Which branch interprets laws? In the United States, the judicial branch, specifically the Supreme Court, holds the power to interpret the Constitution and federal laws. This process, known as judicial review, is a cornerstone of our legal system, ensuring that laws align with the Constitution’s principles.
The judicial branch’s role in interpreting laws extends beyond simply upholding the Constitution. It also involves analyzing the intent of lawmakers, considering societal values, and balancing competing interests. These interpretations have profound implications for individuals, businesses, and the government, shaping the course of our nation’s legal landscape.
The Judicial Branch
The judicial branch, often referred to as the judiciary, is a crucial component of any democratic government. It plays a vital role in interpreting laws and ensuring that they are applied fairly and consistently. This branch is responsible for resolving disputes between individuals, organizations, and the government itself. The judicial branch’s power rests on its ability to interpret the law and determine its meaning in specific cases.
Judicial Review
Judicial review is a fundamental principle of the judicial branch, allowing courts to examine laws and actions of the executive and legislative branches to determine their constitutionality. This process ensures that laws align with the principles enshrined in the Constitution. The concept of judicial review, established in the landmark case of Marbury v. Madison (1803), empowers the judiciary to act as a check on the other branches of government, preventing any one branch from wielding unchecked power.
Judicial review has profoundly shaped the legal landscape, influencing interpretations of the Constitution and impacting numerous aspects of American society. The Supreme Court, as the highest court in the land, holds the ultimate authority in interpreting the Constitution and federal laws. Its decisions have far-reaching consequences, setting precedents that guide lower courts and influence legal interpretations for generations to come.
Landmark Supreme Court Cases
Several landmark Supreme Court cases have significantly influenced legal interpretations. These cases have addressed critical issues related to individual rights, government power, and the interpretation of the Constitution. Here are some examples:
- Brown v. Board of Education (1954): This landmark case overturned the “separate but equal” doctrine established in Plessy v. Ferguson (1896), declaring state-sponsored segregation in public schools unconstitutional. This decision paved the way for the desegregation of schools across the country, significantly impacting the lives of millions of Americans.
- Roe v. Wade (1973): This case established a woman’s constitutional right to abortion, recognizing a woman’s right to privacy under the Fourteenth Amendment. The decision sparked intense debate and continues to be a subject of ongoing legal and social discourse.
- Obergefell v. Hodges (2015): This case legalized same-sex marriage nationwide, recognizing marriage equality as a fundamental right under the Fourteenth Amendment. This landmark decision marked a significant step towards LGBTQ+ rights and equality in the United States.
The Legislative Branch
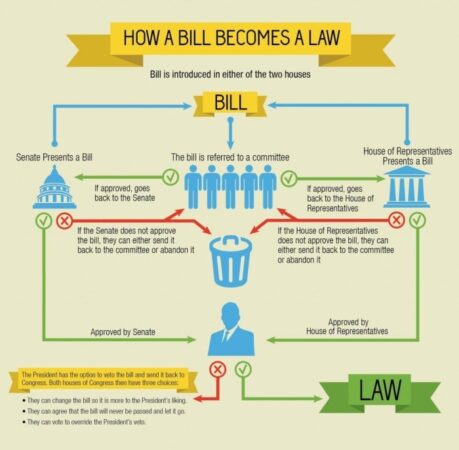
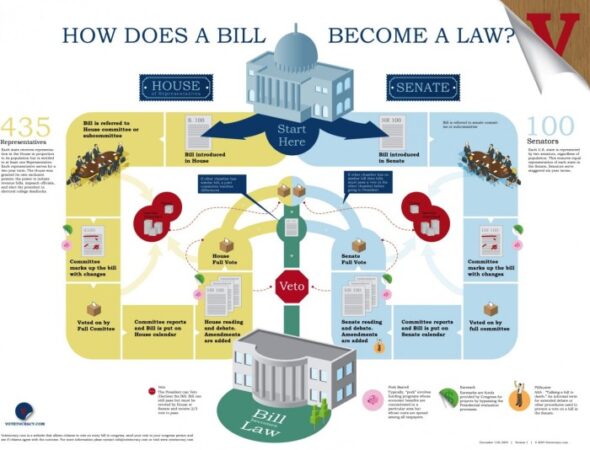
The legislative branch is responsible for creating laws, which are the rules that govern society. This branch, often called Congress in the United States, is composed of elected representatives who are tasked with drafting, debating, and voting on proposed laws.
The Legislative Branch’s Role in Creating Laws
The legislative branch plays a crucial role in the lawmaking process. It starts with the introduction of a bill, a proposed law, by a member of Congress. This bill then undergoes a series of steps, including committee hearings, debates, and amendments, before it can be voted on by the entire legislative body.
If a bill is passed by both houses of Congress (the Senate and House of Representatives in the United States), it is sent to the executive branch for the president’s signature. The president can either sign the bill into law or veto it. If the president vetoes the bill, Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds majority vote in both houses.
Interaction with the Judicial Branch
The legislative branch and the judicial branch work together in the interpretation of laws. The judicial branch, which includes the courts, has the power to interpret laws and determine their meaning. This process of interpretation is called judicial review.
The legislative branch, in turn, can influence how the judicial branch interprets laws by passing new laws or amending existing ones. This interaction is a fundamental aspect of the balance of power in a democratic system.
Examples of Legislative Actions that Have Clarified or Amended Legal Interpretations
There are many examples of legislative actions that have clarified or amended legal interpretations. For instance, the Civil Rights Act of 1964, passed by the United States Congress, outlawed discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. This landmark legislation significantly clarified and amended legal interpretations regarding civil rights, leading to significant social and legal changes.
Another example is the Affordable Care Act, passed in 2010. This act, which aimed to expand health insurance coverage, led to numerous legal challenges and subsequent legislative actions to clarify its provisions and address specific concerns raised by the courts.
The Executive Branch
The Executive Branch, headed by the President of the United States, is responsible for enforcing the laws passed by Congress. This branch plays a crucial role in ensuring that the laws of the land are carried out effectively and fairly.
The Executive Branch’s Role in Enforcing Laws
The President, along with the various executive departments and agencies, has the power to implement and enforce laws passed by Congress. This involves a wide range of activities, including:
* Issuing Executive Orders: The President can issue executive orders, which are directives that have the force of law within the executive branch. These orders can be used to implement existing laws, create new policies, or change the way existing policies are enforced.
* Appointing Federal Officials: The President appoints individuals to key positions within the executive branch, such as cabinet secretaries, federal judges, and ambassadors. These appointments require Senate confirmation.
* Supervising Federal Agencies: The President oversees the day-to-day operations of federal agencies, ensuring that they are carrying out their responsibilities effectively and in accordance with the law.
* Negotiating Treaties: The President negotiates treaties with foreign governments, which must be ratified by the Senate. Treaties become part of U.S. law once ratified.
* Commanding the Armed Forces: The President is the Commander-in-Chief of the U.S. Armed Forces, and has the authority to deploy troops domestically and internationally.
The Executive Branch’s Interaction with the Judicial Branch
The Executive Branch and the Judicial Branch interact in several ways, particularly when it comes to interpreting laws. This interaction is crucial for ensuring that laws are applied consistently and fairly.
* Enforcement of Court Decisions: The Executive Branch is responsible for enforcing the decisions of the federal courts. This includes carrying out court orders, such as releasing prisoners or providing specific services.
* Legal Challenges to Executive Actions: The Judicial Branch can review executive actions to determine if they are constitutional or consistent with existing laws. This can lead to legal challenges and court rulings that shape the interpretation and application of laws.
* Presidential Nominations to the Judiciary: The President nominates individuals to serve as federal judges, including Supreme Court justices. These nominations are subject to Senate confirmation.
Examples of Executive Actions Impacting Legal Interpretations
Throughout history, executive actions have significantly impacted legal interpretations. Here are a few examples:
* Executive Order 9066: During World War II, President Franklin D. Roosevelt issued Executive Order 9066, which authorized the internment of Japanese Americans in concentration camps. This order was later challenged in court, and the Supreme Court upheld its constitutionality in the case of *Korematsu v. United States* (1944). This case had a profound impact on the interpretation of civil liberties during wartime.
* Executive Order 13769: In 2017, President Donald Trump issued Executive Order 13769, which banned travel from several Muslim-majority countries. This order was challenged in court, and the Supreme Court ultimately upheld a revised version of the order. The legal battles surrounding this order raised important questions about the balance between national security and religious freedom.
* Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA): In 2012, President Barack Obama announced the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) program, which provided temporary legal status and protection from deportation to certain undocumented immigrants who came to the United States as children. This program was challenged in court, and the Supreme Court ruled in 2020 that the Trump administration had not followed proper procedures when ending the program. This case highlighted the ongoing legal debate surrounding immigration policy and the role of executive action in shaping immigration law.
The Importance of Legal Interpretation

Legal interpretation is the process of determining the meaning and application of laws. This process is essential for ensuring that laws are applied fairly and consistently in all situations.
The Significance of Consistent and Accurate Legal Interpretations, Which branch interprets laws
Consistent and accurate legal interpretations are crucial for maintaining a stable and predictable legal system. When laws are interpreted consistently, individuals and businesses can rely on the legal system to provide fair and just outcomes. This predictability fosters trust in the legal system and encourages economic growth and social stability. Inconsistent interpretations, on the other hand, can lead to confusion, uncertainty, and a lack of trust in the legal system.
The Impact of Legal Interpretations
Legal interpretations have a significant impact on individuals, businesses, and the government.
Individuals
Legal interpretations affect individuals in numerous ways. For example, the interpretation of a law regarding employment discrimination can determine whether an individual is protected from unfair treatment in the workplace. Similarly, the interpretation of a law regarding family law can determine the outcome of a divorce or child custody case.
Businesses
Businesses rely on legal interpretations to make informed decisions about their operations. For instance, the interpretation of a law regarding environmental regulations can determine the cost of complying with those regulations. Similarly, the interpretation of a law regarding intellectual property can determine whether a business can protect its trademarks or patents.
Government
The government relies on legal interpretations to enforce laws and policies. For example, the interpretation of a law regarding taxation can determine how much revenue the government collects. Similarly, the interpretation of a law regarding national security can determine how the government responds to threats.
Scenarios Where Legal Interpretations are Crucial
| Scenario | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|
| Interpretation of a law regarding free speech | The interpretation of a law regarding free speech can determine the extent to which individuals are free to express their opinions without fear of government censorship. An overly broad interpretation could stifle dissent and limit freedom of expression, while an overly narrow interpretation could allow for the spread of harmful or hateful speech. |
| Interpretation of a law regarding environmental protection | The interpretation of a law regarding environmental protection can determine the level of pollution that is allowed and the extent to which businesses are required to reduce their environmental impact. A strict interpretation could lead to increased costs for businesses and potentially limit economic growth, while a lax interpretation could result in environmental damage. |
| Interpretation of a law regarding criminal justice | The interpretation of a law regarding criminal justice can determine the severity of punishments for crimes and the rights of defendants. A strict interpretation could lead to harsher punishments and potentially limit the rights of defendants, while a lenient interpretation could result in lighter punishments and potentially increase crime rates. |
Challenges in Legal Interpretation
Interpreting laws is a complex and multifaceted task that often presents significant challenges for the judicial branch. Judges must navigate a labyrinth of legal texts, precedents, and societal values to arrive at a just and equitable interpretation. This process is further complicated by the inherent ambiguity and evolving nature of language, which can lead to varying interpretations of the same legal provisions.
Potential Biases and Limitations
Judges, like all humans, are susceptible to biases that can influence their decision-making. These biases can stem from personal experiences, societal norms, or even unconscious prejudices. For instance, a judge’s background or upbringing might shape their understanding of certain social issues, potentially leading to interpretations that favor one side over another. Additionally, judges may be influenced by their own personal beliefs, values, and political leanings, which can impact their interpretation of legal texts.
Different Approaches to Legal Interpretation
The judicial branch employs various approaches to interpret laws, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Textualism: This approach emphasizes the literal meaning of the words in the law, prioritizing the plain language of the text. Textualists argue that the legislature’s intent is best reflected in the words they chose. However, this approach can be criticized for ignoring the context and potential unintended consequences of a strict interpretation.
- Originalism: This approach focuses on the original intent of the framers of the law. Originalists believe that the Constitution, for example, should be interpreted based on the understanding of the founding fathers. This approach can be difficult to apply in practice, as it requires reconstructing the historical context and intent of individuals who lived centuries ago.
- Purposivism: This approach emphasizes the purpose or goal behind the law. Purposivists argue that judges should interpret laws in a way that fulfills the intended purpose, even if it means departing from the literal text. This approach can be more flexible than textualism, but it can also be subjective and open to different interpretations of the law’s purpose.
The Future of Legal Interpretation: Which Branch Interprets Laws

The field of legal interpretation is poised for significant transformation as emerging trends and technologies reshape how laws are understood and applied. These advancements hold the potential to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility in legal processes, while also raising critical ethical considerations.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The future of legal interpretation is likely to be influenced by several key trends and technologies, each with the potential to revolutionize how legal professionals approach their work.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools are increasingly being used to analyze legal documents, identify relevant precedents, and predict legal outcomes. This technology can automate tasks, improve efficiency, and provide insights that may not be readily apparent to human analysts.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP algorithms are capable of understanding and interpreting human language, enabling them to analyze legal texts, extract key information, and generate summaries. This technology can assist lawyers in quickly understanding complex legal documents and identifying relevant legal arguments.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain offers a secure and transparent platform for recording legal transactions and agreements. This technology can enhance the integrity and immutability of legal records, potentially streamlining legal processes and reducing disputes.
- Big Data Analytics: The availability of vast amounts of legal data, coupled with advanced analytics tools, allows for the identification of patterns and trends that can inform legal decisions. This data-driven approach can help lawyers make more informed judgments and predict legal outcomes with greater accuracy.
Potential Scenarios for the Future of Legal Interpretation
The convergence of these trends and technologies could lead to several potential scenarios for the future of legal interpretation, each with its own set of implications:
| Scenario | Potential Implications |
|---|---|
| Increased Automation and Efficiency: AI and NLP technologies automate tasks such as document review, legal research, and contract analysis, freeing up legal professionals to focus on higher-level tasks. | Improved efficiency, reduced costs, increased access to legal services for individuals and businesses. |
| Enhanced Accuracy and Predictability: Data analytics and AI-powered prediction models can provide insights into legal outcomes, leading to more accurate legal advice and predictions. | More informed legal decisions, reduced litigation costs, increased confidence in legal outcomes. |
| Shifting Legal Profession: The rise of AI and automation could lead to changes in the legal profession, with some tasks being replaced by technology and new roles emerging. | Potential job displacement for some legal professionals, increased demand for legal professionals with expertise in AI and data analytics. |
| Increased Accessibility to Legal Services: AI-powered legal platforms and online legal resources can make legal services more accessible to individuals and businesses, regardless of their location or financial resources. | Increased access to justice, reduced inequality in the legal system, greater empowerment for individuals and businesses. |
Ethical Considerations Surrounding the Use of AI in Legal Interpretation
The use of AI in legal interpretation raises important ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed:
- Bias and Discrimination: AI algorithms are trained on data, and if the data is biased, the algorithm may perpetuate those biases. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes in legal decisions.
- Transparency and Explainability: It is essential to understand how AI algorithms arrive at their conclusions, especially in legal contexts where decisions have significant consequences.
- Accountability: If AI makes a mistake, who is responsible? It is important to establish clear accountability mechanisms for AI-powered legal systems.
- Human Oversight: While AI can provide valuable insights, it should not replace human judgment entirely. Legal professionals must retain the ability to critically evaluate AI-generated outputs and make informed decisions.
“The use of AI in legal interpretation presents both opportunities and challenges. It is essential to carefully consider the ethical implications of this technology and ensure that it is used responsibly and fairly.”
Wrap-Up
The ongoing debate surrounding the role of the judiciary in interpreting laws highlights the complexities and importance of this fundamental process. From landmark Supreme Court decisions to everyday legal disputes, the judicial branch plays a vital role in ensuring a fair and just society. Understanding the principles of legal interpretation and the challenges faced by the judiciary is crucial for informed citizenship and effective participation in our democracy.
Question Bank
What is judicial review?
Judicial review is the power of the courts to review laws and determine whether they are constitutional. If a law is found to be unconstitutional, it is struck down.
How does the judicial branch interact with the legislative and executive branches in interpreting laws?
The judicial branch can interpret laws passed by the legislative branch and can also rule on the constitutionality of executive actions. These interactions ensure that all branches of government operate within the bounds of the Constitution.
What are some examples of landmark Supreme Court cases that have influenced legal interpretations?
Examples include Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which overturned racial segregation in public schools, and Roe v. Wade (1973), which legalized abortion nationwide.