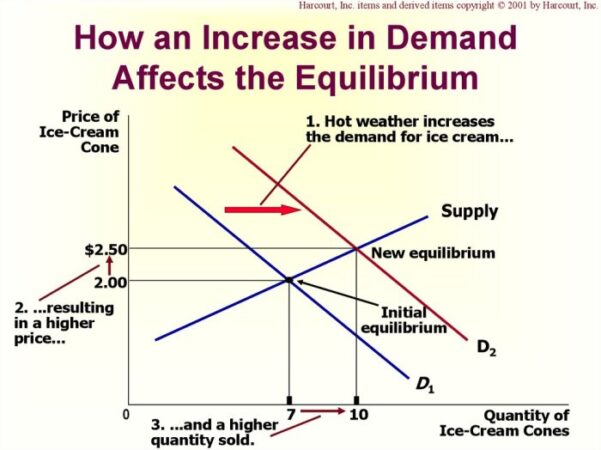
What is law of supply – What is the law of supply? It’s a fundamental economic principle that explains the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity producers are willing to offer in the market. This principle is crucial for understanding how businesses make decisions, how markets function, and how prices are determined.
Imagine a bakery selling croissants. If the price of croissants increases, the bakery might decide to bake more croissants because it’s now more profitable. Conversely, if the price drops, the bakery might reduce its production, as it’s less worthwhile to bake as many croissants. This simple example illustrates the core concept of the law of supply: as the price of a good or service rises, the quantity supplied tends to increase, and vice versa.
Supply Elasticity: What Is Law Of Supply
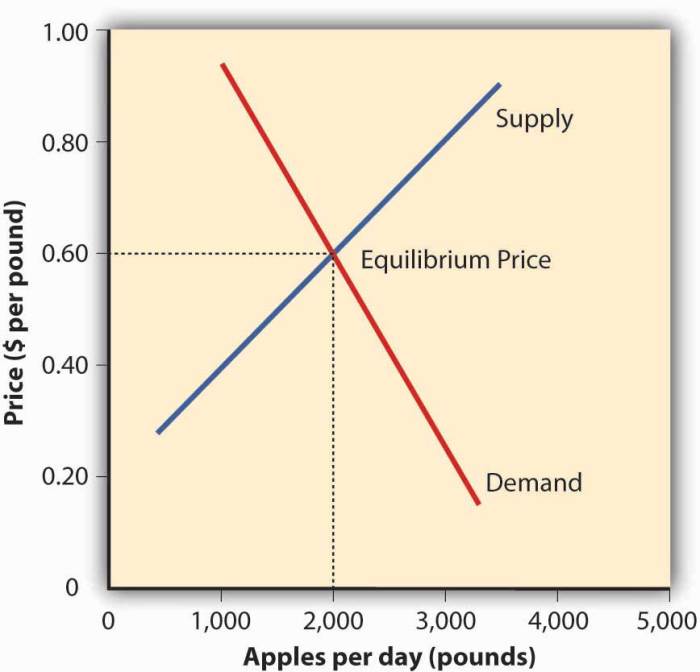
Supply elasticity measures the responsiveness of the quantity supplied of a good or service to changes in its price. It is a crucial concept in economics because it helps us understand how producers will react to price fluctuations and how these reactions will impact market equilibrium.
Definition and Significance
Supply elasticity is the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. It is calculated using the following formula:
Supply Elasticity = (Percentage Change in Quantity Supplied) / (Percentage Change in Price)
A higher supply elasticity indicates that producers are more responsive to price changes, meaning they will significantly increase or decrease production in response to price fluctuations. Conversely, a lower supply elasticity indicates that producers are less responsive to price changes, and their production levels will change minimally despite price variations.
Elastic and Inelastic Supply
Elastic Supply
When supply is elastic, the quantity supplied changes significantly in response to a price change. This typically occurs when producers have flexibility in their production processes, can easily adjust their output levels, and have access to readily available resources. In such cases, a small price increase can lead to a substantial increase in supply, and vice versa.
Inelastic Supply
When supply is inelastic, the quantity supplied changes minimally in response to a price change. This often happens when producers have limited production capacity, face difficulty in acquiring necessary resources, or operate in industries with long production lead times. In these situations, even significant price changes may not result in substantial shifts in supply.
Factors Influencing Supply Elasticity
Several factors can influence the elasticity of supply:
- Availability of Resources: If resources are readily available and easily obtainable, producers can readily adjust their production levels in response to price changes, leading to more elastic supply. Conversely, limited or scarce resources can constrain production flexibility, resulting in inelastic supply.
- Production Time: Goods with short production lead times are more likely to have elastic supply because producers can quickly adjust their output in response to price changes. Conversely, goods with long production lead times tend to have inelastic supply because producers cannot react swiftly to price fluctuations.
- Production Capacity: Producers with excess production capacity can easily increase output in response to price increases, leading to elastic supply. However, producers operating at full capacity may have difficulty expanding production, resulting in inelastic supply.
- Number of Producers: In industries with many producers, a price increase can attract new entrants, leading to an increase in supply and higher elasticity. Conversely, industries with few producers may have limited supply flexibility, resulting in inelastic supply.
- Mobility of Production: Producers with mobile production facilities can readily shift production to areas with higher prices, leading to more elastic supply. Conversely, producers with fixed production facilities may have limited flexibility, resulting in inelastic supply.
Examples of Elastic and Inelastic Supply
Elastic Supply
Examples of goods with elastic supply include:
- Agricultural Products: Farmers can often adjust their production levels in response to price changes by planting different crops or varying the amount of land they cultivate. This makes agricultural products generally have elastic supply.
- Manufactured Goods: Many manufactured goods have elastic supply because producers can readily adjust their production lines to accommodate changes in demand. For example, a car manufacturer can increase production if the price of cars rises.
Inelastic Supply
Examples of goods with inelastic supply include:
- Crude Oil: Crude oil production involves significant investments in exploration, drilling, and refining, making it difficult to adjust production levels quickly in response to price changes. Therefore, crude oil tends to have inelastic supply.
- Medical Services: Medical services often have inelastic supply because the number of qualified medical professionals is limited, and the training process is long and expensive. Even with significant price increases, the supply of medical services may not increase substantially.
Real-World Applications
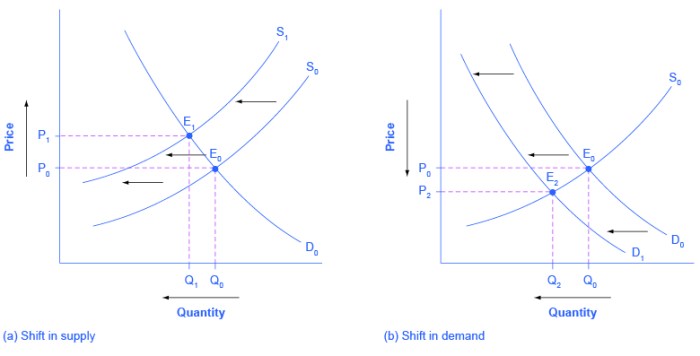
The law of supply is a fundamental principle in economics that has far-reaching implications for businesses, consumers, and the overall economy. Understanding how supply interacts with demand is crucial for making informed decisions in various industries and contexts.
Impact of Supply Disruptions on Market Prices, What is law of supply
Supply disruptions can significantly impact market prices, often leading to price increases. This occurs when the supply of a product or service decreases while demand remains relatively constant or even increases. The scarcity of the product drives up its price as consumers compete for limited availability.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain disruptions led to shortages of essential goods like masks, hand sanitizers, and certain medical supplies. The increased demand coupled with limited supply resulted in a surge in prices for these items.
Businesses Using Supply and Demand Principles
Businesses utilize supply and demand principles to make informed decisions regarding production, pricing, and inventory management. They analyze market trends to anticipate changes in demand and adjust their supply accordingly.
- Pricing Strategies: Businesses can use supply and demand principles to set prices that maximize profits. For instance, if demand for a product is high, businesses may raise prices to capitalize on the increased willingness of consumers to pay more. Conversely, if demand is low, businesses may lower prices to stimulate sales.
- Production Decisions: Businesses consider the anticipated demand for their products when making production decisions. They aim to produce enough to meet demand without overstocking or facing shortages. For example, a clothing retailer might increase production of a particular style if it becomes popular, anticipating continued demand.
- Inventory Management: Supply and demand principles are essential for effective inventory management. Businesses track sales patterns and demand fluctuations to optimize their inventory levels. They aim to have enough stock to meet demand without incurring excessive storage costs or facing stockouts.
Role of Supply in Economic Growth and Development
Supply plays a vital role in economic growth and development by contributing to increased productivity, job creation, and improved living standards.
- Productivity: Increased supply of goods and services leads to greater productivity, as businesses can produce and distribute more efficiently. This can be achieved through technological advancements, improved infrastructure, and access to resources.
- Job Creation: As businesses expand their production to meet increased demand, they often create new jobs. This boosts employment opportunities and contributes to economic growth.
- Living Standards: Increased supply of goods and services can lead to lower prices and greater affordability for consumers, improving their living standards.
Final Summary
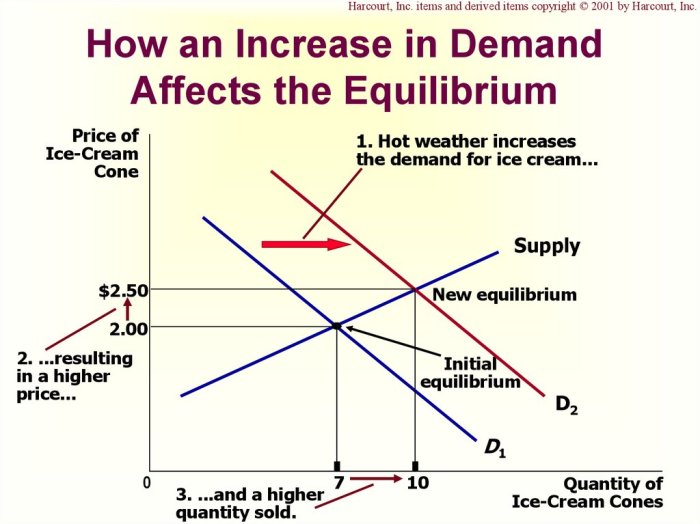
Understanding the law of supply is essential for comprehending the intricate workings of markets and the forces that shape prices. It helps us analyze how businesses respond to changes in market conditions, how technological advancements impact production, and how government policies can influence supply. By grasping this fundamental economic principle, we gain valuable insights into the dynamics of the marketplace and the complex interplay of supply and demand.
FAQ Compilation
What is the difference between supply and demand?
Supply refers to the amount of a good or service that producers are willing to offer at a given price, while demand represents the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing to buy at a given price.
How does the law of supply relate to the law of demand?
The law of supply and the law of demand work together to determine the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. The law of supply states that as prices rise, producers offer more, while the law of demand states that as prices rise, consumers buy less. The point where these two forces meet is the equilibrium point.
What are some real-world examples of the law of supply in action?
Examples include: a surge in gasoline prices leading to increased oil production, a rise in the price of coffee beans causing coffee shops to increase their prices, and a decrease in the price of smartphones resulting in manufacturers producing fewer smartphones.