What are torts in law? In essence, torts are civil wrongs that result in harm to another person or their property. They represent a crucial aspect of our legal system, ensuring that individuals are held accountable for their actions and that victims receive compensation for their losses. From car accidents to defamation, torts encompass a wide range of situations where one party’s actions cause harm to another.
The foundation of tort law lies in the concept of “fault,” where the defendant’s actions or inactions are found to be the cause of the plaintiff’s injuries. Whether it’s intentional wrongdoing, negligence, or strict liability, the legal system aims to restore fairness and balance by providing remedies for those who have been wronged.
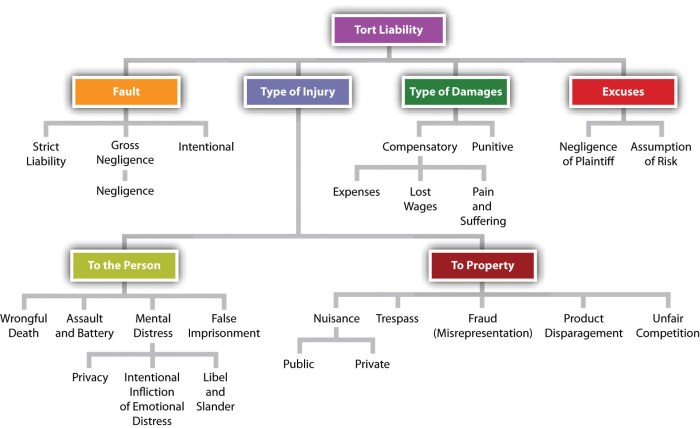
Types of Torts

Torts are civil wrongs that result in harm to another person. They are distinct from crimes, which are offenses against the state. When someone commits a tort, they can be sued in civil court for damages. There are many different types of torts, each with its own specific elements that must be proven in order to establish liability.
Intentional Torts
Intentional torts occur when a person intentionally acts in a way that causes harm to another person. These torts are characterized by the defendant’s intent to cause harm or the knowledge that their actions would likely result in harm. Examples of intentional torts include:
- Battery: The intentional, harmful, or offensive touching of another person without consent.
- Assault: The intentional act of placing another person in apprehension of an imminent harmful or offensive touching.
- False Imprisonment: The intentional confinement of another person without justification or consent.
- Defamation: The publication of false and defamatory statements about another person that harm their reputation.
- Intentional Infliction of Emotional Distress: The intentional act of causing severe emotional distress to another person.
- Trespass to Land: The intentional entry onto the land of another person without permission.
- Trespass to Chattels: The intentional interference with the personal property of another person.
- Conversion: The intentional exercise of dominion or control over the personal property of another person.
Negligence
Negligence is a type of tort that occurs when a person fails to exercise reasonable care and, as a result, causes harm to another person. This is the most common type of tort. The elements of negligence are:
- Duty of Care: The defendant must have owed a duty of care to the plaintiff. This means that the defendant had a legal obligation to act in a way that would not harm the plaintiff.
- Breach of Duty: The defendant must have breached their duty of care by failing to act reasonably. This could be due to a failure to act, or acting in a way that was not reasonable under the circumstances.
- Causation: The defendant’s breach of duty must have caused the plaintiff’s injuries. This means that there must be a direct link between the defendant’s actions and the plaintiff’s harm.
- Damages: The plaintiff must have suffered actual damages as a result of the defendant’s negligence.
Strict Liability, What are torts in law
Strict liability is a type of tort where the defendant is liable for harm caused by their actions, regardless of whether they acted intentionally or negligently. This applies to situations where the activity is considered inherently dangerous, or where the defendant is in a position of control over a dangerous product or animal. Examples of strict liability include:
- Product Liability: Manufacturers and sellers of defective products are strictly liable for injuries caused by those products.
- Dangerous Animals: Owners of wild animals are strictly liable for any injuries caused by those animals.
Outcome Summary: What Are Torts In Law
Understanding torts is essential for navigating the complexities of civil law. From the definition of a tort to the various types and defenses, this exploration has shed light on the critical role that tort law plays in protecting individuals and upholding societal order. By recognizing the principles and implications of tort law, we can better understand our rights and responsibilities as members of society.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between a tort and a crime?
A tort is a civil wrong, while a crime is a violation of criminal law. Torts are generally pursued in civil court, while crimes are prosecuted in criminal court. The primary goal of a tort lawsuit is to compensate the victim, while the goal of a criminal prosecution is to punish the offender.
What are some examples of common torts?
Common torts include negligence (e.g., car accidents), intentional torts (e.g., battery, assault, defamation), and strict liability (e.g., product liability, dangerous animals).
What are the main types of damages awarded in tort cases?
The main types of damages awarded in tort cases include compensatory damages (to compensate for losses), punitive damages (to punish the defendant), and nominal damages (to recognize a legal wrong without substantial harm).




