable laws.