What’s the under 18 labor law in vriginia – What’s the under 18 labor law in Virginia? This question is crucial for parents, teenagers, and employers alike, as Virginia has specific regulations governing the employment of minors. Understanding these laws is essential to ensure safe and legal working conditions for young people while balancing their educational needs.
Virginia’s Child Labor Laws encompass various aspects, including minimum working age, permitted job types, working hours, and hazardous occupations. These regulations are designed to protect minors from exploitation and ensure they can pursue their education without compromising their well-being.
Virginia’s Child Labor Laws
Virginia’s child labor laws are designed to protect the well-being of minors while allowing them to gain valuable work experience. These laws Artikel the minimum age requirements, permissible work types, and limitations on working hours for minors.
Minimum Age for Working
The minimum age for working in Virginia varies depending on the type of work. Generally, minors aged 14 and 15 are allowed to work in certain non-hazardous jobs, while those aged 16 and 17 have more employment options.
- Minors aged 14 and 15 can work in non-hazardous jobs during non-school hours, with limitations on the number of hours they can work each day and week.
- Minors aged 16 and 17 can work in a wider range of jobs, including those considered hazardous, but still face restrictions on working hours and the types of jobs they can perform.
- Minors under 14 years old are generally prohibited from working in Virginia, except for certain limited exceptions, such as working for their parents or in family-owned businesses.
Types of Jobs Permitted for Minors
Virginia’s child labor laws categorize jobs into different categories based on their potential hazards.
- Non-Hazardous Jobs: These are jobs considered safe for minors, such as retail sales, office work, and food service.
- Hazardous Jobs: These jobs involve potential risks to minors’ safety and health. Minors under 18 are generally prohibited from performing these jobs. Examples include operating machinery, working in construction, and handling hazardous materials.
- Agricultural Jobs: Minors aged 14 and 15 are allowed to work in agriculture, but there are restrictions on the types of tasks they can perform. For example, they cannot operate certain types of farm machinery or work in hazardous conditions.
Working Hours Restrictions
Virginia’s child labor laws impose limits on the number of hours minors can work each day and week.
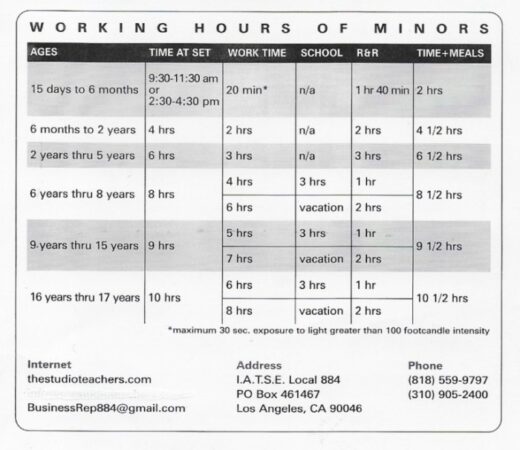
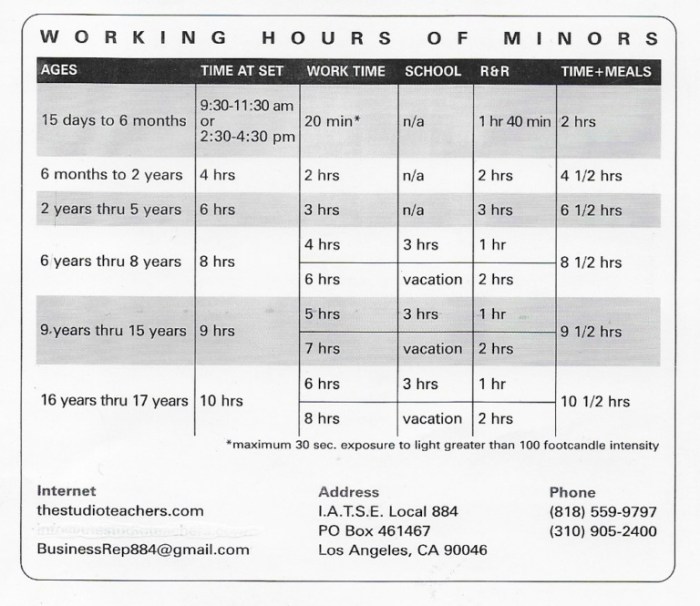
- Minors aged 14 and 15: They can work a maximum of 3 hours per day and 18 hours per week during the school year, and 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during the summer vacation.
- Minors aged 16 and 17: They can work a maximum of 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week during the school year, and 10 hours per day and 48 hours per week during the summer vacation.
Exceptions to General Child Labor Laws
There are a few exceptions to Virginia’s general child labor laws.
- Family Businesses: Minors under 14 may work in family-owned businesses, but they must be closely supervised and cannot perform hazardous tasks.
- Performing Arts: Minors under 14 may work in the performing arts, but they must be supervised and their work hours must be limited.
- Newspapers: Minors aged 12 and older may work in the delivery and distribution of newspapers, but they must be supervised and their work hours must be limited.
Work Permits
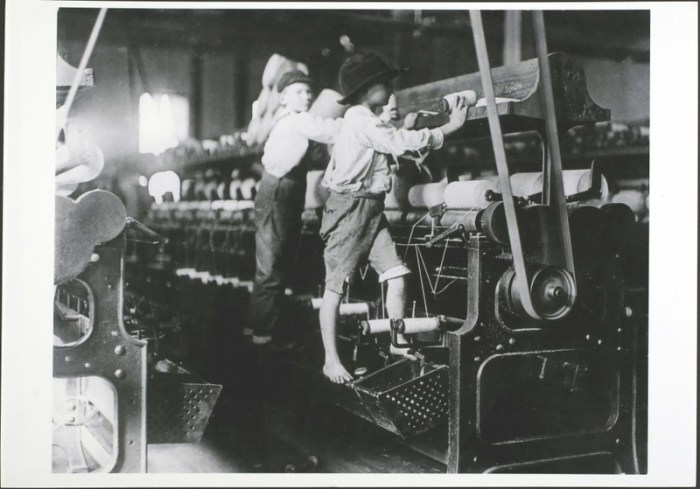
In Virginia, minors under the age of 18 are generally required to obtain a work permit before they can legally work. This requirement ensures that young workers are protected from exploitation and that their education and well-being are not compromised.
The Process for Obtaining a Work Permit
To obtain a work permit, a minor must follow a specific process involving their school, parents, and the Virginia Department of Labor and Industry (DOLI).
Documents Needed to Apply for a Work Permit
The following documents are typically required to apply for a work permit in Virginia:
- Application for Employment Certificate: This form is available online from the Virginia Department of Labor and Industry or can be obtained from the school. It must be completed by the minor, their parent or guardian, and the employer.
- Proof of Age: This can be a birth certificate, passport, or other official document that verifies the minor’s age.
- School Records: The minor must provide evidence of their school enrollment and attendance. This may include a report card, transcript, or letter from the school.
- Employer’s Information: The employer must provide details about the job, including the hours of work, the type of work, and the wage rate.
- Parent or Guardian Consent: The minor’s parent or guardian must sign the application form, indicating their consent to the minor’s employment.
The Role of the School in the Work Permit Process
The school plays a crucial role in the work permit process. The school is responsible for verifying the minor’s age, enrollment, and attendance records. The school counselor or principal will typically review the application and issue a work permit if all requirements are met.
Hazardous Occupations: What’s The Under 18 Labor Law In Vriginia

Virginia’s Child Labor Laws aim to protect young workers by restricting their participation in certain hazardous occupations. These restrictions are designed to safeguard minors from potential risks and ensure their well-being. This section Artikels the prohibited hazardous occupations for minors in Virginia.
Prohibited Hazardous Occupations
The following table lists the occupations prohibited for minors in Virginia, along with the age restrictions and relevant legal citations.
| Occupation | Description | Age Restriction | Legal Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logging | Operating, assisting in the operation of, or being employed in proximity to logging equipment, such as chainsaws, skidders, and logging trucks. | Under 18 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
| Mining | Working in underground mines, surface mines, or mills that process minerals. | Under 18 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
| Meatpacking | Working in meatpacking plants where there is exposure to hazardous machinery, chemicals, or biological hazards. | Under 18 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
| Construction | Performing tasks involving the operation of heavy equipment, working at heights, or handling hazardous materials. | Under 16 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
| Agriculture | Operating farm machinery, handling pesticides, or working in confined spaces. | Under 16 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
| Manufacturing | Working in factories or manufacturing plants where there is exposure to hazardous machinery, chemicals, or dust. | Under 18 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
| Transportation | Operating motor vehicles, trucks, or buses for commercial purposes. | Under 18 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
| Firefighting | Engaging in firefighting activities, including responding to emergencies and operating fire apparatus. | Under 18 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
| Law Enforcement | Performing law enforcement duties, such as making arrests, carrying firearms, or conducting investigations. | Under 18 years of age | Virginia Code § 40.1-103 |
Educational Requirements
In Virginia, the law requires minors to attend school, and this obligation can sometimes conflict with their desire to work. This section delves into the specific regulations regarding school attendance and the impact of employment on a minor’s educational journey. It also explores how minors can effectively manage their time and responsibilities to ensure a successful balance between work and school.
Mandatory School Attendance Laws
Virginia’s compulsory school attendance laws mandate that children between the ages of 5 and 18 attend school or be enrolled in an approved home schooling program. The law requires children to attend school for at least 180 days each year, and they must be enrolled in a school until they reach the age of 18 or graduate from high school, whichever comes first.
Impact of Work on School Attendance
While working can offer valuable life skills and financial independence, it can also pose challenges to a minor’s school attendance. Working long hours or shifts that clash with school schedules can lead to fatigue, reduced concentration, and difficulty keeping up with schoolwork. Furthermore, balancing work and school can create stress and anxiety, potentially impacting a minor’s academic performance.
Balancing Work and Education
Minors who work should prioritize their education. Here are some strategies for managing work and school effectively:
- Choose a job that aligns with your schedule: Look for jobs that offer flexible hours, such as evenings or weekends, to minimize disruption to school.
- Communicate with your employer: Inform your employer about your school commitments and any potential conflicts with work schedules.
- Prioritize schoolwork: Set aside dedicated time for studying and completing assignments, even if it means adjusting your work hours.
- Seek support from teachers and counselors: Reach out to your teachers or school counselors for guidance on managing schoolwork and any academic challenges you might face.
Exemptions to School Attendance Requirements, What’s the under 18 labor law in vriginia
In some cases, minors may be exempt from the mandatory school attendance requirement for work purposes. These exemptions typically apply to situations where a minor is employed in a family business or farm. However, specific conditions and regulations may apply, and it’s essential to consult with the Virginia Department of Labor and Industry for accurate information.
Resources and Information
Navigating Virginia’s child labor laws can be challenging, but there are resources available to help employers and minors understand their rights and responsibilities. This section provides information about the Virginia Department of Labor and Industry, as well as other relevant resources for employers and minors.
Virginia Department of Labor and Industry
The Virginia Department of Labor and Industry (VDOL) is the primary source of information and enforcement for Virginia’s child labor laws. They offer a range of services to employers and minors, including:
- Providing information about child labor laws and regulations
- Issuing work permits to minors
- Investigating complaints of child labor violations
- Providing educational materials and training on child labor laws
Contact Information
To contact the VDOL, you can use the following information:
| Resource Name | Description | Website | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virginia Department of Labor and Industry | Primary source for child labor information and enforcement | https://www.dli.virginia.gov/ | Phone: (804) 786-2375 Email: dli@dli.virginia.gov |
Other Relevant Resources
In addition to the VDOL, there are other resources available to employers and minors, including:
| Resource Name | Description | Website | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Department of Labor – Wage and Hour Division | Federal agency responsible for enforcing child labor laws | https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd | Phone: (866) 4US-WAGE (487-9243) Email: whdservices@dol.gov |
| National Child Labor Committee | Non-profit organization dedicated to ending child labor | https://www.nclc.org/ | Phone: (212) 679-5785 Email: info@nclc.org |
Ultimate Conclusion
Navigating Virginia’s child labor laws can seem complex, but understanding the basics is crucial for everyone involved. Whether you’re a parent, a teenager seeking employment, or an employer hiring minors, staying informed about these regulations is essential. Remember, adhering to these laws safeguards the well-being of young workers while fostering a fair and responsible work environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the penalties for violating child labor laws in Virginia?
Penalties for violating child labor laws in Virginia can include fines, imprisonment, or both. The severity of the penalty depends on the nature of the violation and the circumstances surrounding it.
Can minors work in family businesses in Virginia?
Yes, minors can work in family businesses in Virginia, but they must still comply with the state’s child labor laws. This means they must be of the minimum working age, work permitted hours, and not engage in hazardous occupations.
What are the age restrictions for working in restaurants in Virginia?
The age restrictions for working in restaurants in Virginia vary depending on the type of work. For example, minors under 16 can work as bussers or food runners, while those 16 and older can work as servers or cooks.